How Blippar Education supports special needs students to improve learning — from blippar.com

Excerpts:
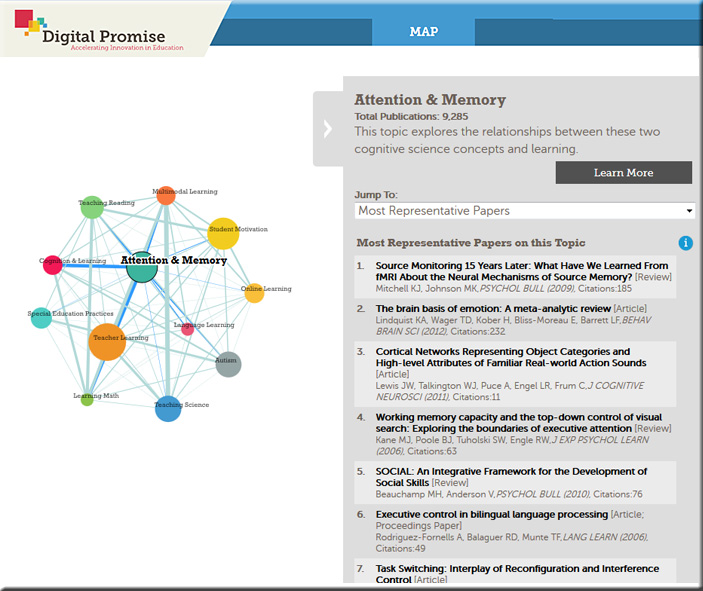
Firstly, high school teacher Katrine Pinkpank’s class made individual, blippable posters for their Earth Day projects in April. When passers-by blipped these posters – all of which were hung in beautiful frames in the hallways – they were taken to a video of the students doing their Earth Day presentation in front of the class. One student in the class is legally blind, so the braille on his poster was used to trigger the blipp. These hallway boards have become living, breathing, 3D tributes to the work of our students.
In Room 407, students used Blippar in many different ways. Wendy Thompson, an early adopter of the technology, used it for a Women’s History Month project where students created an app-smash between Blippar and Trading Cards. The students created trading cards about famous women in history – such as Ella Fitzgerald, Frida Kahlo, and Mary Shelley – then used Blippar to add photo galleries, hyperlinks, and videos so people passing the bulletin board could scan the cards and view pop-up content about these remarkable women.
Secondly, the class made the school newsletter blippable.
…
Using Blippar and Tellagami, the students created talking digital avatar videos that illustrated their post-secondary and transition goals.
From DSC:
Though this posting focuses on the use of Blippar, an augmented reality app, I also think beacons (such as from Estimote), machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, and apps like locly could be used to relay information from students, teachers, and faculty members who could record and provide presentations concerning their work — with pieces of their work being located out in the hallways or actually anywhere on a campus. When someone approaches a piece in the hallway, a pre-loaded application on that person’s mobile device — such as locly — would be activated to display a “card”/link to the video describing that piece. The author, creator, designer doesn’t need to be physically present in order to tell people about their work.
Also see:
Elements 4D
ZooKazam
NASA’s Spacecraft 3D
Anatomy 4D