The Future of Jobs and Jobs Training — from by Lee Rainie and Janna Anderson
As robots, automation and artificial intelligence perform more tasks and there is massive disruption of jobs, experts say a wider array of education and skills-building programs will be created to meet new demands. There are two uncertainties: Will well-prepared workers be able to keep up in the race with AI tools? And will market capitalism survive?
Excerpt:
Machines are eating humans’ jobs talents. And it’s not just about jobs that are repetitive and low-skill. Automation, robotics, algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) in recent times have shown they can do equal or sometimes even better work than humans who are dermatologists, insurance claims adjusters, lawyers, seismic testers in oil fields, sports journalists and financial reporters, crew members on guided-missile destroyers, hiring managers, psychological testers, retail salespeople, and border patrol agents. Moreover, there is growing anxiety that technology developments on the near horizon will crush the jobs of the millions who drive cars and trucks, analyze medical tests and data, perform middle management chores, dispense medicine, trade stocks and evaluate markets, fight on battlefields, perform government functions, and even replace those who program software – that is, the creators of algorithms.
Several policy and market-based solutions have been promoted to address the loss of employment and wages forecast by technologists and economists. A key idea emerging from many conversations, including one of the lynchpin discussions at the World Economic Forum in 2016, is that changes in educational and learning environments are necessary to help people stay employable in the labor force of the future. Among the six overall findings in a new 184-page report from the National Academies of Sciences, the experts recommended: “The education system will need to adapt to prepare individuals for the changing labor market. At the same time, recent IT advances offer new and potentially more widely accessible ways to access education.”
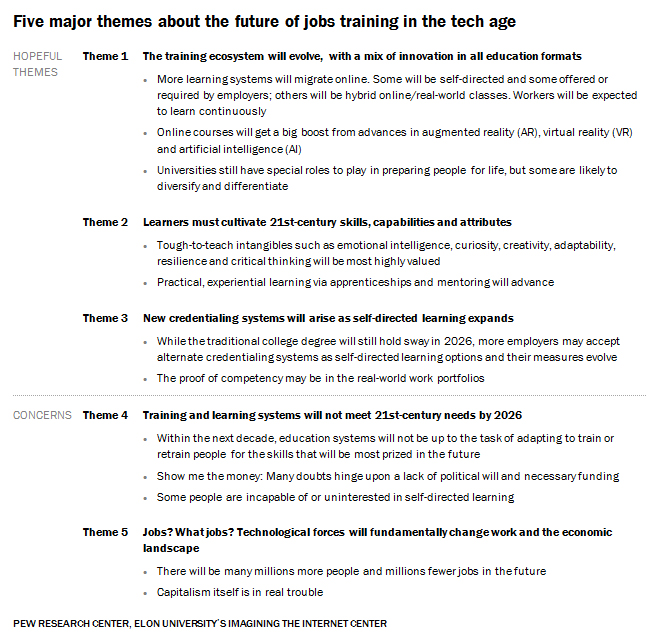
In the next 10 years, do you think we will see the emergence of new educational and training programs that can successfully train large numbers of workers in the skills they will need to perform the jobs of the future?
From DSC:
The following questions (from the article) might be fodder for initial conversations regarding what changes need to immediately occur within higher education. Those changes might be to establish teams/task forces/etc. charged with answering these kinds of questions.
- What are the most important skills needed to succeed in the workforce of the future?
- Which of these skills can be taught effectively via online systems – especially those that are self-directed – and other nontraditional settings?
- Which skills will be most difficult to teach at scale?
- Will employers be accepting of applicants who rely on new types of credentialing systems, or will they be viewed as less qualified than those who have attended traditional four-year and graduate programs?
The following section further supports a vision that I’ve been tracking entitled, “Learning from the Living [Class] Room” — where I see the “New Amazon.com of Higher Education” unfolding. Blockchain-based technologies will likely be involved here.
A diversifying education and credentialing ecosystem: Most of these experts expect the education marketplace – especially online learning platforms – to continue to change in an effort to accommodate the widespread needs. Some predict employers will step up their own efforts to train and retrain workers. Many foresee a significant number of self-teaching efforts by jobholders themselves as they take advantage of proliferating online opportunities.
Respondents see a new education and training ecosystem emerging in which some job preparation functions are performed by formal educational institutions in fairly traditional classroom settings, some elements are offered online, some are created by for-profit firms, some are free, some exploit augmented and virtual reality elements and gaming sensibilities, and a lot of real-time learning takes place in formats that job seekers pursue on their own.
A considerable number of respondents to this canvassing focused on the likelihood that the best education programs will teach people how to be lifelong learners. Accordingly, some say alternative credentialing mechanisms will arise to assess and vouch for the skills people acquire along the way.

DC: Many societies around the globe are looking at massive change coming at them. What changes should those of us working in higher education begin to make — immediately? In the longer term?
These respondents suggest that workers of the future will learn to deeply cultivate and exploit creativity, collaborative activity, abstract and systems thinking, complex communication, and the ability to thrive in diverse environments.
Addendum on 5/6/17:
- How to Prepare for an Automated Future — from nytimes.com by Claire Cain Miller
Excerpt:
We don’t know how quickly machines will displace people’s jobs, or how many they’ll take, but we know it’s happening — not just to factory workers but also to money managers, dermatologists and retail workers. The logical response seems to be to educate people differently, so they’re prepared to work alongside the robots or do the jobs that machines can’t. But how to do that, and whether training can outpace automation, are open questions.











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)