DC: Likely a piece of our future learning ecosystems… #AI #LearningEcosystems #Learning #LifelongLearning #Platforms https://t.co/rIISC4BQ8b via @YouTube
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) July 5, 2019




DC: Likely a piece of our future learning ecosystems… #AI #LearningEcosystems #Learning #LifelongLearning #Platforms https://t.co/rIISC4BQ8b via @YouTube
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) July 5, 2019
4 models to reinvent higher education for the 21st century — from edtechmagazine.com by Eli Zimmerman
To appeal to Gen Z students and employers, universities will adopt new ways to deliver academic materials, focusing on customizable courses and experiences outside of the classroom.
Excerpts:
Also see:
The World’s First Full in VR Semester Course Taught by Survios CTO — from medium.com by Rahel Demant
Excerpt:
VR First is excited to announce its strategic partnership with Axon Park?—?the world’s first educational campus in VR. To kick things off, they are running a full semester course taught in VR. Launching this fall, the course will teach expert-level Unreal Engine VR development, taught remotely by Survios CTO and Co-Founder Alex Silkin with support from the Unreal Engine team.
To enable Axon Park’s commitment to diversity and inclusion through immersive education, VR First has signed a strategic partnership with Axon Park, an organization which maintains the largest network of VR lab enabled universities and science parks internationally. Together, Axon Park and VR First are announcing a needs-based scholarship program that will provide students with low cost or free access to VR hardware and resources through their partner network of 850 universities. With their expertise in VR/AR workforce education and regional tech cluster facilities, VR First is the international distribution partner for Axon Park training solutions to universities, businesses and governments.
Also see:
This is likely the No. 1 thing affecting your job performance — from fastcompany.com by Art Markman
Hint: It all starts with figuring out what you don’t know.
Excerpts:
Learning on the job is probably the single most important factor driving your performance at work. You won’t know everything you need to about your job when you’re hired, no matter how good your education is or how much experience you had in previous positions. The road to learning starts with a willingness to admit what you don’t know and an interest in learning new things.
The ability to know what you know and what you don’t know is called metacognition—that is, the process of thinking about your thinking. Your cognitive brain has a sophisticated ability to assess what you do and don’t know. You use several sources of information to make this judgment.
…
One important social aspect of the Dunning-Kruger effect is that it often leads to tension between younger employees and the firms they work for. People who don’t really understand what skills are required for success in a particular domain may overestimate their own abilities and minimize their perception of the gap between themselves and more senior members of a firm. As a result, they won’t understand why they aren’t being promoted faster and will quickly get frustrated in the early stages of their career. The more you appreciate everything involved in expert performance, the more patient you can be with your own development.
After you get the hang of a new position, be strategic about what you learn. You probably need a wider range of expertise than you think. Solving hard problems at work requires drawing not just on expertise from within the domain of your work, but also on knowledge about other areas that may not have seemed relevant at first.
Blockchain: The move from freedom to the rigid, dominant system in learning — from oeb.global by Inge de Waard
In this post Inge de Waard gives an overview of current Blockchain options from industry and looks at its impact on universities as well as philosophises on its future.
Excerpt:
I mentioned a couple of Blockchain certification options already, but an even more advanced blockchain in learning example has entered on my radar too. It is a Russian implementation called Disciplina. This platform combines education (including vocational training), recruiting (comparable with what LinkedIn is doing with its economic graph) and careers for professionals. All of this is combined into a blockchain solution that keeps track of all the learners’ journey. The platform includes not only online courses as we know it but also coaching. After each training, you get a certificate.
TeachMePlease, which is a partner of Disciplina, enables teachers and students to find each other for specific professional training as well as curriculum-related children’s schooling. Admittedly, these initiatives are still being rolled out in terms of courses, but it clearly shows where the next learning will be located: in an umbrella above all the universities and professional academies. At present, the university courses are being embedded into course offerings by corporations that roll out a layer post-university, or post-vocational schooling.
Europe embraces blockchain, as can be seen with their EU Blockchain observatory and forum. And in a more national action, Malta is storing their certifications in a blockchain nationwide as well. We cannot deny that blockchain is getting picked up by both companies and governments. Universities have been piloting several blockchain certification options, and they also harbour some of the leading voices in the debate on blockchain certification.
