Colleges cut academic programs in the face of budget shortfalls due to Covid-19 — from cnbc.com by Jessica Dickler
Key points:
- As colleges face extreme budget shortfalls, some institutions are cutting academic programs that were once central to a liberal arts education.
- The University of Alaska system announced it will cut 39 academic departments in all, including sociology, creative writing, chemistry and environmental science.
Even before the global pandemic caused craters in the economy, some institutions were facing financial hardship after years of declines in state funding for higher education. A number of private schools had already made wrenching budget cuts, from curriculum changes to complete overhauls of their liberal arts programs.
From DSC:
A screenshot from the video (below) shows a new type of liberal arts program at Hiram College.
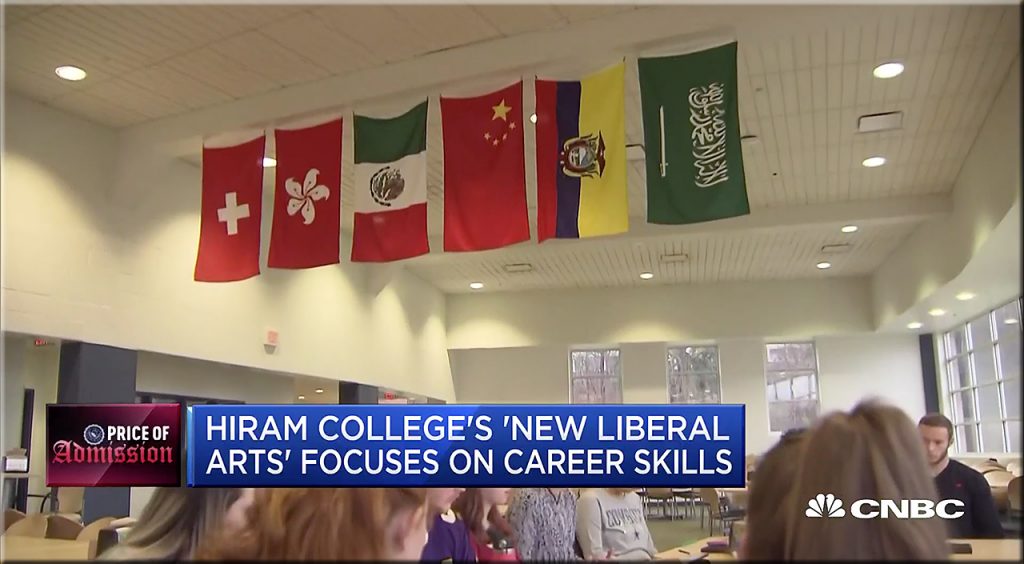

It could very well be that online-based learning turns out to save the liberal arts!!!!! How ironic is that!?!!
That is, many college presidents, provost, and faculty members — especially from smaller liberal arts types of schools — have disdained online-based learning for decades now. It was always viewed as “less than” in their minds…they didn’t want to go that route, as doing so would dilute their precious (and often overpriced) brands. (To be clear, this is not my view…but it was, and still is in many cases, their view.)
Anyway, it looks like more of these same folks will be losing their jobs in the next few years (if they haven’t already). At that point, we may see some of these same folks encounter a sudden paradigm shift. (A shift many of their colleagues have already gone through in prior years.) These same folks may come to appreciate that people will be willing to pay them for their knowledge — but only willing to do so at a much more affordable price…which will likely mean online.
Fewer people — especially when 47 million people in the U.S. alone have filed for unemployment over the last 14 weeks — can afford the cost of getting a degree. They are looking for inexpensive, convenient, efficient, effective means of reinventing themselves.

Huh…another potential irony here…it appears that colleges and universities are coming to know what many of us have known and experienced for years…and that is, the struggle to:
- Reinvent oneself
- Stay relevant
- Survive