Research study suggests VR can have a huge impact in the classroom — from uploadvr.com by Joe Durbin
Excerpt:
“Every child is a genius in his or her own way. VR can be the key to awakening the genius inside.”
This is the closing line of a new research study currently making its way out of China. Conducted by Beijing Bluefocus E-Commerce Co., Ltd and Beijing iBokan Wisdom Mobile Internet Technology Training Institution, the study takes a detailed look at the different ways virtual reality can make public education more effective.
“Compared with traditional education, VR-based education is of obvious advantage in theoretical knowledge teaching as well as practical skills training. In theoretical knowledge teaching, it boasts the ability to make abstract problems concrete, and theoretical thinking well-supported. In practical skills training, it helps sharpen students’ operational skills, provides an immersive learning experience, and enhances students’ sense of involvement in class, making learning more fun, more secure, and more active,” the study states.
VR for Education – what was and what is — from researchvr.podigee.io
Topics discussed:
- VR for education: one time use vs everyday use
- Ecological Validity of VR Research
- AR definition & history
- Tethered vs untethered
- Intelligent Ontology-driven Games for Teaching Human Anatomy
- Envelop VR
- VR for Education
- Gartner curve – then and now
Virtual reality industry leaders come together to create new association — from gvra.com
Excerpt:
CALIFORNIA — Acer Starbreeze, Google, HTC VIVE, Facebook’s Oculus, Samsung, and Sony Interactive Entertainment [on 12/7/16] announced the creation of a non-profit organization of international headset manufacturers to promote the growth of the global virtual reality (VR) industry. The Global Virtual Reality Association (GVRA) will develop and share best practices for industry and foster dialogue between public and private stakeholders around the world.
The goal of the Global Virtual Reality Association is to promote responsible development and adoption of VR globally. The association’s members will develop and share best practices, conduct research, and bring the international VR community together as the technology progresses. The group will also serve as a resource for consumers, policymakers, and industry interested in VR.
VR has the potential to be the next great computing platform, improving sectors ranging from education to healthcare, and contribute significantly to the global economy. Through research, international engagement, and the development of best practices, the founding companies of the Global Virtual Reality Association will work to unlock and maximize VR’s potential and ensure those gains are shared as broadly around the world as possible.
For more information, visit www.GVRA.com.
Occipital shows off a $399 mixed reality headset for iPhone — from techcrunch.com by Lucas Matney
Excerpt:
Occipital announced today that it is launching a mixed reality platform built upon its depth-sensing technologies called Bridge. The headset is available for $399 and starts shipping in March; eager developers can get their hands on an Explorer Edition for $499, which starts shipping next week.
From DSC:
While I hope that early innovators in the AR/VR/MR space thrive, I do wonder what will happen if and when Apple puts out their rendition/version of a new form of Human Computer Interaction (or forms) — such as integrating AR-capabilities directly into their next iPhone.
Enterprise augmented reality applications ready for prime time — from internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com by Beth Stackpole
Pokémon Go may have put AR on the map, but the technology is now being leveraged for enterprise applications in areas like marketing, maintenance and field service.
Excerpt:
Unlike virtual reality, which creates an immersive, computer-generated environment, the less familiar augmented reality, or AR, technology superimposes computer-generated images and overlays information on a user’s real-world view. This computer-generated sensory data — which could include elements such as sound, graphics, GPS data, video or 3D models — bridges the digital and physical worlds. For an enterprise, the applications are boundless, arming workers walking the warehouse or selling on the shop floor, for example, with essential information that can improve productivity, streamline customer interactions and deliver optimized maintenance in the field.
15 virtual reality trends we’re predicting for 2017 — from appreal-vr.com by Yariv Levski
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
2016 is fast drawing to a close. And while many will be glad to see the back of it, for those of us who work and play with Virtual Reality, it has been a most exciting year.
By the time the bells ring out signalling the start of a new year, the total number of VR users will exceed 43 million. This is a market on the move, projected to be worth $30bn by 2020. If it’s to meet that valuation, then we believe 2017 will be an incredibly important year in the lifecycle of VR hardware and software development.
