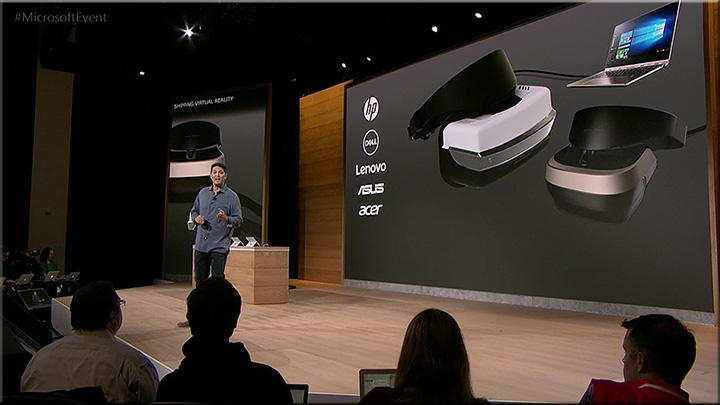
The gigantic list of augmented reality use cases — from uploadvr.com by Sarah Downey
Excerpt:
This gigantic list of future AR use cases should get you reeling with the possibilities. Although most of these are future applications, they’ll arrive within the next 10 to 15 years. Let’s make this a living document: if I missed a major use of AR, comment below and I’ll add it.
Three quick notes before we start. First, let’s clarify the difference between AR and VR.
VR blocks out the real world and immerses the user in a digital experience.
If you’re putting on a headset in your living room and suddenly transported to a zombie attack scenario, that’s VR.
AR adds digital elements on top of the real world.
If you’re walking down the street in real life and a Dragonite pops up on the sidewalk, that’s AR.
…
AR is more focused on bridging digital and physical spaces. It accompanies you as you move through the world and augments your activities with information, whereas you typically step out of that world to immerse yourself in VR. When we talk about AR headsets, they’re big helmet-like visors now, but they’re heading toward normal-looking glasses and ultimately contact lenses.
Third, AR and VR are converging into the same thing. Our ability to tell what’s “real” and not digital will decrease as graphics get increasingly better. An AR sign outside a building could be as real and as significant as a physical one if everyone is using AR tech, everyone sees it when they walk by, and it is persistent in that location. Ultimately, we’ll have hardware that lets us switch between AR and VR modes, with less and more opacity for the context. We’re discussing AR and VR distinctly for now because they’re developing separately and on different timelines.
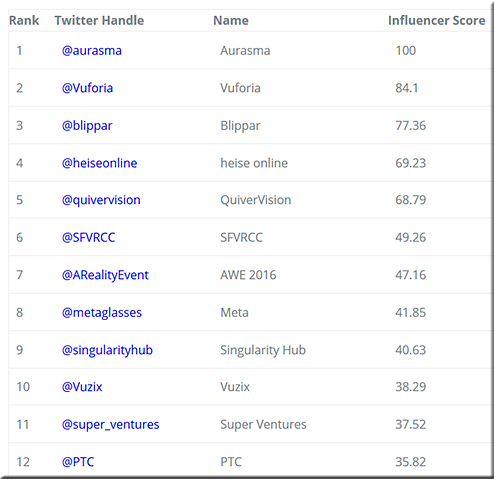
Augmented Reality: Top 100 Influencers and Brands — from onalytica.com
Augmented reality is going from ‘Pokémon Go’ to the factory floor — from businessinsider.com by Matt Weinberger
Excerpt:
That data, readily available from other sources, is just the tip of the iceberg, though, Campbell says. It also overlays a graphic showing how the pieces fit together, how to disassemble it, and what other pieces of the machine that part might connect to. It combines the physical world of the machine part with the digital world of the IoT-gleaned info.
Just being able to look at a machine, and say, yes, this is the one that needs work, and this is the work that needs doing, can vastly improve the speed with which work gets done, and thus operational efficiency of the whole enterprise.
“There’s so much value in visualizing information,” Campbell says.
Virtual Reality Changes Global Engineering Schools — from by Ilana Kowarski
Engineering professors say virtual reality contributes to the student experience.
Excerpt:
At engineering schools throughout the world, professors are turning to virtual reality technology in the classroom.
The technology provides 3-D visuals that help engineering students improve their designs, alerting them to flaws before the building process starts.
Engineering schools are researching technologies that could transform the way people communicate and interact by – for instance – allowing people to visit one another in a virtual space if they can’t meet in person. Engineering schools are also exploring medical applications of virtual reality that could save lives, such as 3-D X-rays that allow doctors to peer inside the bodies of patients.
Some engineering schools are taking virtual reality lessons a step further and challenging students to develop new virtual reality programs.

Broward Students Learning Through Augmented Reality — from nbcmiami.com by Ari Odzer
Excerpt:
We hear about technology’s impact on education all the time. Usually, that means computers, new apps, or 3D printers. Now there’s a new tool that has the promise of revolution, the potential for creating a new paradigm in how students learn. It’s called augmented reality.
Augmented Reality And Kinect Create Unique Art Experience At Cleveland Museum — from forbes.com by Jennifer Hicks
Addendum on 11/1/16:
- Alibaba introduces new shopping experience in virtual reality — from haptical











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)