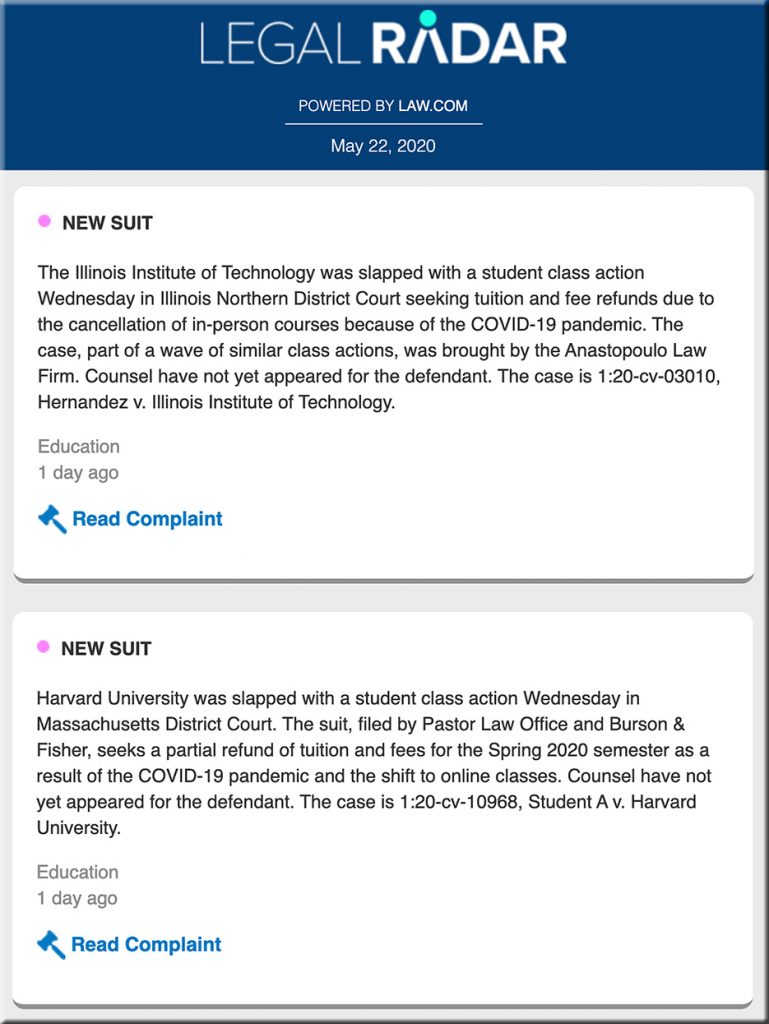
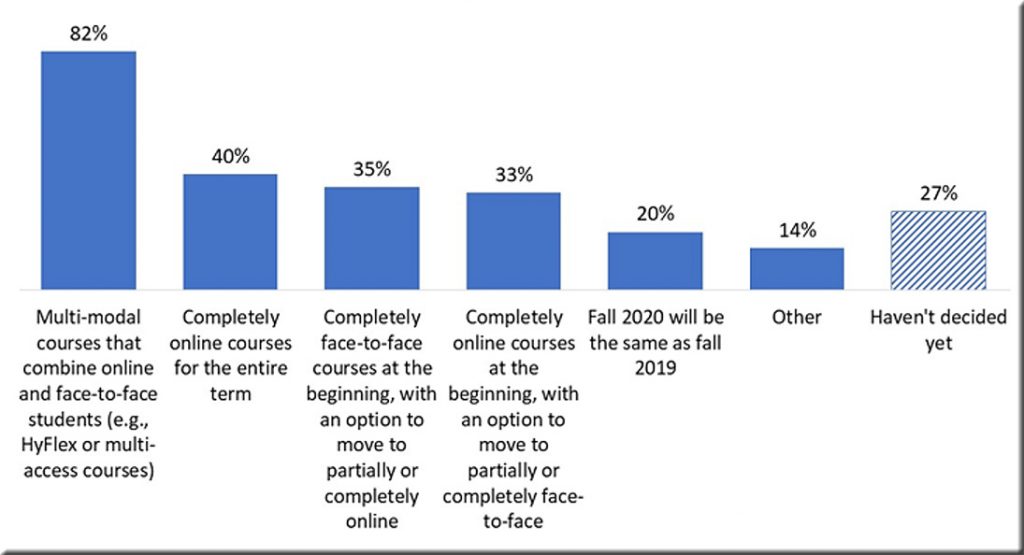
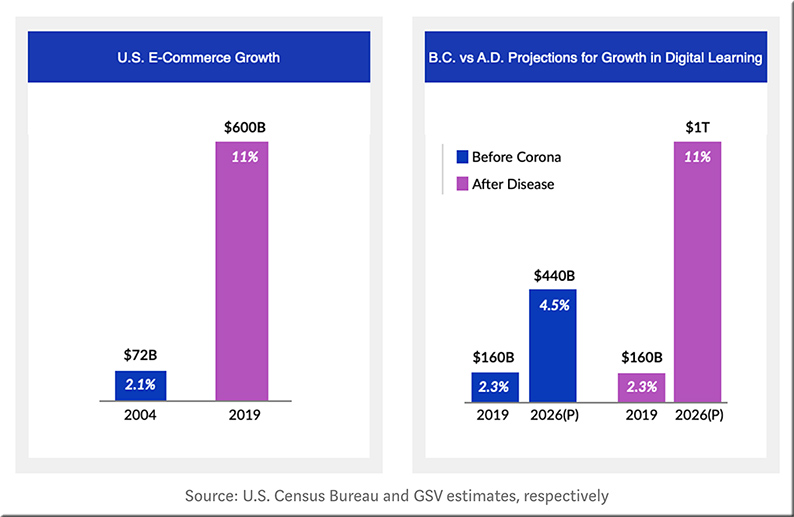
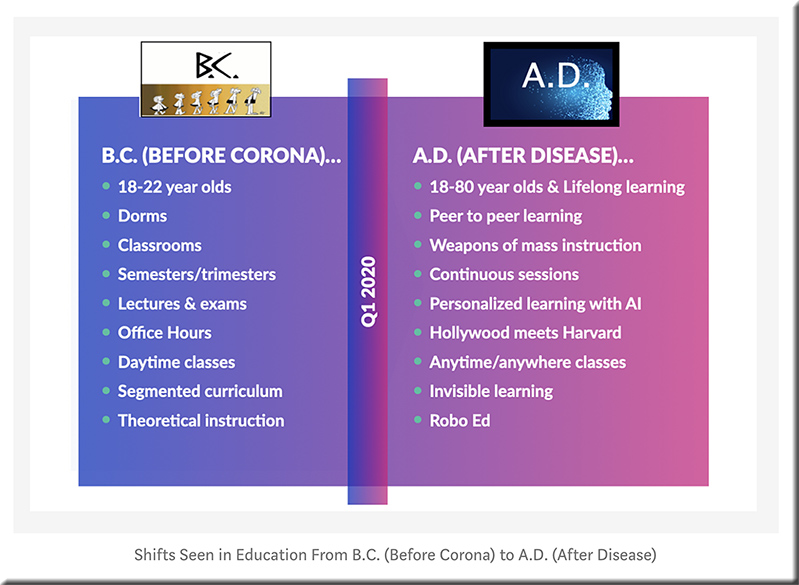
From DSC:
I saw the piece below from Graham Brown-Martin’s solid, thought-provoking posting entitled, “University as a Service (UaaS)” out at medium.com. My question is: “What happens if Professor Scott Galloway is right?!”
Excerpt:
Prof Scott Galloway predicts lucrative future partnerships between the FAANG mega-corporations and major higher education brands emerging as a result of current disruptions. Galloway wonders what a partnership between MIT and Apple would look like?
The education conveyor belt of the last century that went school to university to work and a job for life just doesn’t work in an era of rapid transformation. Suppose we truly embrace the notion of continuous or lifelong learning and apply that to the university model. It wouldn’t just stop in your twenties would it?
University as a Service (UaaS), where higher education course and degree modules are unbundled and accessed via a monthly subscription, could be a landing spot for the future of higher education and lifelong learners.
Below are some other items
regarding the future of higher education.
Also relevant/see:
- Updating the Higher Education Playbook to Stay Relevant in 2020 — from info.destinysolutions.com (Note: You have to complete the form to get access to the whitepaper.)
Also relevant/see:
- Shaping the Future of Post-Secondary Education — from Cherry Tree & Associates
A Time of Transformation in Post-Secondary Education and the American Workforce.
Also relevant/see:
Also relevant/see:
- Fast Forward: Looking to the Future Workforce and Online Learning — from evolllution.com by Joann Kozyrev (VP Design and Development, Western Governors University) and Amrit Ahluwalia
Excerpt:
With employers and students looking to close the gap in workforce skills, it’s critical for them to know what skills are in need the most. Postsecondary institutions need to be the resource to provide learners with the education the workforce needs and to make both parties understand the value of the students’ education. With the remote and online shift, it’s a new territory for institutions handle. In this interview, Joann Kozyrev discusses the impact remote learning has on an online institution, concerns about the future of online learning and how to get people back into the workforce fast and efficiently.