Potentially-useful sites for developing writers out there:
Several reasons lie behind this growth.




Potentially-useful sites for developing writers out there:
10 Tips for Supporting Students with Special Needs in #RemoteLearning — from jakemiller.net by Jake Miller
Excerpt:
How can we support learners with special needs in remote learning?
While, certainly, some educators are doing great things to support these students, from my observations, this has taken a backseat to other elements of remote learning. And these students NEED OUR HELP.
Unfortunately, I am not an expert in special education, accessibility features or assistive technology. I am, however, skilled at asking other people to share their expertise. ? So, in episode 40 of the Educational Duct Tape podcast and in the 4.8.20 #EduDuctTape Twitter Chat I asked educators one simple question:
How can we support learners with special needs in remote learning?
And they DELIVERED. I mean, the awesome suggestions and resources, all from a perspective of support rather than judgment, POURED in. And so, here they are.
Student-Centered Remote Teaching: Lessons Learned from Online Education — from er.educause.edu by Shannon Riggs
Excerpt:
Student-content interaction is all about having students DO something with the course content or topic. Reading and listening to lectures will be part of many classes, but the passive receipt of information isn’t sufficient to help students engage with the course and meet course learning outcomes. Instead, we should create opportunities for active learning, which is when students DO something meaningful related to the course content and then reflect on their learning.
After students complete a course reading, ask them to do a follow-up assignment. Here are a few examples:
After students attend a synchronous lecture via web conference, ask them to complete a follow-up activity:
From DSC:
NOTE: The K-12 education system that I’m talking about in this posting is the pre-COVID-19 education system.
What Cory Henwood describes here…

…is what I describe as the quickly moving K-12 education train that stops for no one!

This becomes especially troublesome for those on either side of the 80% bell curve. I know about this, as one of our daughters has been living through this phenomenon for years. We are seriously considering homeschooling for her as we want her learning experiences to be more positive ones for her. We want to provide more choice, more control for what she wants to learn about — and the pace at which she can go through those experiences. We want there to be more joy in her learning experiences. This will hopefully help her build more positive perspectives about learning in general.
This is not a mute issue…nor is this a topic that’s focused on just students with special needs. In fact, this topic is relevant to every single student in America — as everyone is now required to be lifelong learners these days. Grades need to diminish in importance. The enjoyment of learning needs to rise.
Note: There were some times in public and charter schools that provided courses and topics of great interest to her, and provided some great joy to her. Plus, there were some incredibly-dedicated teachers and staff that created a team around our daughter. I’m very grateful for them and for their efforts. But positive learning experiences were becoming too few and too far between. The train left the station *for everyone* at such-and-such a time, and stopped *for everyone* at such and such a time. The education system required that she and her classmates move at a certain (high) speed — regardless of their mastery of the content. Teachers know what I’m talking about here…big time.
We need to get to what Cory discusses about when he discusses competency-based education.
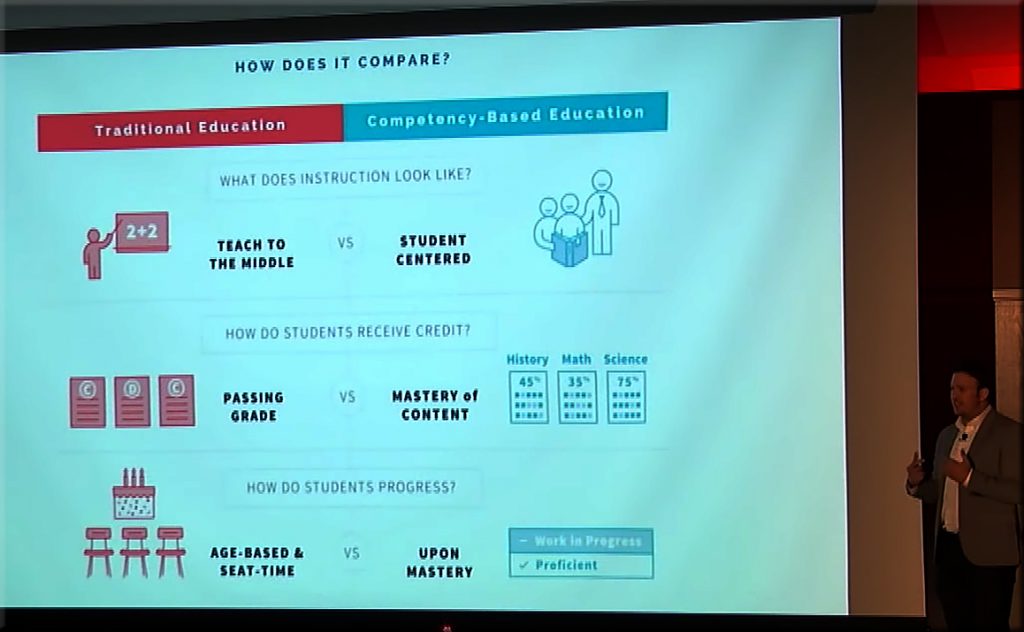
Plus, we need to get to a place where there is:

