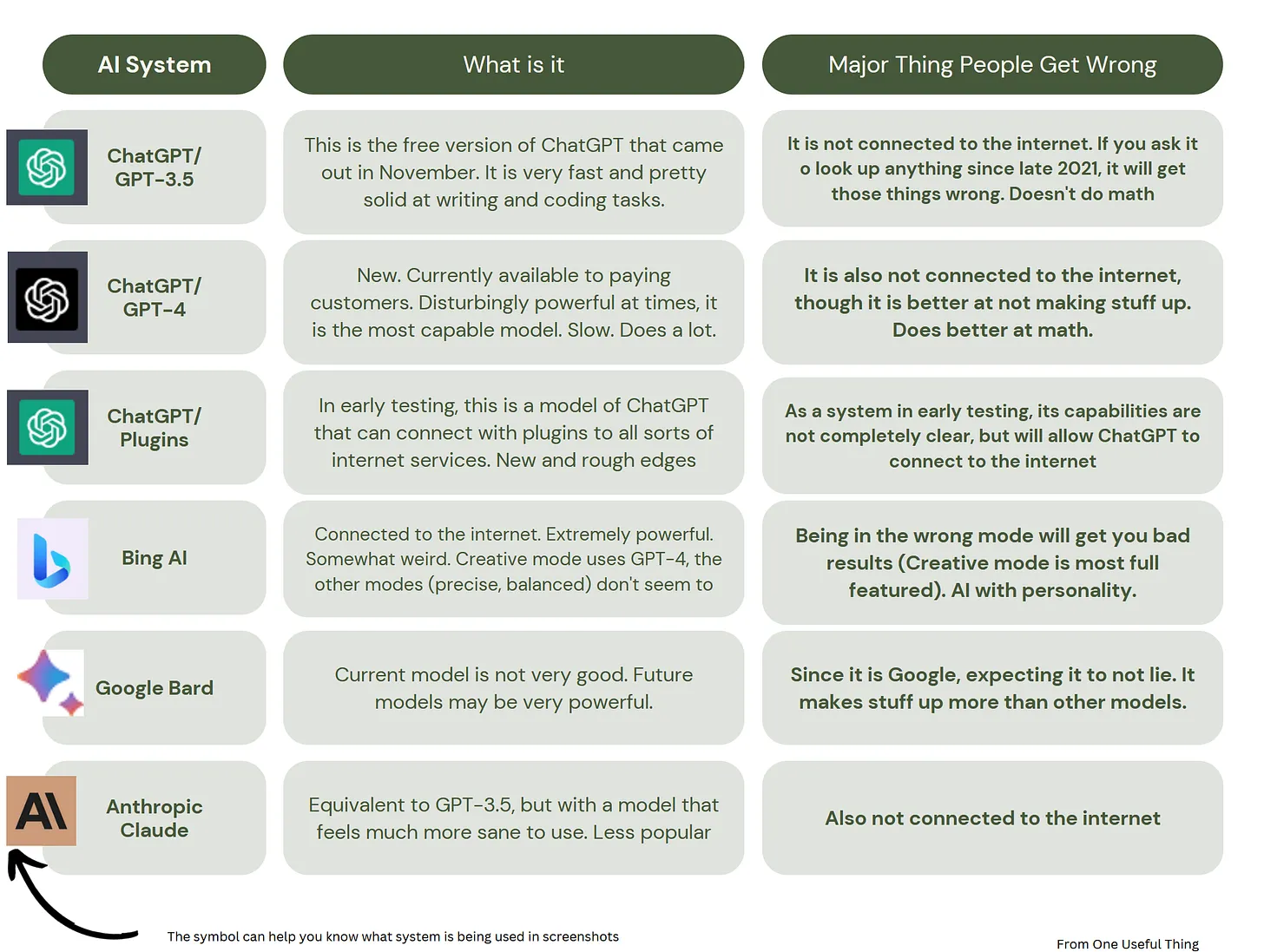
ChatGPT is Everywhere — from chronicle.com by Beth McMurtrie
Love it or hate it, academics can’t ignore the already pervasive technology.
Excerpt:
Many academics see these tools as a danger to authentic learning, fearing that students will take shortcuts to avoid the difficulty of coming up with original ideas, organizing their thoughts, or demonstrating their knowledge. Ask ChatGPT to write a few paragraphs, for example, on how Jean Piaget’s theories on childhood development apply to our age of anxiety and it can do that.
Other professors are enthusiastic, or at least intrigued, by the possibility of incorporating generative AI into academic life. Those same tools can help students — and professors — brainstorm, kick-start an essay, explain a confusing idea, and smooth out awkward first drafts. Equally important, these faculty members argue, is their responsibility to prepare students for a world in which these technologies will be incorporated into everyday life, helping to produce everything from a professional email to a legal contract.
“Artificial-intelligence tools present the greatest creative disruption to learning that we’ve seen in my lifetime.”
Sarah Eaton, associate professor of education at the University of Calgary
Artificial intelligence and academic integrity, post-plagiarism — from universityworldnews.com Sarah Elaine Eaton; with thanks to Robert Gibson out on LinkedIn for the resource
Excerpt:
The use of artificial intelligence tools does not automatically constitute academic dishonesty. It depends how the tools are used. For example, apps such as ChatGPT can be used to help reluctant writers generate a rough draft that they can then revise and update.
Used in this way, the technology can help students learn. The text can also be used to help students learn the skills of fact-checking and critical thinking, since the outputs from ChatGPT often contain factual errors.
When students use tools or other people to complete homework on their behalf, that is considered a form of academic dishonesty because the students are no longer learning the material themselves. The key point is that it is the students, and not the technology, that is to blame when students choose to have someone – or something – do their homework for them.
There is a difference between using technology to help students learn or to help them cheat. The same technology can be used for both purposes.
From DSC:
These couple of sentences…
In the age of post-plagiarism, humans use artificial intelligence apps to enhance and elevate creative outputs as a normal part of everyday life. We will soon be unable to detect where the human written text ends and where the robot writing begins, as the outputs of both become intertwined and indistinguishable.
…reminded me of what’s been happening within the filmmaking world for years (i.e., such as in Star Wars, Jurrasic Park, and many others). It’s often hard to tell what’s real and what’s been generated by a computer.