VR will be enjoyed by an increasingly mainstream audience very soon, and here we take a quick look at some of the trends we expect to develop over the next 12 months for that to happen.
Murdoch University hosts trial of virtual reality classroom TeachLivE — from communitynews.com.au by Josh Zimmerman
Excerpt:
IN an Australian first, education students will be able hone their skills without stepping foot in a classroom. Murdoch University has hosted a pilot trial of TeachLivE, a virtual reality environment for teachers in training.
The student avatars are able to disrupt the class in a range of ways that teachers may encounter such as pulling out mobile phones or losing their pen during class.
8 Cutting Edge Virtual Reality Job Opportunities — from appreal-vr.com by Yariv Levski
Today we’re highlighting the top 8 job opportunities in VR to give you a current scope of the Virtual Reality job market.
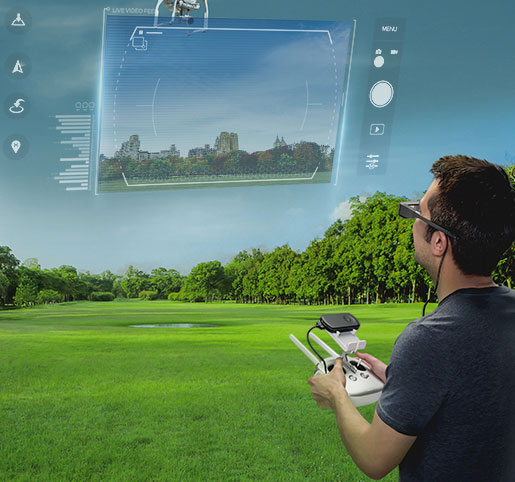
Epson’s Augmented Reality Glasses Are a Revolution in Drone Tech — from dronelife.com by Miriam McNabb
Excerpt:
The Epson Moverio BT-300, to give the smart glasses their full name, are wearable technology – lightweight, comfortable see-through glasses – that allow you to see digital data, and have a first person view (FPV) experience: all while seeing the real world at the same time. The applications are almost endless.
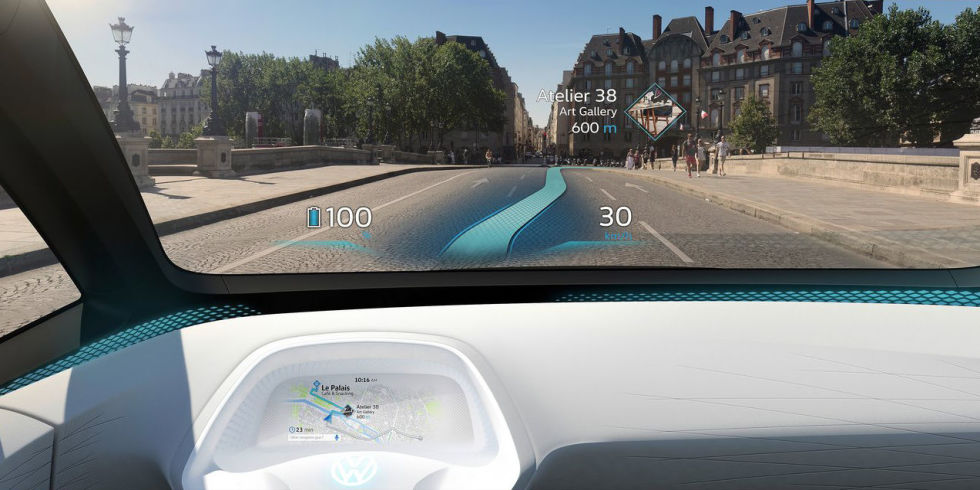
Volkswagen Electric Car To Feature Augmented Reality Navigation System — from gas2.org by Steve Hanley
Excerpt:
Volkswagen’s pivot away from diesel cars to electric vehicles is still a work in progress, but some details about its coming I.D. electric car — unveiled in Paris earlier this year — are starting to come to light. Much of the news is about an innovative augmented reality heads-up display Volkswagen plans to offer in its electric vehicles. Klaus Bischoff, head of the VW brand, says the I.D. electric car will completely reinvent vehicle instrumentation systems when it is launched at the end of the decade.
