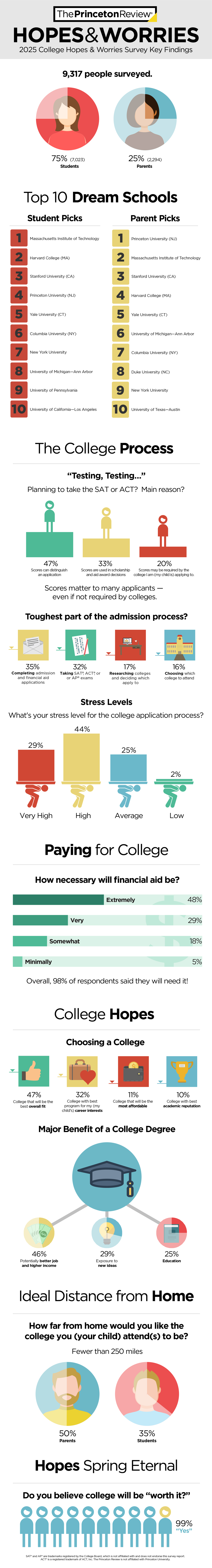
The legal tech trends that defined 2024 — from abajournal.com by Nicole Black
The year 2024 was one of change. In the midst of a largely unpopular back-to-office push, technological innovation and development occurred at a rapid clip. Legal professionals approached technology with a newfound curiosity and appreciation gained as a result of pandemic-era remote work experimentation. The increasing demand for generative artificial intelligence tools fueled heavy investments in the legal technology industry.
Simultaneously, law firm technology adoption was supported by a flurry of guidance released by ethics committees across the country. As technology upended traditional ways of working, some state bars reconsidered bar exam requirements and others experimented with loosening licensing regulations.
No matter where you looked, change was occurring at a breakneck pace as technology’s impact on the practice of law became inescapable. Through it all, a few key trends emerged that offer clues on where we’re headed in the coming year.
Meanwhile, some states, including Oregon, Washington and Nevada, explored allowing unlicensed professionals to practice law in limited areas, such as family law and small claims. These efforts seek to improve access to justice, representing a revised perspective on long-standing rules about who can —and cannot—deliver legal services.
What to Expect in 2025: AI Legal Tech and Regulation (65 Expert Predictions) — from natlawreview.com by Oliver Roberts
As 2024 comes to a close, it’s time to look ahead to how AI will shape the law and legal practice in 2025. Over the past year, we’ve witnessed growing adoption of AI across the legal sector, substantial investments in legal AI startups, and a rise in state-level AI regulations. While the future of 2025 remains uncertain, industry leaders are already sharing their insights.
Along with 2025 predictions from The National Law Review’s Editor-in-Chief Oliver Roberts, this article presents 65 expert predictions on AI and the law in 2025 from federal judges, startup founders, CEOs, and leaders of AI practice groups at global law firms.
The Potential of GenAI to Promote Access to Justice — from law.com by Joanne Sprague
GenAI-assisted legal support is not a substitute for lawyers, but may help legal aid professionals serve more clients efficiently and effectively.
Generative AI (GenAI) has been heralded as a transformative force, poised to revolutionize everything from medicine to education to law. While GenAI won’t perform surgery or earn diplomas, it holds the promise of enabling lawyers to get due process for more of their clients or even empowering individuals to represent themselves in court. The harsh reality is that low-income individuals do not receive sufficient legal help for 92% of their civil legal problems, and legal aid organizations must turn away one of every two requests they get, according to the 2022 Justice Gap Report. GenAI-assisted legal support is not a substitute for lawyers, but may help legal aid professionals serve more clients efficiently and effectively.
If implemented equitably, GenAI could democratize legal knowledge and empower individuals to navigate the complexities of the justice system more easily.
In her new book “Law Democratized,” Renee Knake Jefferson says that GenAI “has the potential to become the single most important tool in solving the legal justice crisis … if harnessed to do so ethically.” With GenAI, we can envision a possible future of informed self-representation and legal decision-making regardless of ability to pay.
Experimenting in the sandbox — from nationalmagazine.ca by Julie Sobowale
Ontario Bar Association launches AI platform for lawyers to learn tech
The Ontario Bar Association has launched a new, free interactive learning platform for lawyers looking to learn about generative AI.
…
The new learning platform, created to clarify some of that and help lawyers navigate this technology, is part of OBA’s Real Intelligence on AI project. It is being spearheaded by Colin Lachance, the association’s innovator-in-residence.
Users can ask questions to LawQI, an AI assistant specializing in Canadian law, and work through learning modules about prompt engineering, different generative AI tools and best practices. The portal is free for OBA members and Ontario law students.
“Lawyers need to know how AI works,” says Lachance, principal at PGYA Consulting and former president and CEO of the Canadian Legal Information Institute (CanLII).
“I wanted to create an environment where lawyers can experiment. By using the technology, you learn how to use it.”
The Innovation Strategist: Nicole Black — from substack.com by Tom Martin and Nicole Black
Where I interview Nicole Black about how she merged her legal expertise with her passion for technology to become a leading voice in legal innovation
Excerpt from Key Takeaways:
- Her role as employee #1 at MyCase in 2012 allowed her to combine her legal expertise with her passion for technology, leading to her current position as Principal Legal Insight Strategist at Affinipay
- She believes generative AI will fundamentally transform the legal profession, potentially more significantly than previous technological innovations like PCs and the internet
- Her advice for new lawyers includes actively experimenting with AI tools like ChatGPT and preparing for significant changes in legal education and entry-level legal work
Legal Liabilities of AI for Attorneys and Small Firms — from ethicalailawinstitute.org by Trent Kubasiak
Many small firms and solo attorneys could be in for a nasty shock when it comes to the use of AI. A detailed report from NYU’s Journal of Legislation and Public Policy is shedding light on the potential legal liabilities of using generative AI. Co-authored by EqualAI CEO Miriam Vogel, former Homeland Security Secretary Michael Chertoff, and others, the report underscores a widespread misconception—that liability for AI-related outcomes rests solely with the developers of these technologies.
For attorneys and small business owners, this misconception can be dangerous. As Vogel explains, “There are so many laws on the books that people need to know are applicable.” From lending and housing regulations to employment law, the use of AI—even indirectly—can expose firms to significant risks.
Challenges And Opportunities Of Digital Transformation In US Law Firms — from forbes.com by Chad Sands
So, what is driving the transformation?
Some adoption of new “legal tech” is literally being forced by legacy software companies who are shutting down older, server-based technology platforms. But most law firms are now increasingly becoming more proactive in planning and executing their digital transformation strategies on their own.
This is no longer a choice or matter of “Why should we?”
It’s a question of “When will we?”
There are several factors driving this shift, one being client expectations.
Fresh Voices On Legal Tech with Ilona Logvinova — from legaltalknetwork.com by Dennis Kennedy, Tom Mighell, and Ilona Logvinova
The world of AI and legal tech is evolving ever more rapidly, and it is all too common for lawyers to feel intimidated at the thought of keeping up with the constant barrage of change. How should lawyers maintain their tech competence? Dennis and Tom talk with Ilona Logvinova about her work in tech and AI innovations for lawyers. She shares her career journey and offers perspectives on leveraging technology to create new and better opportunities for attorneys to thrive in their work.
AI Insights for Legal: Ten Key Takeaways from Summit AI New York — from techlawcrossroads.com by Stephen Embry
Despite the shortcomings, it still was a good Conference. (i.e., the Summit AI New York). I learned some things and confirmed that many of the AI related issues being faced by legal are also being faced by many other businesses. What were my top ten takeaways? Here they are in no particular order: