A message about learning from the C-suite — from chieflearningofficer.com by Patricia A. McLagan
Executives are increasingly saying they want to create “learning organizations” and support “lifelong learning.” So, what should executives be saying to their workforce about learning today? Consider this sample letter to employees from the C-suite.
Excerpts:
How are you keeping up your skills and knowledge in our increasingly complex and fast-changing world of work? As today’s pandemic turmoil reminds us, it is hard to predict how the future will evolve. But one thing we do know is that continuous learning will be a key survival meta-skill for all of us — learning that each of us consciously guides every day, moment to moment, alone, in teams, with any resource, anywhere and anytime.
…
Consider: More than 50 percent of today’s jobs will probably disappear or change radically within 10 years. There are many reasons for this.
…
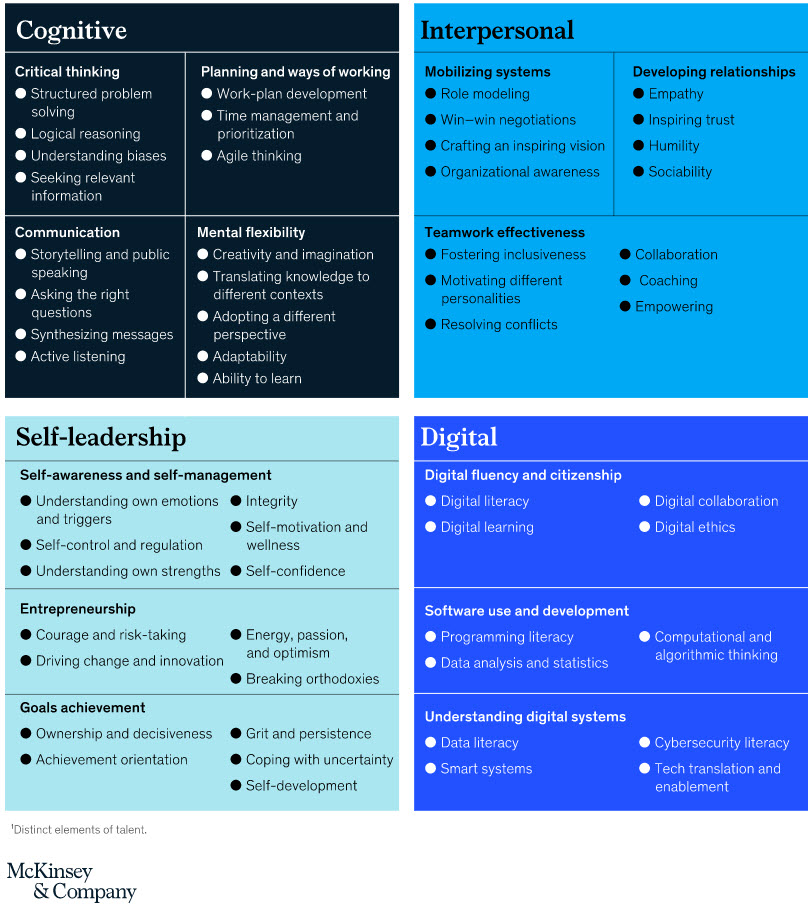
Beyond technology, companies like ours need more agility, innovation and self-management from everyone. We used to manage more by job descriptions, and you were best described as a box on the organization chart — probably with little expectation that you could experiment, take risks, and act with discretion and autonomy. But today and into the future, your skills and creative thinking matter more. Your “job” responsibilities shift as you move into and out of teams and as we call on you to support new strategies, customer groups and priorities.
From DSC:
I really appreciated reading this solid article from Patricia McLagan. She captured so many solid points. That said, I was bummed to see the following item included in this article (emphasis DSC):
Of course, our company is committed to supporting your learning and development, to providing formal training and access to learning opportunities for everyone. But even in the best of times, we will only be able to formally support a small part of what you will need and want. This is why I am sending this note to you: to tell you that we care about your learning and development, that we will do our best to support it, but that 95 percent of your learning is in your hands.
Of course, our company is committed to supporting your learning and development, to providing formal training and access to learning opportunities for everyone. But even in the best of times, we will only be able to formally support a small part of what you will need and want. This is why I am sending this note to you: to tell you that we care about your learning and development, that we will do our best to support it, but that 95 percent of your learning is in your hands.
Our company is committed to supporting your learning development — yeh…right…all 5% of it.
Whoopie. The other 95% of it belongs to you and me. (Which reminds me that words are so easy to say but much harder to truly back up.) And you and I will likely do it on your/our own time. That seems to be more of the reality…the expectation…especially when job cuts are occurring all over the place and the job plates continue to expand for those who survived the cuts.
My experience over my career has been that corporations used to promote and truly support their employees’ professional development. They sent more people to courses and significantly helped many people obtain their MBA’s as well as other relevant master’s degrees and/or certifications/ and/or just to support some professional interests.
For example, I’m forever indebted to one of my formers bosses, Irvin Charles Coleman III. I worked for Irv at Kraft Foods’ HQ’s and he once let me go to a seminar on Photoshop. Though I used Photoshop in my work, it wasn’t in my formal description. That seminar changed many things for me. It supported my growth and learning and it fed my passion for designing and creating content.
I’m sure this kind of thing still occurs, but from what I can tell, it doesn’t happen at nearly the level that it used to. That said, I don’t blame the corporate world for getting bummed out at their employees that they had invested in — only to see those same employees grab the degrees and credentials and leave for greener pastures. Through the years, it seemed like the corporate world backed off from providing such a level of training/professional development.
These days, it seems like the corporations and the businesses out there have the hiring expectation that you will hit the ground running from day one. Learning and development are up to you and me. Nevermind that the way learning is supposed to go is that you:
- introduce the learning objectives to someone
- give them the information/content
- provide the relevant and aligned learning activities that help them truly engage with the content
- provide aligned formative and summative assessments along the way to ascertain whether they learned the material/concepts or not.
So I’m amazed that corporations are putting recent grads through their own tests on things that many of these students have never actually studied. (Yeh, I can hear the push backs now…and while I agree with some of them, it’s not fair to the students. They just followed what the colleges and universities offered for$100,000-$400,000+).
I could go on, but I need to go do my taxes. Gotta run. I hope to pick this line of thought up later.