The future of work in America — from mckinsey.com by Jacques Bughin, James Manyika. and Jonathan Woetzel | July 2019
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Local economies across the country have been on diverging trajectories for years, and ***they are entering the automation age from different starting points.*** Our view incorporates the current state of local labor markets as well as the jobs that could be lost and gained in the decade ahead.
The US labor market looks markedly different today than it did two decades ago. It has been reshaped by dramatic events like the Great Recession but also by a quieter ongoing evolution in the mix and location of jobs. In the decade ahead, the next wave of technology may accelerate the pace of change. Millions of jobs could be phased out even as new ones are created. More broadly, the day-to-day nature of work could change for nearly everyone as intelligent machines become fixtures in the American workplace.
…
The labor market could become even more polarized. Workers with a high school degree or less are four times as likely as those with a bachelor’s degree to be displaced by automation. Reflecting more limited access to education, Hispanic workers are most at risk of displacement, followed by African Americans. Jobs held by nearly 15 million workers ages 18–34 may be automated, so young people will need new career paths to gain an initial foothold in the working world. Roughly 11.5 million workers over age 50 could also be displaced and face the challenge of making late-career moves. The hollowing out of middle wage work could continue.
…
The future of work is not just about how many jobs could be lost and gained. Technology is altering the day-to-day mix of activities associated with more and more jobs over time. The occupational mix of the economy is changing, and the demand for skills is changing along with it. Employers will need to manage large-scale workforce transformations that could involve redefining business processes and workforce needs, retraining and moving some people into new roles, and creating programs for continuous learning. This could be an opportunity to upgrade jobs and make them more rewarding. The choices that employers make will ripple through the communities in which they operate.
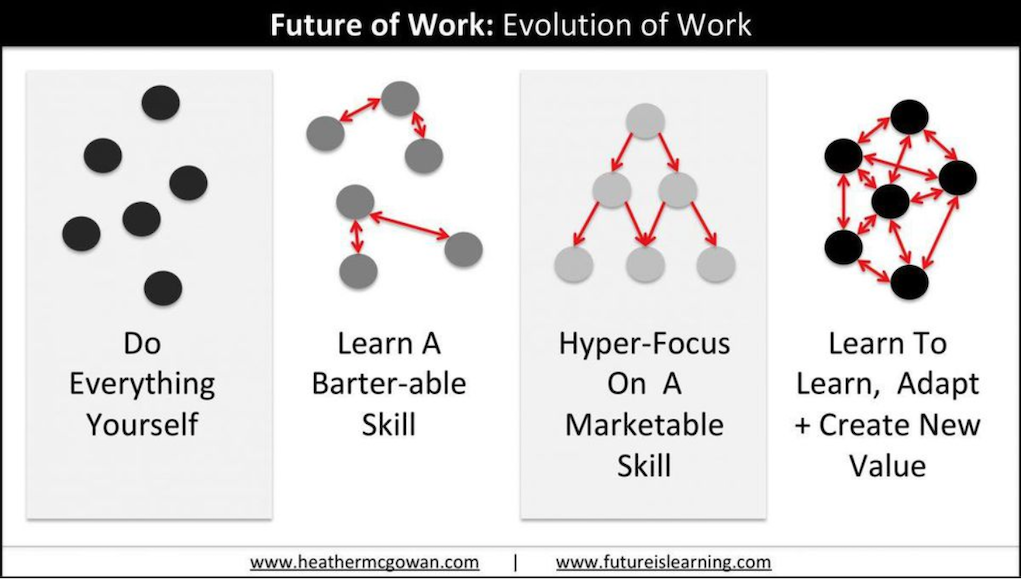
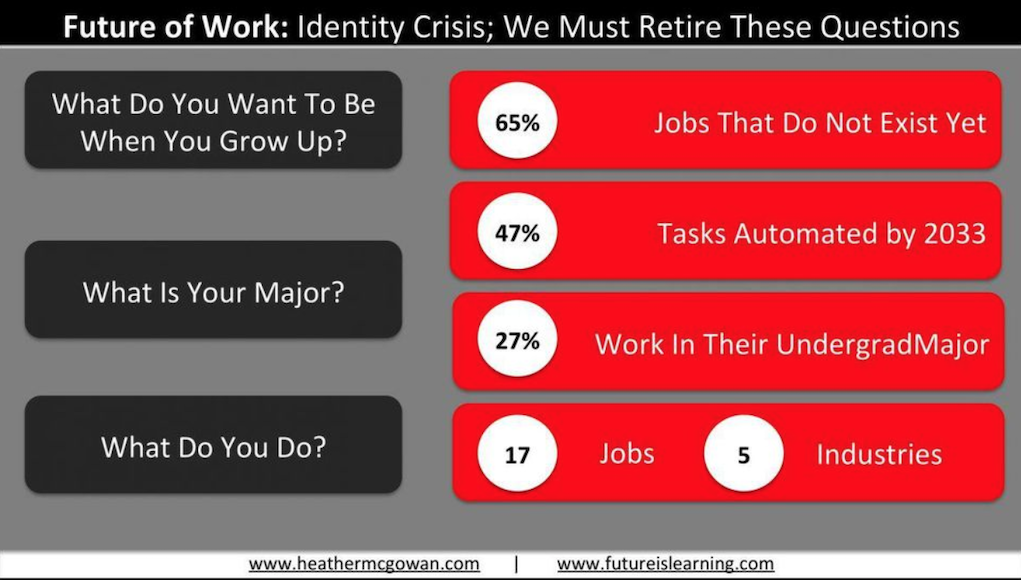
The need for a next gen learning platform is quickly approaching us!
Either that, or colleges and universities better get FAR more
responsive/nimble, and focus FAR more on lifelong learning.
This is not a joke.
This is not just text on a web page.
This is a future that’s barreling at us at amazingly fast speeds.
A new chapter is coming at us quickly.