This posting can also be seen out at evoLLLution.com (where LLL stands for lifelong learning):

From DSC:
What might our learning ecosystems look like by 2025?
In the future, learning “channels” will offer more choice, more control. They will be far more sophisticated than what we have today.

That said, what the most important aspects of online course design end up being 10 years from now depends upon what types of “channels” I think there will be and what might be offered via those channels. By channels, I mean forms, methods, and avenues of learning that a person could pursue and use. In 2015, some example channels might be:
- Attending a community college, a college or a university to obtain a degree
- Obtaining informal learning during an internship
- Using social media such as Twitter or LinkedIn
- Reading blogs, books, periodicals, etc.
In 2025, there will likely be new and powerful channels for learning that will be enabled by innovative forms of communications along with new software, hardware, technologies, and other advancements. For examples, one could easily imagine:
- That the trajectory of deep learning and artificial intelligence will continue, opening up new methods of how we might learn in the future
- That augmented and virtual reality will allow for mobile learning to the Nth degree
- That the trend of Competency Based Education (CBE) and microcredentials may be catapulted into the mainstream via the use of big data-related affordances
Due to time and space limitations, I’ll focus here on the more formal learning channels that will likely be available online in 2025. In that environment, I think we’ll continue to see different needs and demands – thus we’ll still need a menu of options. However, the learning menu of 2025 will be more personalized, powerful, responsive, sophisticated, flexible, granular, modularized, and mobile.
Highly responsive, career-focused track
One part of the menu of options will focus on addressing the demand for more career-focused information and learning that is available online (24×7). Even in 2015, with the U.S. government saying that 40% of today’s workers now have ‘contingent’ jobs and others saying that percentage will continue climbing to 50% or more, people will be forced to learn quickly in order to stay marketable. Also, the 1/2 lives of information may not last very long, especially if we continue on our current trajectory of exponential change (vs. linear change).
However, keeping up with that pace of change is currently proving to be out of reach for most institutions of higher education, especially given the current state of accreditation and governance structures throughout higher education as well as how our current teaching and learning environment is set up (i.e., the use of credit hours, 4 year degrees, etc.). By 2025, accreditation will have been forced to change to allow for alternative forms of learning and for methods of obtaining credentials. Organizations that offer channels with a more vocational bent to them will need to be extremely responsive, as they attempt to offer up-to-date, highly-relevant information that will immediately help people be more employable and marketable. Being nimble will be the name of the game in this arena. Streams of content will be especially important here. There may not be enough time to merit creating formal, sophisticated courses on many career-focused topics.

