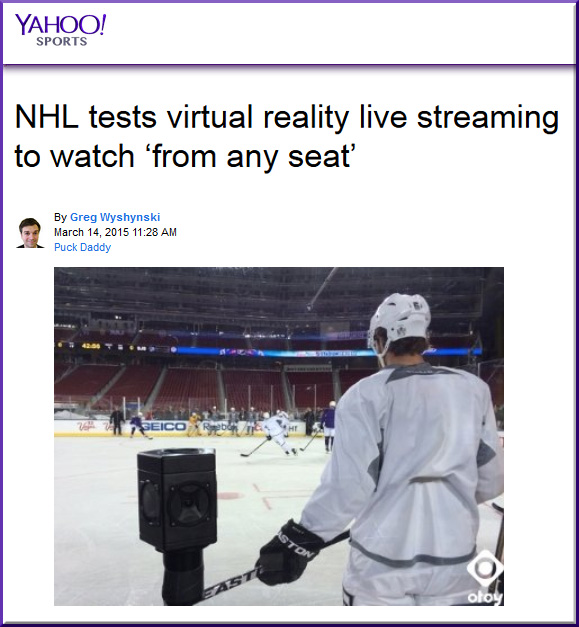
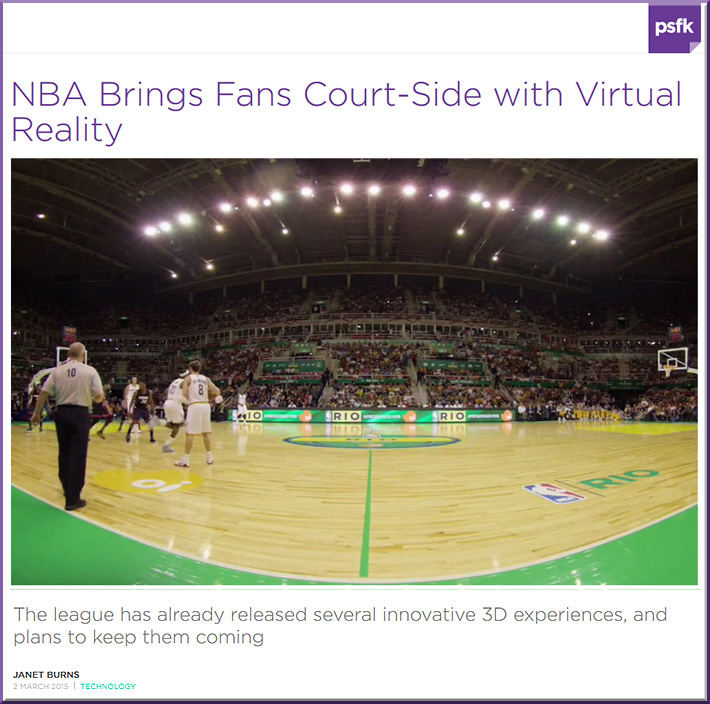
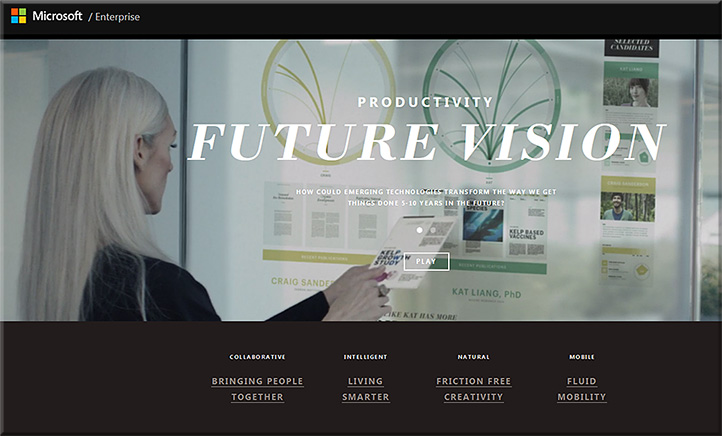
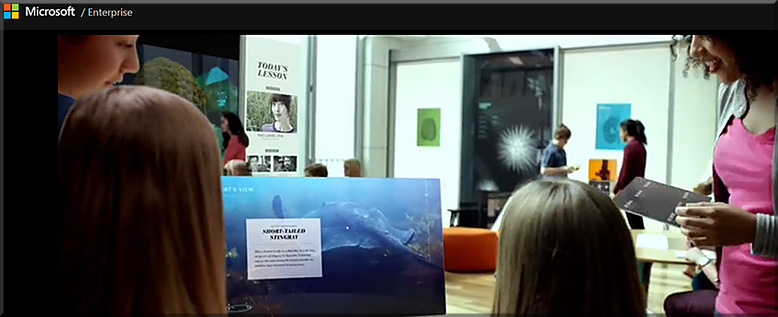
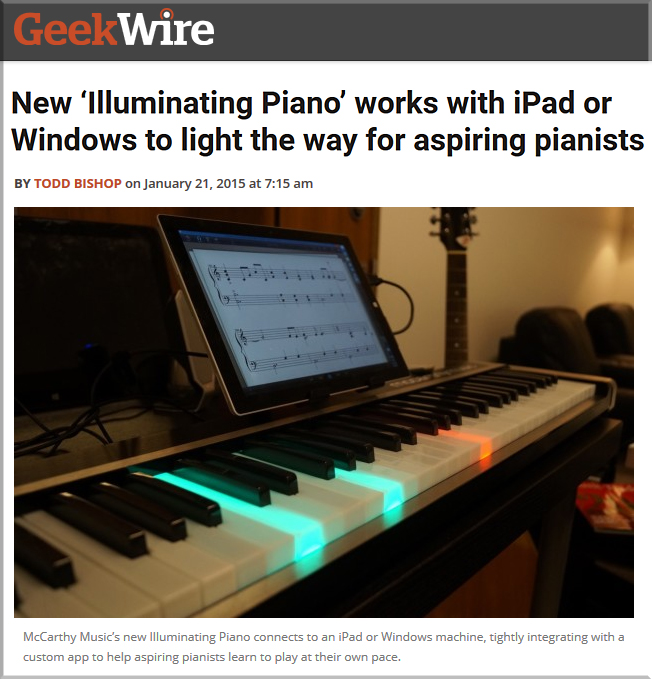
4 ways technology can make your music lessons sing — from thejournal.com by David Raths
New tech tools that give students control over their music also inspire them to create and innovate.