These global research centers are a proof that virtual reality is more than gaming — from haptic.al by Deniz Ergürel
Excerpt:
For decades, numerous research centers and academics around the world have been working the potential of virtual reality technology. Countless research projects undertaken in these centers are an important indicator that everything from health care to real estate can experience disruption in a few years.
…
- Virtual Human Interaction Lab — Stanford University
- Virtual Reality Applications Center — Iowa State University
- Institute for Creative Technologies—USC
- Medical Virtual Reality — USC
- The Imaging Media Research Center — Korea Institute of Science and Technology
- Virtual Reality & Immersive Visualization Group — RWTH Aachen University
- Center For Simulations & Virtual Environments Research — UCIT
- Duke immersive Virtual Environment —Duke University
- Experimental Virtual Environments (EVENT) Lab for Neuroscience and Technology — Barcelona University
- Immersive Media Technology Experiences (IMTE) — Norwegian University of Technology
- Human Interface Technology Laboratory — University of Washington
Where Virtual and Physical Worlds Converge — from disruptionhub.com
Excerpt:
Augmented Reality (AR) dwelled quietly in the shadow of VR until earlier this year, when a certain app propelled it into the mainstream. Now, AR is a household term and can hold its own with advanced virtual technologies. The AR industry is predicted to hit global revenues of $90 billion by 2020, not just matching VR but overtaking it by a large margin. Of course, a lot of this turnover will be generated by applications in the entertainment industry. VR was primarily created by gamers for gamers, but AR began as a visionary idea that would change the way that humanity interacted with the world around them. The first applications of augmented reality were actually geared towards improving human performance in the workplace… But there’s far, far more to be explored.
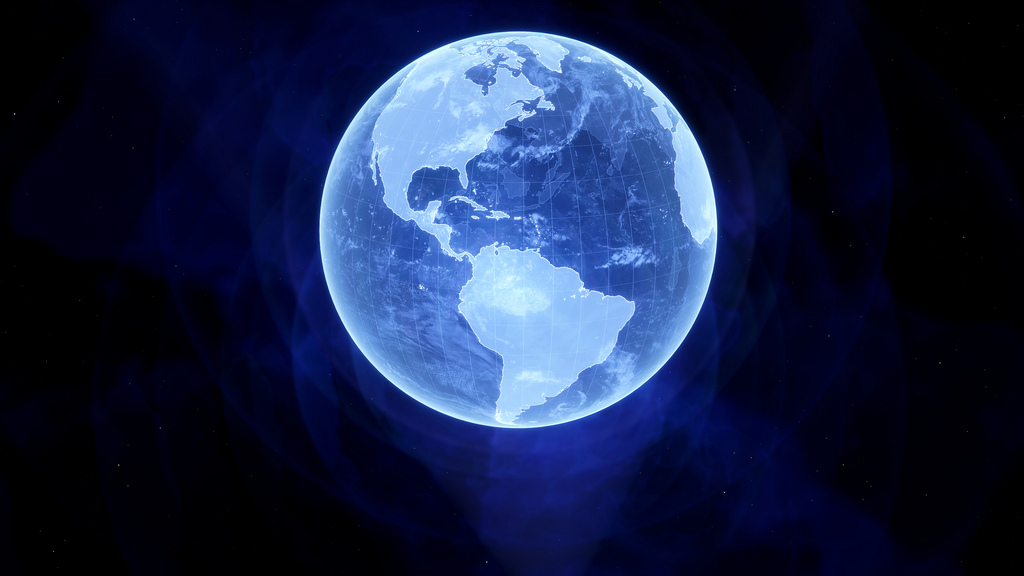
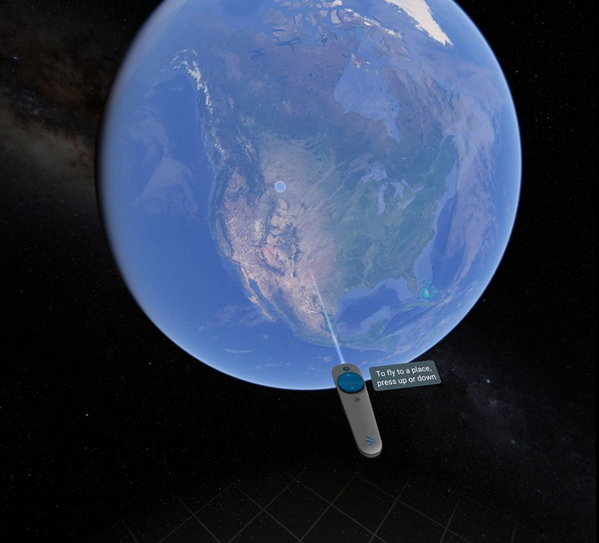
VR’s killer app has arrived, and it’s Google Earth — from arstechnica.com by Sam Machkovech
Squishy geometry aside, you won’t find a cooler free VR app on any device.