Also see:
Also see:
Survey: Students Choosing Online Programs Closer to Home — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
Mentioned in that article:
Also see:
“It’s encouraging to see that a majority of students who are studying fully online are reporting great value and satisfaction with their online programs which are largely tied to ambitious career goals,” said Todd Zipper, president and CEO of Learning House, in a prepared statement. “With an increasing population of savvier consumers with high expectations, institutions need to do better at offering more quality, diverse programs that are sensitive to cost in order to keep up with the growing demands of online college students.”
From DSC:
If, in the year 2019, most students say online learning is as good or better than face-to-face, what will they say come 2025? 2035?
Many people will still prefer to have F2F-based learning experiences no matter what year it is. That said, as the innovation continues to occur mainly in the digital/online/virtual realms, F2F will likely find it harder and harder to compete. My advice to current faculty members? Get experience teaching online — and do so as soon as you possibly can.
Going Beyond the Digital Diploma — from campustechnology.com by Sara Friedman
Excerpts:
“We see great opportunities with this platform to create a more streamlined approach to help with students transferring, receiving degrees, honoring requests to verify degrees and to admit new students and evaluate their transcripts,” said ECPI University CIO Jeff Arthur. “The ability to let someone hold all of their accomplishments on their phone and have them to share with anybody in a way that is secure and reliable — without having to chase down entities to verify — is attractive to us.”
…
College and university CIOs also hope that blockchain technology can help to streamline other administrative functions. For instance, the ability to transfer credits between institutions could be simplified, according to Arthur.
The next big leap for blockchain in the higher education space is likely to be the ability to put badges and certificates for technical skills on the chain.
“We want to create a lifelong learning approach where people who want to represent their skills and experience can do so through a blockchain-based app,” said Callahan.

Online directory of college alternatives launches — from educationdive.com by Natalie Schwartz
Excerpt / Dive Brief:
Has Technology Made State Regional Universities Obsolete? — from campustechnology.com by Richard Rose
While SRUs do some things well, the current model is not sustainable, with students taking on enormous debt and receiving relatively little income benefit in return. Here’s how technology can help change the equation.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
What if the State Board of Higher Education assembled a team to create one exceptionally fine Official Texas Version of the sophomore Western Civilization course? The team would include brilliant subject-matter experts, the best graphic artists, senior instructional designers, professional film editors and sharp-eyed text editors, who could produce a 48-clock-hour video course of previously unimaginable quality.
…
When technology is fully embraced because the need for a better and cheaper product finally trumps the political protection of the status quo, the state regional university will be replaced as part of new state university systems in which local institutions will play a very different role. These new local institutions could be called Learning Satellite Centers (LSCs).
…
Much content will take the form of high-budget, high-quality multimedia productions with delivery available to all popular devices, from desktop computers to cell phones. Access to learning materials, from course movies and podcasts to reading materials, will be through an expanded electronic distribution system that will eliminate the need for paper-based academic libraries.
…
The goal of the University Center plus Learning Satellite Center model is to transfer agency back into the hands of the students, where it belongs. No longer will a self-appointed privileged group of professional academics with their arcane degrees and funny ceremonial robes be dictating to the rest of society what we all need to learn and how we need to learn it. Technology will be the great leveler and the marketplace will help individual students decide what choices are best.
Of course, a brief sketch like this one will raise many questions that cannot be explored in a single article, but the conversation must begin. The current State Regional University is not sustainable and can only be propped up by politics and sentiment for so long. Too many students are piling up huge debt to earn dubious degrees that don’t lead to marketable skills or significant economic benefits. Technology has made more effective models of higher education attainable and at a lower price. We need to fearlessly explore such models before our charming old regional campuses drift into irrelevance.
From DSC:
While the article has a bit of a bite to it (which I suppose readers of this blog would say they might see in my writings/comments as well from time to time), THIS is the kind of innovative, creative thinking that will get us somewhere. I really appreciate Richard’s article and the deep thought he was put into this topic.
In fact, as readers of this blog will know, I have long been a supporter of a TEAM-BASED approach. And listed below are some graphics that prove it — as well as this article I wrote for evolllution.com (where the “lll” stands for lifelong learning) back from 2016.