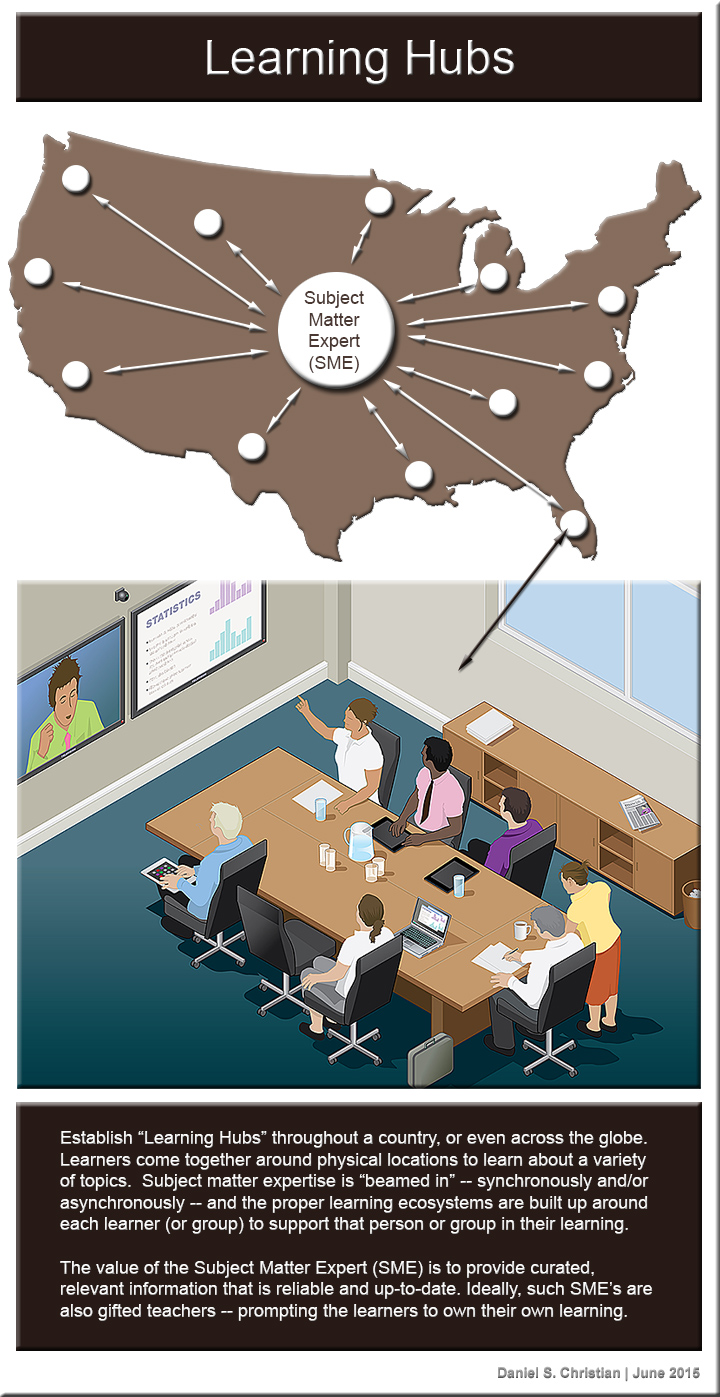
With streams of content, the key value provided by institutions will be to curate the most relevant, effective, reliable, up-to-date content…so one doesn’t have to drink from the Internet’s firehose of information. Such streams of content will also offer constant potential, game-changing scenarios and will provide a pulse check on a variety of trends that could affect an industry. Social-based learning will be key here, as learners contribute to each other’s learning. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) will need to be knowledgeable facilitators of learning; but given the pace of change, true experts will be rare indeed.
Microcredentials, nanodegrees, competency-based education, and learning from one’s living room will be standard channels in 2025. Each person may have a web-based learner profile by then and the use of big data will keep that profile up-to-date regarding what any given individual has been learning about and what skills they have mastered.
For example, even currently in 2015, a company called StackUp creates their StackUp Report to add to one’s resume or grades, asserting that their services can give “employers and schools new metrics to evaluate your passion, interests, and intellectual curiosity.” Stackup captures, categorizes, and scores everything you read and study online. So they can track your engagement on a given website, for example, and then score the time spent doing so. This type of information can then provide insights into the time you spend learning.
Project teams and employers could create digital playlists that prospective employees or contractors will have to advance through; and such teams and employers will be watching to see how the learners perform in proving their competencies.
However, not all learning will be in the fast lane and many people won’t want all of their learning to be constantly in the high gears. In fact, the same learner could be pursuing avenues in multiple tracks, traveling through their learning-related journeys at multiple speeds.
The more traditional liberal arts track
To address these varied learning preferences, another part of the menu will focus on channels that don’t need to change as frequently. The focus here won’t be on quickly-moving streams of content, but the course designers in this track can take a bit more time to offer far more sophisticated options and activities that people will enjoy going through.
Along these lines, some areas of the liberal arts* will fit in nicely here.
*Speaking of the liberal arts, a brief but important tangent needs to be addressed, for strategic purposes. While the following statement will likely be highly controversial, I’m going to say it anyway. Online learning could be the very thing that saves the liberal arts.
Why do I say this? Because as the price of higher education continues to increase, the dynamics and expectations of learners continue to change. As the prices continue to increase, so do peoples’ expectations and perspectives. So it may turn out that people are willing to pay a dollar range that ends up being a fraction of today’s prices. But such greatly reduced prices won’t likely be available in face-to-face environments, as offering these types of learning environment is expensive. However, such discounted prices can and could be offered via online-based environments. So, much to the chagrin of many in academia, online learning could be the very thing that provides the type of learning, growth, and some of the experiences that liberal arts programs have been about for centuries. Online learning can offer a lifelong supply of the liberal arts.
But I digress…
By 2025, a Subject Matter Expert (SME) will be able to offer excellent, engaging courses chocked full of the use of:
- Engaging story/narrative
- Powerful collaboration and communication tools
- Sophisticated tracking and reporting
- Personalized learning, tech-enabled scaffolding, and digital learning playlists
- Game elements or even, in some cases, multiplayer games
- Highly interactive digital videos with built-in learning activities
- Transmedia-based outlets and channels
- Mobile-based learning using AR, VR, real-world assignments, objects, and events
- …and more.
However, such courses won’t be able to be created by one person. Their sophistication will require a team of specialists – and likely a list of vendors, algorithms, and/or open source-based tools – to design and deliver this type of learning track.
Final reflections
The marketplaces involving education-related content and technologies will likely look different. There could be marketplaces for algorithms as well as for very granular learning modules. In fact, it could be that modularization will be huge by 2025, allowing digital learning playlists to be built by an SME, a Provost, and/or a Dean (in addition to the aforementioned employer or project team). Any assistance that may be required by a learner will be provided either via technology (likely via an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled resource) and/or via a SME.
We will likely either have moved away from using Learning Management Systems (LMSs) or those LMSs will allow for access to far larger, integrated learning ecosystems.
Functionality wise, collaboration tools will still be important, but they might be mind-blowing to us living in 2015. For example, holographic-based communications could easily be commonplace by 2025. Where tools like IBM’s Watson, Microsoft’s Cortana, Google’s Deepmind, and Apple’s Siri end up in our future learning ecosystems is hard to tell, but will likely be there. New forms of Human Computer Interaction (HCI) such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) will likely be mainstream by 2025.
While the exact menu of learning options is unclear, what is clear is that change is here today and will likely be here tomorrow. Those willing to experiment, to adapt, and to change have a far greater likelihood of surviving and thriving in our future learning ecosystems.
















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)