Q: For those who prefer or need to handwrite their essays, what are some ways/methods that students can use to scan in — and then submit — their essays into Canvas?
A: Below are a few different options, potential solutions, and resources:
Also see:
From DSC:
If you are using a tool like Cisco Webex in your school, consider implementing the idea below. I’d like to thank Mr. Steve Grant and Mr. Nelson Miller from the WMU-Cooley Law School for their work in implementing/recommending this approach.
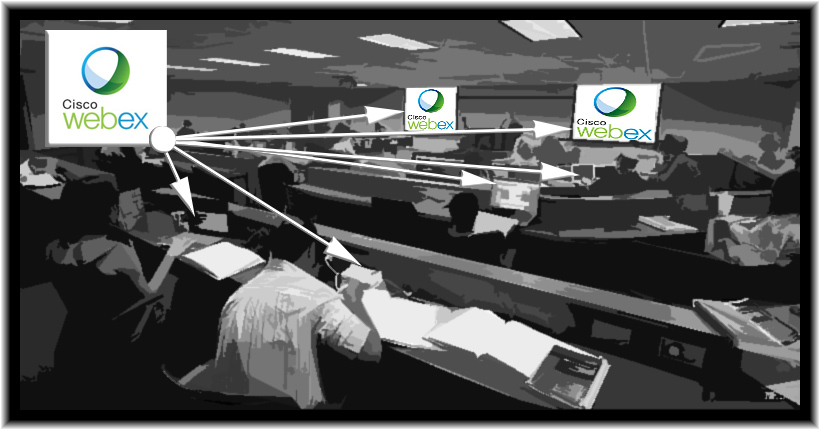

If you are using a tool like Cisco Webex, you can use it to share content to displays, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. If the professor starts a Cisco Webex Meeting Center session using their own personal room, the students can then join that meeting via their devices. (To eliminate noise and confusion — as well as to reduce bandwidth — the students should mute their microphones and choose not to send the video from their webcams.)
If you were doing a think-pair-share, for example, and you really liked what a certain pair of students had going on, one of the students could share their work with the rest of the class. By doing so, whatever was going on on that student’s device could be displayed by any projectors in the room, as well as on any other devices that were connected to the Cisco Webex Meeting Room.
“So you could project any student’s work as students proceed with in-class exercises. Projecting student work adds another level of accountability, excitement, and concentration to in-class exercises.”
*********
Also, using the Cisco Webex Meeting Center in your face-to-face classroom not only opens up that sort of collaboration channel, but, via the chat feature, it can also open up a running backchannel to draw out your more introverted students, or those students who have questions but don’t want to have the spotlight thrown on them.
*********
Generation Z and online tutoring: natural bedfellows? — from innovatemyschool.com by John Ingram
Excerpt:
The K-12 online tutoring market is booming around the world, with recent research estimating it to grow by 12% per year over the next five years, a USD $60bn increase. By breaking down geographic barriers and moving beyond the limits of local teaching expertise, online tutoring is an especially valuable tool for those looking to supplement their studies in the developing world, and students globally are increasingly signing up to online tuition early on in their secondary education schooling.
Several reasons lie behind this growth.
Below are some thoughts from Michal Borkowski, CEO and Co-Founder of Brainly, regarding some emerging edtech-related trends for 2020.
2020 is coming at us fast, and it’s bringing a haul of exciting EdTech trends along with it. A new decade means new learning opportunities created to cater to the individual rather than a collective hive. There are more than one or two ways of learning — by not embracing all of the ways to teach, we risk leaving students behind in subjects they may need extra help in.
Michal Borkowski, CEO and Co-Founder of Brainly– the world’s largest online learning platform with 150 million monthly users in 35 countries– has his finger on the pulse of global education trends. He was selected to speak at Disrupt Berlin, the world’s leading authority in debuting revolutionary startups and technologies, this year and has some insightful predictions on the emerging trends 2020 will bring in EdTech.
2020 is the year that education forms itself around each student’s individual needs rather than leaving kids behind who don’t benefit from traditional instruction.
Per RetrievalPractice.org:
Download ALL our free guides, research, and resources!
We’re here to make your life easier. In order to unleash the science of learning, we strive to make it easy to access and quick to implement.
That’s why we really want you to download everything from our library, including free practice guides, book club resources, research, and more.
2019 study of undergraduate students & information technology — from library.educause.edu
Excerpts:
Drawing on survey data from more than 40,000 students across 118 US institutions, this report highlights a number of important findings related to students’ technology preferences, supports, and experiences, with the goal of aiding technology and higher education professionals in improving student learning experiences and success.
…
But they want to be more than in-class spectators:
Figure 2. Student learning environment preferences for specific course-related activities and assignments
Recommendations
From DSC:
Well students…you might find that you have a major surprise ahead of you — as a significant amount of your future learning/training will take place completely online. Go ask some folks who have graduated about their onboarding experiences. Then go ask people who have been in the workplace for over a decade. You’ll see what I mean.
From DSC:
This posting is for those students who are studying Education in college and/or for those adult learners who are making a right turn in their careers to become teachers.
Don’t underestimate the learning potential in a hashtag on Twitter! Consider a few:
Look at the individuals and the organizations who are posting in those hashtags — then follow those who are contributing solid resources, ideas, thoughts, and content.
Top ten podcasts every teacher needs to hear — from wiley.com; with thanks to Emily Liebtag for her posting on Twitter for this resource
Excerpt:
Listening to podcasts is an easy way to dive into a topic that interests you and learn something new from others who share your passion for education.
We’re highlighting the following ten podcast episodes featuring Jossey-Bass authors that you can listen to whenever, wherever to help you master your craft or reignite your love of teaching.
So, take some time for yourself, grab your earbuds, and press play on these…
Using technology to inspire creativity boosts student outcomes — from thejournal.com by Sara Friedman
Transformative technology uses include using tablets or computers to create multimedia projects, conduct research and analyze information.
Teachers’ use of creativity in learning was determined how many times students were allowing to: