From DSC:
On the positive side…
What I appreciate about John Villasenor‘s article is that it’s asking us to think about future scenarios in regards to higher education. Then, it’s proposing some potential action steps to take now to address those potential scenarios if they come to fruition. It isn’t looking at the hood when we’re traveling 180 mph. Rather, it’s looking out into the horizon to see what’s coming down the pike.
6 Steps to Prepare for an Online Fall Semester — from chronicle.com by John Villasenor
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Plan for a multiyear impact. If colleges are forced to maintain online-only instruction in the fall and to defer reopening their campuses to in-person instruction to January 2021, the impact will be felt for years. College leaders should start thinking now about how to manage and potentially adjust spring-2021 (and beyond) course offerings, course sequencing, and degree requirements to avoid saddling students with graduation delays and the accompanying direct and indirect financial costs. In addition, colleges should anticipate a smaller-than-normal entering first-year class in fall 2020 (and thus a larger-than-normal enrollment a year later) and devise strategies to help mitigate the resulting stresses on admission rates and classroom and dorm capacity for first-year students entering in fall 2021 and beyond.
If instruction remains online-only in the fall, colleges won’t be able to afford that sort of inefficiency. College departments should start now to identify opportunities for collaborations that would draw on the collective wisdom and labor of faculty members from multiple institutions who are teaching similar courses. This would lessen the burden of migrating teaching materials and techniques to an online format.
From DSC:
I’ve often wondered about the place of consortiums within higher ed…i.e., pooling resources. Will the impacts of the Coronavirus change this area of higher ed? Not sure. Perhaps.
On the negative side…
I take issue with some of John’s perspectives, which are so common amongst the writers and academics out there. For example:
Conversely, an entire generation of current college students is now learning that it can be pretty boring to be one of several hundred people simultaneously watching a Zoom lecture.
You know what? I did that very same thing — over and over again — at Northwestern University (NU), but in a face-to-face format. And quite frankly, it’s a better view on videoconferencing. It’s far more close up, more intimate online. I agree it’s a different experience. But our auditoriums were large and having 100-200+ students in a classroom was common. There was no interaction amongst the students. There were no breakout groups. The faculty members didn’t know most of our names and I highly doubt that the well-paid researchers at Northwestern — who were never taught how to teach in the first place nor did they or NU regard the practice of teaching and learning highly anyway — gave a rat’s ass about body language. Reading the confusion in the auditorium? Really? I highly doubt it. And those TA’s that we paid good money for? Most likely, they were never taught how to teach either. The well-paid researchers often offloaded much of the teaching responsibilities onto the teacher assistants’ backs.
Bottom line:
Face-to-face learning is getting waaaay more credit than it sometimes deserves — though sometimes it IS warranted. And online-based learning — especially when it’s done right — isn’t getting nearly enough credit.
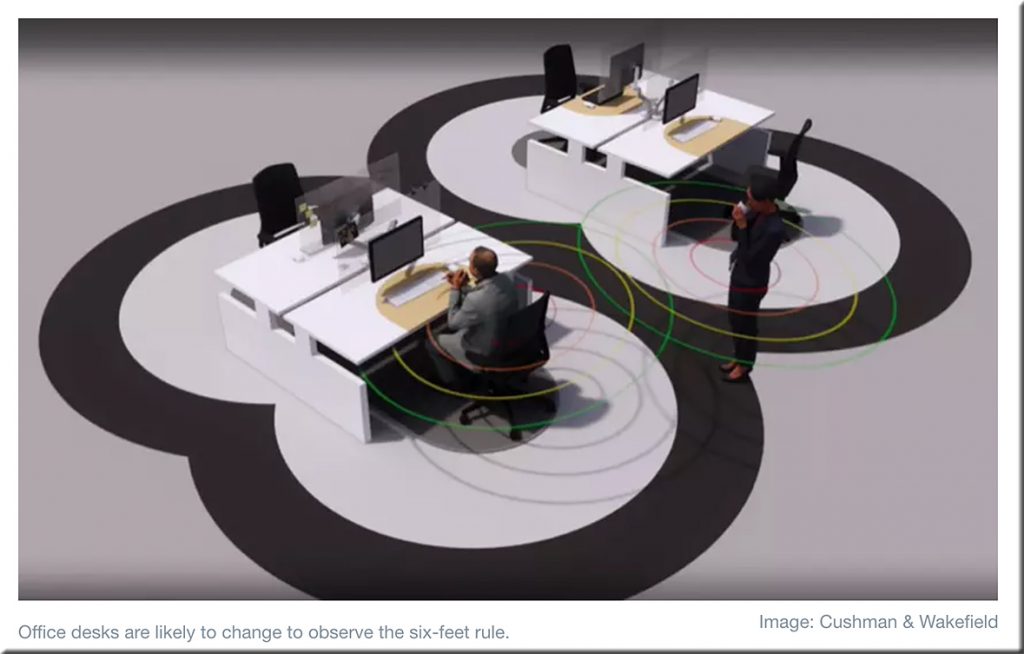
Addendum: Another example of practicing futures thinking in higher ed: