The scary amount that college will cost in the future — from cnbc.com by Annie Nova
Excerpt:
Think college is expensive now? Then new parents will probably want to take a seat for this news.
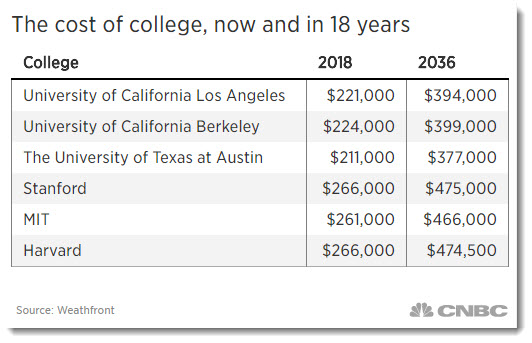
In 2036, just 18 years from now, four years at a private university will be around $303,000, up from $167,000 today.
To get a degree at a public university you’ll need about $184,000, compared with $101,000 now.
These forecasts were provided by Wealthfront, an automated investment platform that offers college saving options. It uses Department of Education data on the current cost of schools along with expected annual inflation to come up with its projections.
Excerpted graphic:
From DSC:
We had better be at the end of the line of thinking that says these tuition hikes can continue. It’s not ok. More and more people will be shut out by this kind of societal gatekeeper. The ever-increasing cost of obtaining a degree has become a matter of social justice for me. Other solutions are needed. The 800 pound gorilla of debt that’s already being loaded onto more and more of our graduates will impact them for years…even for decades in many of our graduates’ cases.
It’s my hope that a variety of technologies will make learning more affordable, yet still provide a high quality of education. In fact, I’m hopeful that the personalization/customization of learning will take some major steps forward in the very near future. We will still need and want solid teachers, professors, and trainers, but I’m hopeful that those folks will be aided by the heavy lifting that will be done by some powerful tools/technologies that will be aimed at helping people learn and grow…providing lifelong learners with more choice, more control.
I love the physical campus as much as anyone, and I hope that all students can have that experience if they want it. But I’ve seen and worked with the high costs of building and maintaining physical spaces — maintaining our learning spaces, dorms, libraries, gyms, etc. is very expensive.
I see streams of content becoming more prevalent in the future — especially for lifelong learners who need to reinvent themselves in order to stay marketable. We will be able to subscribe and unsubscribe to curated streams of content that we want to learn more about. For example, today, that could involve RSS feeds and Feedly (to aggregate those feeds). I see us using micro-learning to help us encode information and then practice recalling it (i.e., spaced practice), to help us stop or lessen the forgetting curves we all experience, to help us sort information into things we know and things that we need more assistance on (while providing links to resources that will help us obtain better mastery of the subject(s)).










![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)