Excerpt:
I stood at the peak of Mount Rainier, the tallest mountain in Washington state. The sounds of wind whipped past my ears, and mountains and valleys filled a seemingly endless horizon in every direction. I’d never seen anything like it—until I grabbed the sun.
Using my HTC Vive virtual reality wand, I reached into the heavens in order to spin the Earth along its normal rotational axis, until I set the horizon on fire with a sunset. I breathed deeply at the sight, then spun our planet just a little more, until I filled the sky with a heaping helping of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Virtual reality has exposed me to some pretty incredible experiences, but I’ve grown ever so jaded in the past few years of testing consumer-grade headsets. Google Earth VR, however, has dropped my jaw anew. This, more than any other game or app for SteamVR’s “room scale” system, makes me want to call every friend and loved one I know and tell them to come over, put on a headset, and warp anywhere on Earth that they please.
VR is totally changing how architects dream up buildings — from wired.com by Sam Lubell
Excerpt:
In VR architecture, the difference between real and unreal is fluid and, to a large extent, unimportant. What is important, and potentially revolutionary, is VR’s ability to draw designers and their clients into a visceral world of dimension, scale, and feeling, removing the unfortunate schism between a built environment that exists in three dimensions and a visualization of it that has until now existed in two.
How VR can democratize Architecture — from researchvr.podigee.io
Excerpt:
Many of the VR projects in Architecture are focused on the final stages of design process, basically for selling a house to a client. Thomas sees the real potential in the early stages: when the main decisions need to be made. VR is so good for this, as it helps for non professionals to understand and grasp the concepts of architecture very intuitively. And this is what we talked mostly about.
How virtual reality could revolutionize the real estate industry — from uploadvr.com by Benjamin Maltbie
Will VR disrupt the airline industry? Sci-Fi show meets press virtually instead of flying — from singularityhub.com by Aaron Frank
Excerpt:
A proposed benefit of virtual reality is that it could one day eliminate the need to move our fleshy bodies around the world for business meetings and work engagements. Instead, we’ll be meeting up with colleagues and associates in virtual spaces. While this would be great news for the environment and business people sick of airports, it would be troubling news for airlines.
How theaters are evolving to include VR experiences — from uploadvr.com by Michael Mascioni
#AI, #VR, and #IoT Are Coming to a Courthouse Near You! — from americanbar.org by Judge Herbert B. Dixon Jr.
Excerpt:
Imagine during one of your future trials that jurors in your courtroom are provided with virtual reality headsets, which allow them to view the accident site or crime scene digitally and walk around or be guided through a 3D world to examine vital details of the scene.
How can such an evidentiary presentation be accomplished? A system is being developed whereby investigators use a robot system inspired by NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover using 3D imaging and panoramic videography equipment to record virtual reality video of the scene.6 The captured 360° immersive video and photographs of the scene would allow recreation of a VR experience with video and pictures of the original scene from every angle. Admissibility of this evidence would require a showing that the VR simulation fairly and accurately depicts what it represents. If a judge permits presentation of the evidence after its accuracy is established, jurors receiving the evidence could turn their heads and view various aspects of the scene by looking up, down, and around, and zooming in and out.