Excerpt:
Russell can send students audio recordings that they can play along with as they practice. His students can use a music-writing app such as Notion to make their own practice tracks and compose their own songs. “That is a complete redefinition of what you do with students,” he said. “It was inconceivable before they had these devices.”
Russell said he is also excited about a relatively new app called NotateMe, which allows him to write musical notation and convert it to digital notation. The app also allows you to take a picture of a score and convert it to digital music.
…
But now with tools such as NoteFlight, second- and third-graders can create wonderful melodic compositions and play them on their recorder,” she said.
…
Pirzer now uses her Epson BrightLink interactive projector in conjunction with Smart Notebook collaborative learning software and apps such as TonalEnergy Tuner, which lets users understand and improve every aspect of their sound.
How to find free music for videos — from mccoyproductions.net by Jason McCoy <– Jason’s posting includes 31 Amazing Sites With Free Creative Commons Music
Excerpt:
If you’re embarking on a video project, perhaps an explainer video, podcast, school project or video presentation, using the right production music can be the key to successfully drawing your viewers in; but finding the perfect song can seem a daunting task.
Of course you could commission a track to be composed especially for you, but that can run into tens of thousands of dollars.
Luckily, there are plenty of places available for you to find free music for your video project, but where can you get it from and how do you know if you have the legal right to use it for your project?
Music Notation on the iPad – NotateMe Rules! — from ipadmusiced.wordpress.com by Paul Shimmons
Excerpt:
I’ve just got to mention the fact that the NotateMe app combined with the PhotoScore plug-in is an absolutely astounding tool!
THE SCENARIO –
I’ve got a contra-alto clarinet player and I really want her to play lower notes then what is written on the Baritone Sax part.
Automatic Music Generator Jukedeck Wins Le Web Startup Competition — from techcrunch.com by Mike Butcher
Excerpt:
London-based JukeDeck has received a small seed funding round for its platform which literally composes original music based on a user’s settings, giving video creators, games developers and other users a simple way of sourcing music. This might be based on the actions inside a video or a game, without any human intervention. The idea is that it’s “responsive music software”. It doesn’t use loops, but writes the music note by note, as a composer would.
This means it can, say its makers, create an unlimited amount of unique, copyright-free music, and users can choose the music’s style and what should happen in the music at various points. The first market will be for user-generated videos. The idea here is not to compete with human composers but to produce machine-made music that is listenable and eventually malleable by real musicians.
From DSC:
Then there’s an idea I had about being able to hear whichever parts you want to hear as you practice a piece of music. Don’t have a piano? No problem. You can’t play the piano even if you do have access to one? No problem. Want to hear just the tenor and alto parts? No problem. Want to hear just your bass part? No problem. Want to hear all parts together? No problem. Jump to measure 121? No problem. Publishers of music could provide music recorded in parts and let you select which part(s) you want to play and hear.
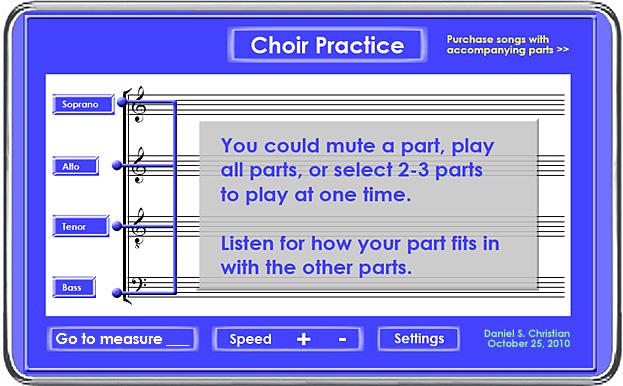
Addendum on 12/15/14:









![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)