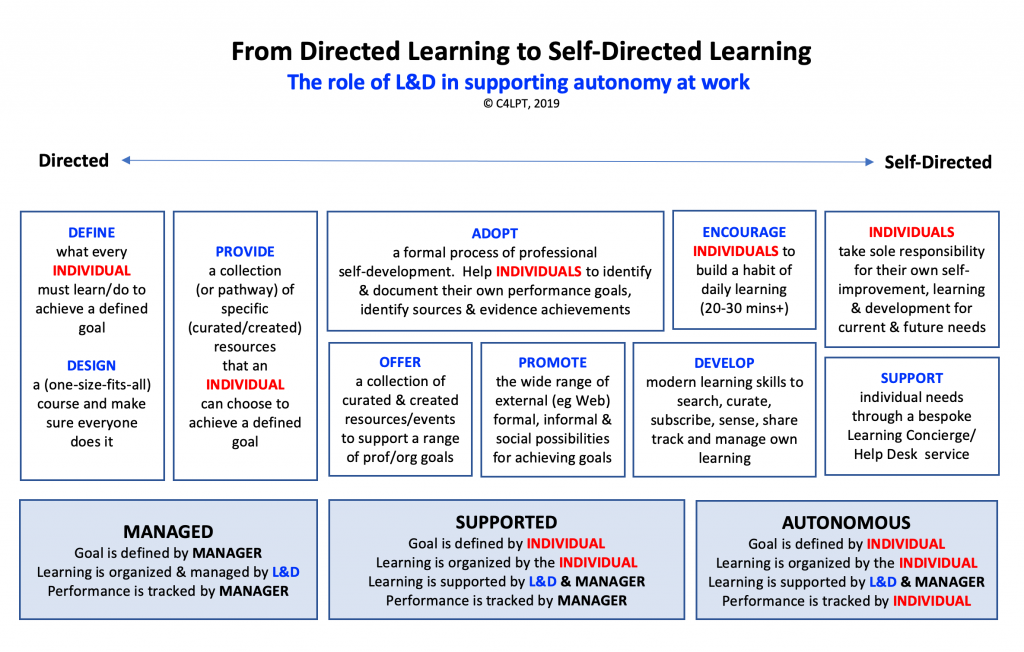
From DSC:
The two postings below show the need for more collaboration and the use of teams:
The future of law and computational technologies: Two sides of the same coin — from legaltechlever.com by Daniel Linna Jr.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
An increasing number of lawyers today work with allied professionals to improve processes, better manage projects, embrace data-driven methods, and leverage technology to improve legal services and systems. Legal-services and lawyer regulations are evolving. And basic technologies and AI are slowly making their way into the legal industry, from legal aid organizations and courts to large law firms, corporate legal departments, and governments.
If we are to realize the potential to improve society with computational technologies, law, regulation, and ethical principles must be front and center at every stage, from problem definition, design, data collection, and data cleaning to training, deployment, and monitoring and maintenance of products and systems. To achieve this, technologists and lawyers must collaborate and share a common vocabulary. Lawyers must learn about technology, and technologists must learn about law. Multidisciplinary teams with a shared commitment to law, regulation, and ethics can proactively address today’s AI challenges, and advance our collaborative problem-solving capabilities to address tomorrow’s increasingly complex problems. Lawyers and technologists must work together to create a better future for everyone.
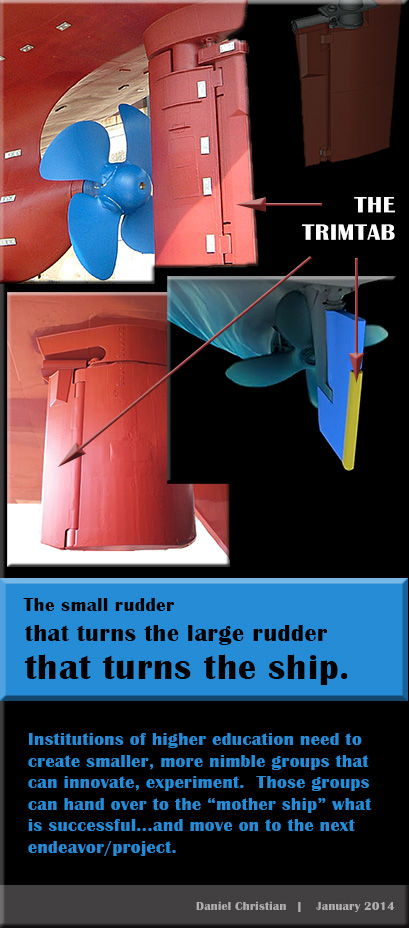
From DSC:
As with higher education in general, we need more team-based efforts in the legal realm as well as more TrimTab Groups.
Excerpts:
Why does this distinction matter? Because law—like so many industries—is undergoing a tectonic shift. It is morphing from a lawyer dominated, practice-centric, labor-intensive guild to a tech-enabled, process and data-driven, multi-disciplinary global industry. The career paths, skills, and expectations of lawyers are changing. So too are how, when, and on what financial terms they are engaged; with whom and from what delivery models they work; their performance metrics, and the resources—human and machine—they collaborate with. Legal practice is shrinking and the business of delivering legal services is expanding rapidly.
Law is no longer the exclusive province of lawyers. Legal knowledge is not the sole element of legal delivery—business and technological competencies are equally important. It’s a new ballgame—one that most lawyers are unprepared for.
…
How did we get here and are legal careers for most a dead end? Spoiler alert: there’s tremendous opportunity in the legal industry. The caveat: all lawyers must have basic business and technological competency whether they pursue practice careers or leverage their legal knowledge as a skill in legal delivery and/or allied professional careers.
Upskilling the legal profession is already a key issue, a requisite for career success. Lawyers must learn new skills like project management, data analytics, deployment of technology, and process design to leverage their legal knowledge. Simply knowing the law will not cut it anymore.
From DSC:
I really appreciate the work of the above two men whose articles I’m highlighting here. I continue to learn a lot from them and am grateful for their work.
That said, just like it’s a lot to expect a faculty member (in higher ed) who teaches online to not only be a subject matter expert, but also to be skilled in teaching, web design, graphic design, navigation design, information design, audio design, video editing, etc…it’s a lot to expect for a lawyer to be a skilled lawyer, business person, and technician. I realize that Mark was only saying a basic level of competency…but even that can be difficult to achieve at times. Why? Because people have different skillsets, passions, and interests. One might be a good lawyer, but not a solid technician…or vice versa. One might be a solid professor, but isn’t very good with graphic design.