Unlike an animation or edited video initially created to demonstrate one party’s point of view, the purpose of this type of evidence would be to gather data and objectively preserve the scene without staging or tampering. Even further, this approach would allow investigators to revisit scenes as they existed during the initial forensic examination and give jurors a vivid rendition of the site as it existed when the events occurred.
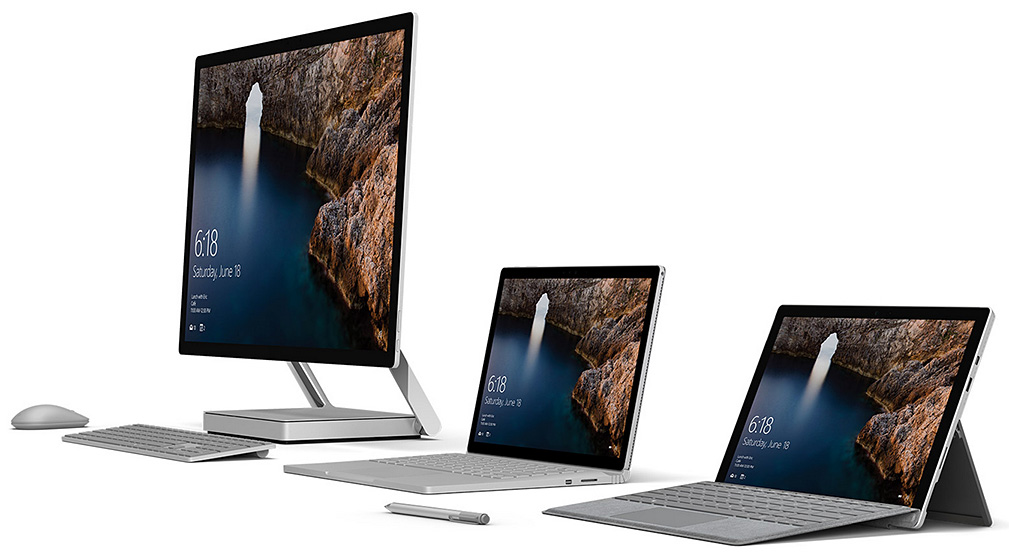
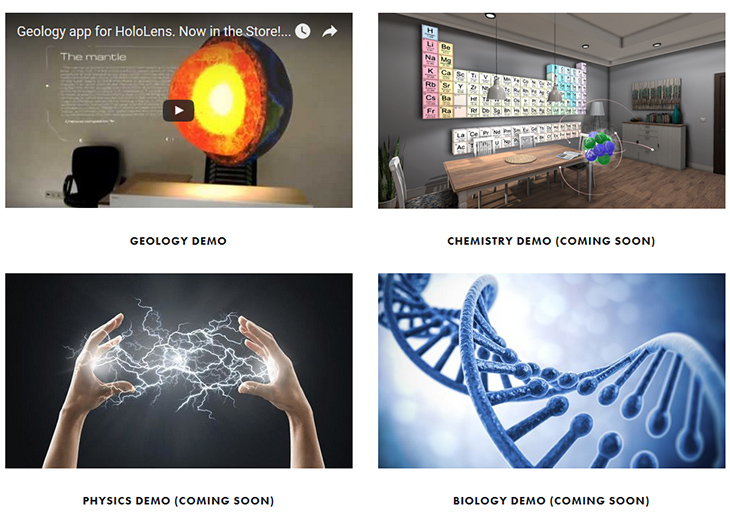
Microsoft goes long for mixed reality — from next.reality.news
Excerpt:
The theme running throughout most of this year’s WinHEC keynote in Shenzhen, China was mixed reality. Microsoft’s Alex Kipman continues to be a great spokesperson and evangelist for the new medium, and it is apparent that Microsoft is going in deep, if not all in, on this version of the future. I, for one, as a mixed reality or bust developer, am very glad to see it.
As part of the presentation, Microsoft presented a video (see below) that shows the various forms of mixed reality. The video starts with a few virtual objects in the room with a person, transitions into the same room with a virtual person, then becomes a full virtual reality experience with Windows Holographic.



























![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)