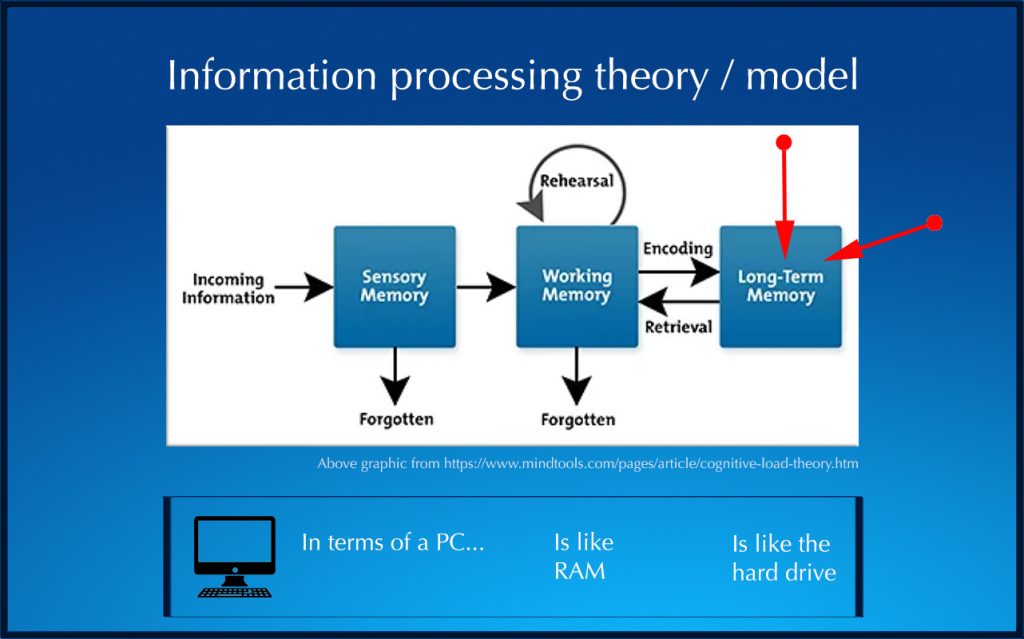
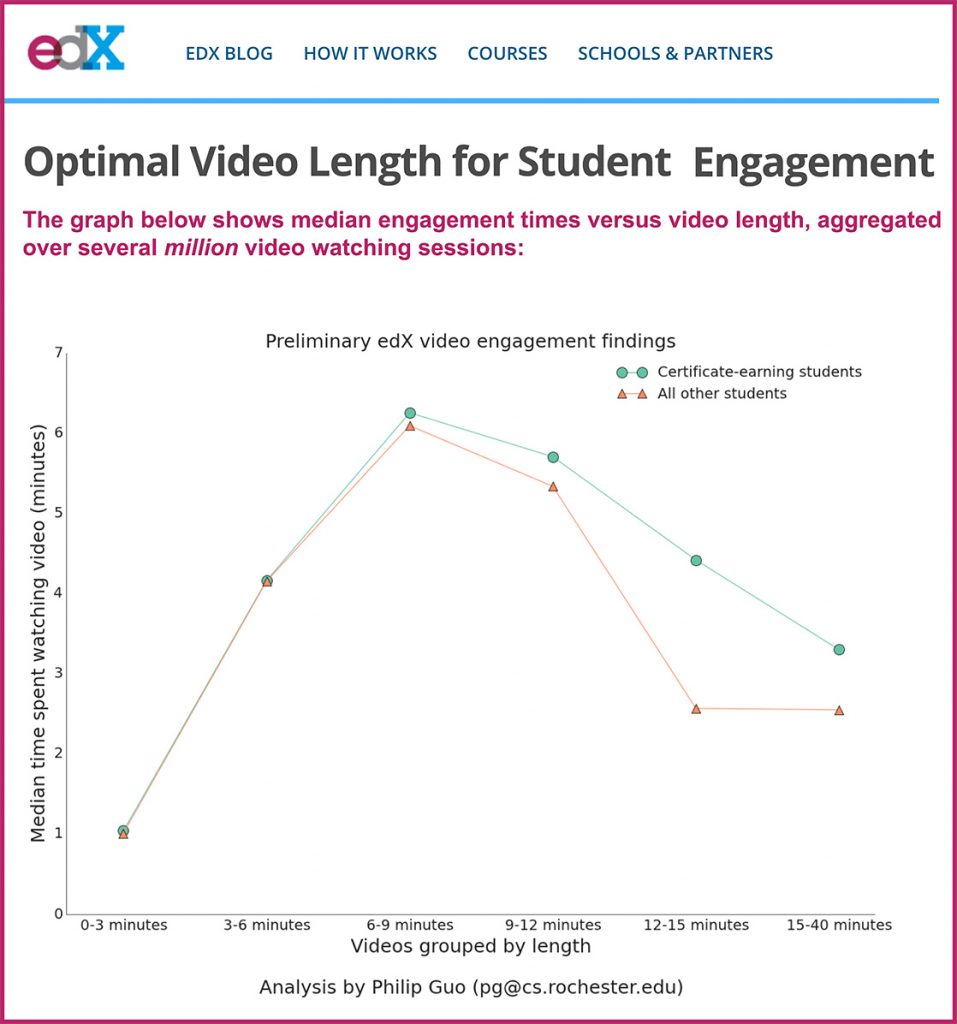
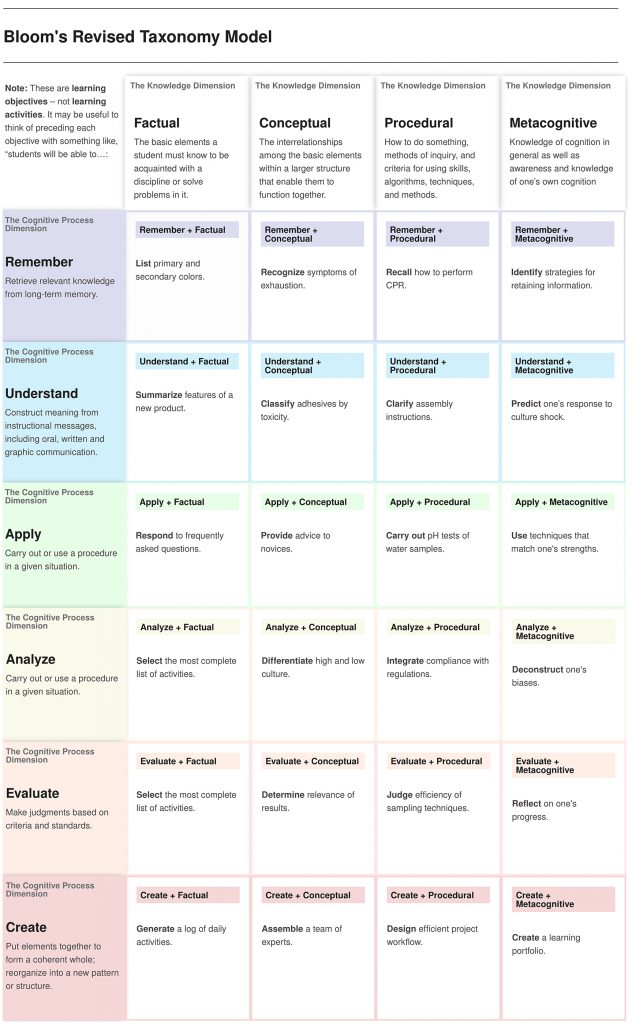
Coronavirus school cancellations lead to education tech surge –– from finance.yahoo.com by Reggie Wade
Excerpt:
Online learning tools like Zoom (ZM), Instructure’s (INST) Canvas, Cisco System’s (CSCO) WebEx and a host of other ed tech companies are coming to the aid of schools across the U.S. as they suspend or shift classes online due to the coronavirus outbreak.
Columbia University, Amherst College, the University of Washington, and Harvard University are among the growing list of universities that have announced that they will provide online classes, as campuses temporarily shut down in response to the contagion. More than 500 K-12 schools have also made the shift.
Jamie Candee, CEO of Edmentum, tells Yahoo Finance that since the outbreak of the coronavirus in the U.S. in January, the company has seen a surge in interest in its online educational tools. On March 9, the company had over 140 districts register for its online platform in under an hour.
Top Learning Tools when School is Closed — from cyber-kap.blogspot.com
Here is a list of suggested tools that can be used to keep the learning happening when schools are closed…
From DSC:
Some of these tools might also useful for some homeschooling situations I would think.
What Katrina Taught Us About Online Delivery — from insidehighered.com by Ray Schroeder
In 2005, more than 120 U.S. universities came to the aid of some 20 colleges and universities that had been impacted by Hurricane Katrina through shared online classes.
Cisco, Google Hangouts follow Zoom’s lead in offering free video conferencing features amid coronavirus outbreak — from bizjournals.com
Coronavirus causes work-from-home technology use to skyrocket — from foxbusiness.com
Microsoft usage in China increasing because more people are working remotely, company VP says