This page* lists those graphics plus the list of team members that I thought of in December 2008:
*BTW, I renamed this idea from the Forthcoming Walmart of Education
to the Forthcoming Amazon.com of Higher Education


.
While I’m at it…below are a couple of ideas that I documented back in 2009 that Richard might like…
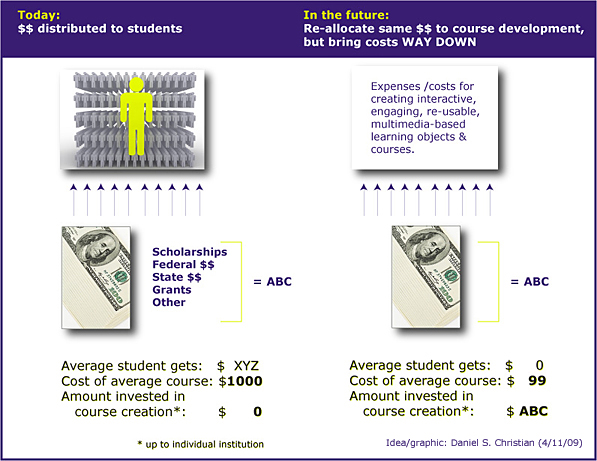
.
As of today…I would simplify that last graphic to
include a subscription model to streams of content.
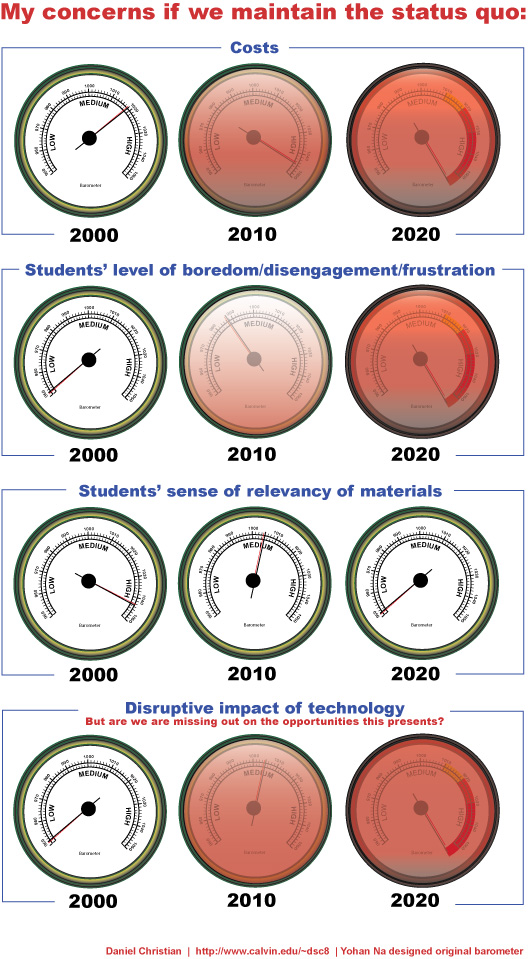
Ok…one more graphic from 5/21/09 that describes what I thought would happen if institutions of traditional higher education maintained the status quo through the years. I feel pretty good about how these predictions turned out, but I wish that we would have made even more progress along these lines than we have (since the time I created this graphic).
Introduction: Leading the social enterprise—Reinvent with a human focus
2019 Global Human Capital Trends — from deloitte.com by Volini?, Schwartz? ?, Roy?, Hauptmann, Van Durme, Denny, and Bersin
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Learning in the flow of life. The number-one trend for 2019 is the need for organizations to change the way people learn; 86 percent of respondents cited this as an important or very important issue. It’s not hard to understand why. Evolving work demands and skills requirements are creating an enormous demand for new skills and capabilities, while a tight labor market is making it challenging for organizations to hire people from outside. Within this context, we see three broader trends in how learning is evolving: It is becoming more integrated with work; it is becoming more personal; and it is shifting—slowly—toward lifelong models. Effective reinvention along these lines requires a culture that supports continuous learning, incentives that motivate people to take advantage of learning opportunities, and a focus on helping individuals identify and develop new, needed skills.
