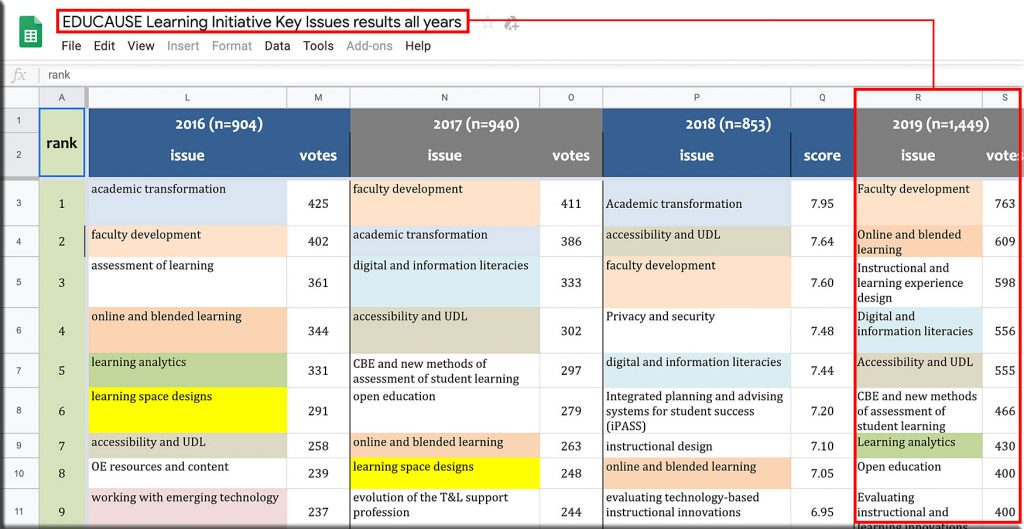
Presentation Translator for PowerPoint — from Microsoft (emphasis below from DSC:)
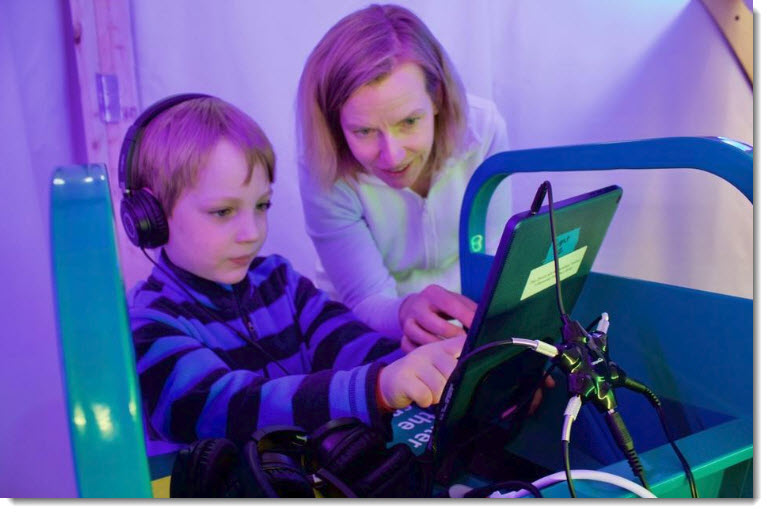
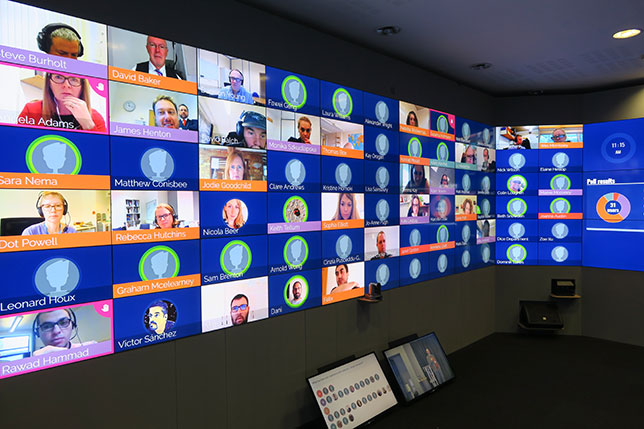
Presentation Translator breaks down the language barrier by allowing users to offer live, subtitled presentations straight from PowerPoint. As you speak, the add-in powered by the Microsoft Translator live feature, allows you to display subtitles directly on your PowerPoint presentation in any one of more than 60 supported text languages. This feature can also be used for audiences who are deaf or hard of hearing.
Additionally, up to 100 audience members in the room can follow along with the presentation in their own language, including the speaker’s language, on their phone, tablet or computer.
From DSC:
Up to 100 audience members in the room can follow along with the presentation in their own language! Wow!
Are you thinking what I’m thinking?! If this could also address learners and/or employees outside the room as well, this could be an incredibly powerful piece of a next generation, global learning platform!
Automatic translation with subtitles — per the learner’s or employee’s primary language setting as established in their cloud-based learner profile. Though this posting is not about blockchain, the idea of a cloud-based learner profile reminds me of the following graphic I created in January 2017.

A couple of relevant quotes here:
A number of players and factors are changing the field. Georgia Institute of Technology calls it “at-scale” learning; others call it the “mega-university” — whatever you call it, this is the advent of the very large, 100,000-plus-student-scale online provider. Coursera, edX, Udacity and FutureLearn (U.K.) are among the largest providers. But individual universities such as Southern New Hampshire, Arizona State and Georgia Tech are approaching the “at-scale” mark as well. One could say that’s evidence of success in online learning. And without question it is.
But, with highly reputable programs at this scale and tuition rates at half or below the going rate for regional and state universities, the impact is rippling through higher ed. Georgia Tech’s top 10-ranked computer science master’s with a total expense of less than $10,000 has drawn more than 10,000 qualified majors. That has an impact on the enrollment at scores of online computer science master’s programs offered elsewhere. The overall online enrollment is up, but it is disproportionately centered in affordable scaled programs, draining students from the more expensive, smaller programs at individual universities. The dominoes fall as more and more high-quality at-scale programs proliferate.
— Ray Schroeder
Education goes omnichannel. In today’s connected world, consumers expect to have anything they want available at their fingertips, and education is no different. Workers expect to be able to learn on-demand, getting the skills and knowledge they need in that moment, to be able to apply it as soon as possible. Moving fluidly between working and learning, without having to take time off to go to – or back to – school will become non-negotiable.
Anant Agarwal
From DSC:
Is there major change/disruption ahead? Could be…for many, it can’t come soon enough.