From DSC:
For anyone out there who thinks that teaching and learning is easy and who agrees with the uninformed saying that goes “Those who can’t do…teach”…might I recommend a few potential to-do’s for you to try out…?
- Try teaching 30-35 students yourself for at least 4-6 weeks about a topic that you just found out that you’ll be teaching and one that you don’t know much about. (And see if you enjoy the process that some teachers sometimes have to go through…putting down the tracks right in front of the trains that are rapidly moving down the tracks right behind them.) Also, you must have at least one student in your class who requires an Individualized Education Program (IEP) as well as 4-5 students who constantly cause trouble and who don’t want to be in school at all.
.
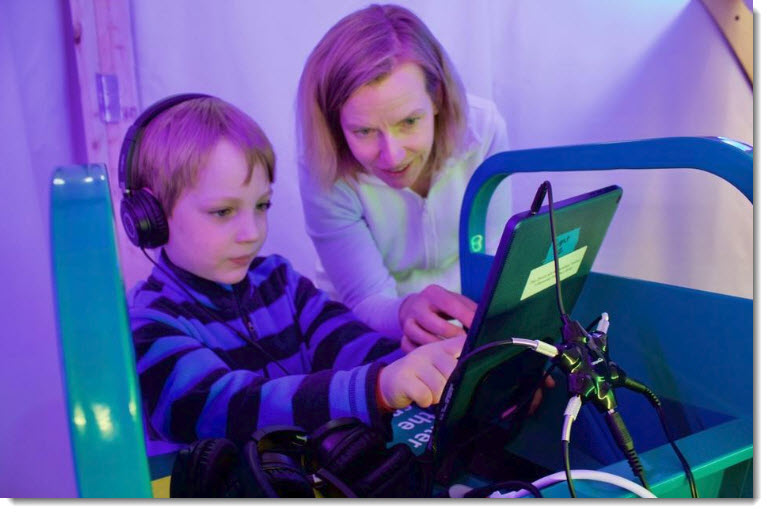
- Identify each student’s strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences — and their Zone of Proximal Development — then customize the learning that each of your 30-35 learners receives (with the goal of keeping each student moving forward at their most appropriate pace, while staying encouraged and yet appropriately challenged).
.
- Attend Individualized Education Program (IEP) meetings and work with other IEP team members to significantly contribute to the appropriate student’s (or students’) teaching and learning environment(s). For a real challenge, at least one of those students will be someone who is struggling, but is very much hanging in there — someone who is “right in the middle of the pack,” so to speak. (My guess is that if you did this, you would never think of teaching, nor teachers, nor other specialists in quite the same way again. My guess is that you would develop a whole new appreciation for how complex teaching and learning really is.)
Regarding that last item about at least one of your students requiring an IEP, here are some questions that might come up:
- What specialized services are needed this year?
- What do the teachers need to know about this student’s cognitive processing/executive functioning?
- How has the student been doing with the specialized services and teaching and learning strategies that have been attempted since the last IEP meeting?
- If their scores are going down, how are you going to address that issue (especially given limited resources)?
- How is the student’s motivation level doing? Is attending school still a positive experience? Or are things starting to become negative and/or downright painful for the student? Are they starting to get bummed out about having to come to school?
- How are they relating with and collaborating with other students? If poorly, how are you going to address that issue? How are you going to handle group-related projects (especially after reading all of those articles that assert which skills the workplace values these days)?
- What do you do with grades and assessments? Do you treat the student differently and give them higher grades to keep them encouraged? But if you do that, will your school system back you up on that or will someone come down hard on you for doing that? Or, perhaps you will find yourself struggling internally — trying to figure out what grades are really for and wondering if they are helpful in the first place. In fact, you might find yourself wondering if grades aren’t really just a mechanism for ranking and comparing individuals, schools, and even entire school systems (which, as we know, impacts property values)?
- What do grades really produce — game players or (lifelong) learners? It won’t surprise you to know that I would argue that the former is what gets “produced.” Grades don’t really produce as many learners as they do game-players (i.e., students who know the minimum amount of work that they need to do and still get that all important A).
So, as you can hopefully see here, learning is messy. It’s rarely black and white…there’s a lot of gray out there and a lot of things to consider. It’s not a one-size fits all. And teaching others well is certainly NOT easy to do!
RELEVANT IDEAS:
While I’m thinking about related ideas here…wouldn’t it be great if EVERY. SINGLE. STUDENT. could have their own IEP and their own TEAM of specialists — people who care about their learning?
What if each student could have their own cloud-based learner profile — a portion of which would be a series of VoiceThreads per student, per period of time (or per mastering a particular topic or area)? Such VoiceThreads could include multimedia-based comments, insights, and recommendations for how the student is doing and how they best learn. Through the years, those teams of people — people who care about that student’s learning — could help that student identify their:
- strengths
- weaknesses
- passions/interests
- their optimal learning strategies and preferences
- potential careers
The students could periodically review such feedback.
For every single student, we could build a history of feedback, helpful suggestions,
and recommendations via audio, video, text, graphics, etc.