From DSC:
Re: the Learning from the Living [Class] Room vision of a next gen learning platform…
…wouldn’t it be cool if you could use your voice to ask your smart/connected “TV” type of device:
“Show me the test questions for Torts I from WMU-Cooley Law School. Cooley could then charge $0.99 for these questions.”
Then, the system knows how you did on answering those questions. The ones you got right, you don’t get asked to review as often as the ones you got wrong. As you get a question right more often, the less you are asked to answer it.
You sign up for such streams of content — and the system assesses you periodically. This helps a person keep certain topics/information fresh in their memory. This type of learning method would be incredibly helpful for students trying to pass the Bar or other types of large/summative tests — especially when a student has to be able to recall information that they learned over the last 3-5 years.
Come to think of it…this method could help all of us in learning new disciplines/topics throughout our lifetimes. Sign up for the streams of content that you want to learn more about…and drop the (no-longer relevant) subscriptions as needed..

From DSC:
Here’s a ~4 minute piece from CBS News re: student loan debt.
Here are two excerpts from that video:
From DSC to potential college students:
You need to know that the ramifications of this type of debt can last for decades! Do everything you possibly can to either not borrow anything or to minimize these types of loan amounts.
This is another reason why the United States desperately needs a ***next generation learning platform*** — one that’s convenient, very inexpensive, and one that can also help people quickly reinvent themselves! One that is highly social, features human Subject Matter Experts (SME’s), and is backed up by #AI – based apps/features as well.
Along these lines…no longer are we running sprints (i.e., get a 4-year degree and you’re done). We’re now all running marathons (i.e., we’re now into lifelong learning in order to stay relevant and employed).
Also, the following item was announced today:
Also see:
From DSC:
Along these lines, I don’t think Cengage/McGraw-Hill will be the largest company on the Internet by 2030 as predicted by Thomas Frey (a prediction I think he’s right on with…by the way). They were on watch when the prices of learning-related materials soared through the years. As such, they’ve likely burned through a great deal of good will…but we’ll see. They might be able to persuade myself and others that they’re the platform of choice for the future. Time will tell I guess.
Coursera raises $103 million to prepare online learners for the ‘fourth industrial revolution’ — from venturebeat.com by Paul Sawers
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Founded in 2012, Coursera is one of a number of well-funded MOOCs — massive open online courses — to emerge. Coursera partners with universities and other educational institutions to deliver online courses to 40 million students, covering subjects like technology, business, science, and even autonomous cars.
…
“The fourth industrial revolution, marked by advancements in automation and artificial intelligence, is dramatically reshaping our lives, businesses, and jobs,” noted Coursera CEO Jeff Maggioncalda. “Coursera is at the forefront of preparing individuals, companies, and governments to meet that challenge head-on and turn this disruption into opportunity. The additional funding gives us the resources and flexibility to further expand internationally and to accelerate the development of a learning platform that currently serves 40 million learners, 1,800 businesses, and over 150 top universities.”
Minerva’s Innovative Platform Makes Quality Higher Ed Personal and Affordable — from linkedin.com by Tom Vander Ark
Excerpt:
The first external partner, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), loved the course design and platform but told Nelson they couldn’t afford to teach 15 students at a time. The Minerva team realized that to be applicable at major universities, active learning needed to be scalable.
Starting this summer, a new version of Forum will be available for classes of up to 400 at a time. For students, it will still feel like a small seminar. They’ll see the professor, themselves, and a dozen other students. Forum will manage the movement of students from screen to screen. “Everybody thinks they are in the main room,” said Nelson.
…
Forum enables real-time polling and helps professors create and manage breakout groups.
…
Big Implications
With Forum, “For the first time you can deliver better than Ivy League education at absurdly low cost,” said Nelson.
Online courses and MOOCs just repackaged the same format and just offered it with less interaction. As new Forum partners will demonstrate, “It’s possible to deliver a year of undergraduate education that is vastly superior for under $5,000 per student,” added Nelson.
He’s excited to offer a turnkey university solution that, for partners like Oxford Teachers Academy, will allow new degree pathways for paraprofessionals that can work, learn, and earn a degree and certification.
Perhaps another piece of the puzzle is falling into place…