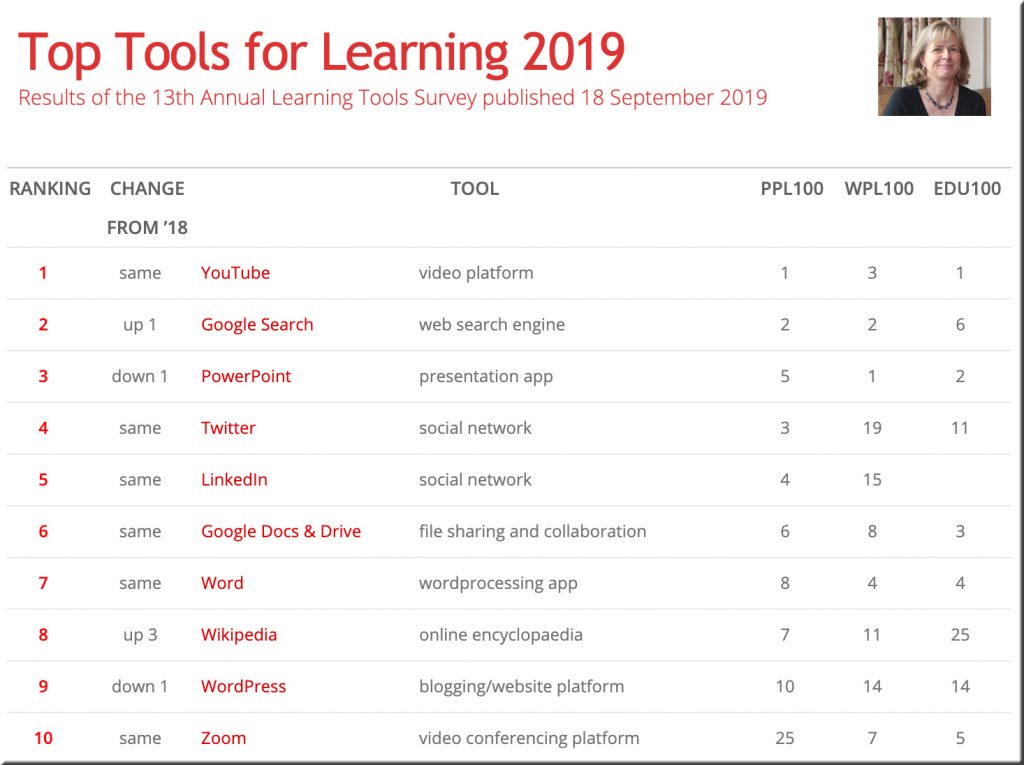
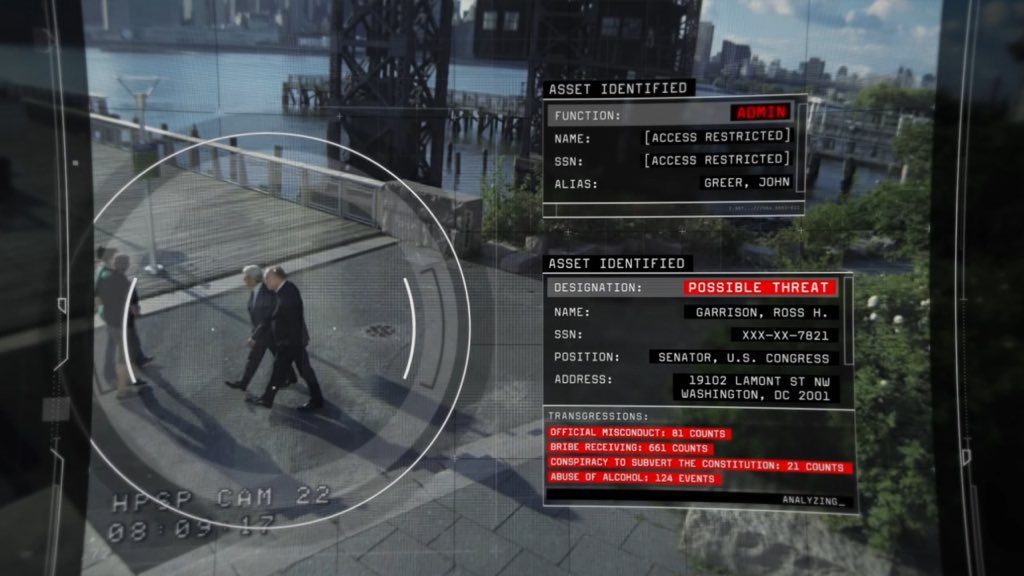
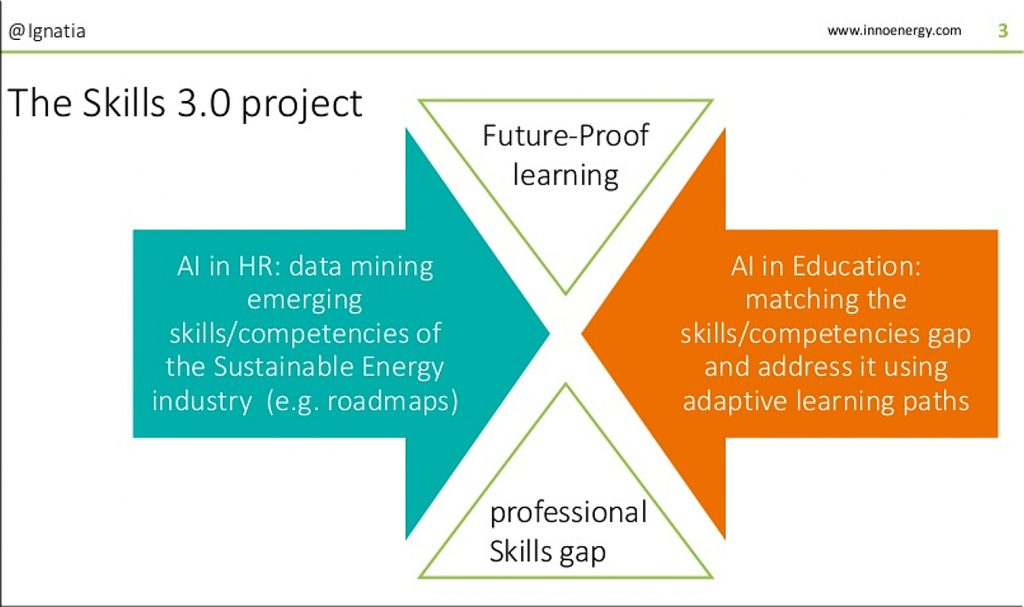
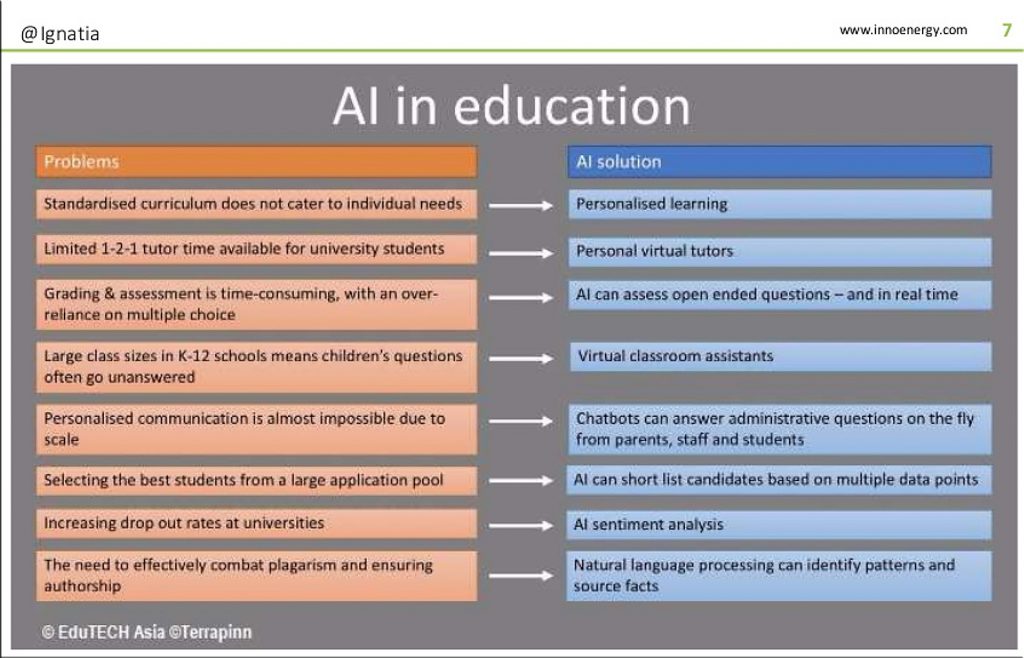
Emerging Tech Trend: Patient-Generated Health Data — from futuretodayinstitute.com — Newsletter Issue 124
Excerpt:
Near-Futures Scenarios (2023 – 2028):
Pragmatic: Big tech continues to develop apps that are either indispensably convenient, irresistibly addictive, or both, and we pay for them, not with cash, but with the data we (sometimes unwittingly) let the apps capture. But for the apps for health care and medical insurance, the stakes could literally be life-and-death. Consumers receive discounted premiums, co-pays, diagnostics and prescription fulfillment, but the data we give up in exchange leaves them more vulnerable to manipulation and invasion of privacy.
Catastrophic: Profit-driven drug makers exploit private health profiles and begin working with the Big Nine. They use data-based targeting to over prescribe patients, netting themselves billions of dollars. Big Pharma target and prey on people’s addictions, mental health predispositions and more, which, while undetectable on an individual level, take a widespread societal toll.
Optimistic: Health data enables prescient preventative care. A.I. discerns patterns within gargantuan data sets that are otherwise virtually undetectable to humans. Accurate predictive algorithms identifies complex combinations of risk factors for cancer or Parkinson’s, offers early screening and testing to high-risk patients and encourages lifestyle shifts or treatments to eliminate or delay the onset of serious diseases. A.I. and health data creates a utopia of public health. We happily relinquish our privacy for a greater societal good.
Watchlist: Amazon; Manulife Financial; GE Healthcare; Meditech; Allscripts; eClinicalWorks; Cerner; Validic; HumanAPI; Vivify; Apple; IBM; Microsoft; Qualcomm; Google; Medicare; Medicaid; national health systems; insurance companies.