So what is the book about? — from donaldclarkplanb.blogspot.com by Donald Clark; which discusses his book entitled, Artificial Intelligence for Learning: How to use AI to Support Employee Development

Excerpt:
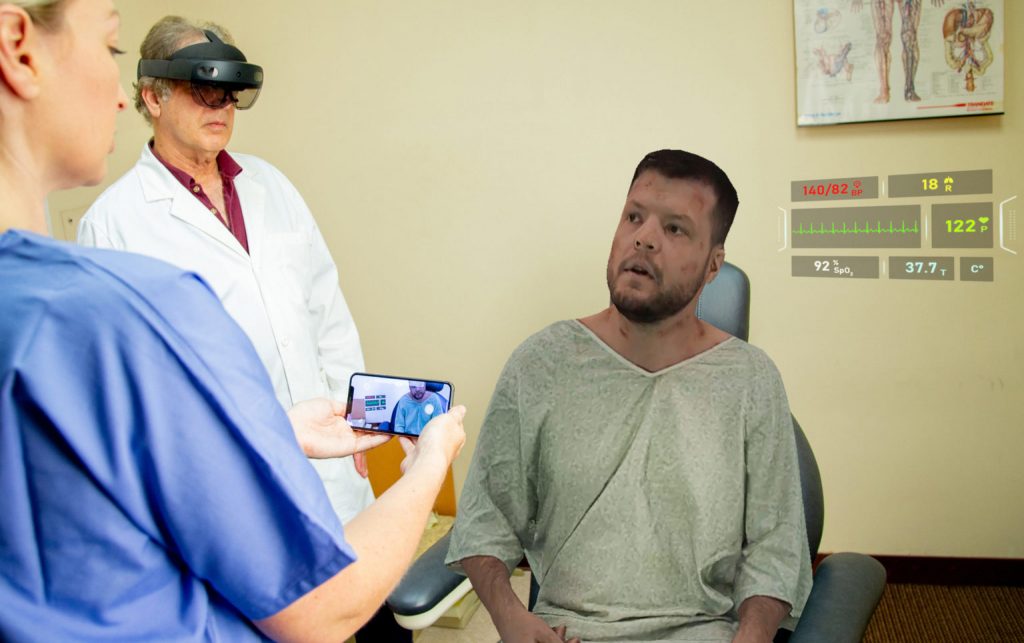
AI changes everything. It changes how we work, shop, travel, entertain ourselves, socialize, deal with finance and healthcare. When online, AI mediates almost everything – Google, Google Scholar, YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, Amazon, Netflix. It would be bizarre to imagine that AI will have no role to play in learning – it already has.
Both informally and formally, AI is now embedded in many of the tools real learners use for online learning – we search for knowledge using AI (Google, Google Scholar), we search for practical knowledge using AI (YouTube), Duolingo for languages, and CPD is becoming common on social media, almost all mediated by AI. It is everywhere, just largely invisible. This book is partly about the role of AI in informal learning but it is largely about its existing and potential role in formal learning – in schools, Universities and the workplace. AI changes the world, so it changes why we learn, what we learn and how we learn.
Also see:
- Abandon lectures: increase attendance, attitudes and attainment — from donaldclarkplanb.blogspot.com by Donald Clark
Excerpt:
The groups were taught a module in a physics course, in three one hour sessions in one week. In short; attendance increased, measured attitudes were better (students enjoyed the experience (90%) and thought that the whole course would be better if taught this way (77%)). More importantly students in the experimental group outperformed the control group, doing more than twice as well in assessment than the control group.