Learning from the Living [Class] Room:
A vision for a global, powerful, next generation learning platform
By Daniel Christian
NOTE: Having recently lost my Senior Instructional Designer position due to a staff reduction program, I am looking to help build such a platform as this. So if you are working on such a platform or know of someone who is, please let me know: danielchristian55@gmail.com.
I want to help people reinvent themselves quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively — while providing more choice, more control to lifelong learners. This will become critically important as artificial intelligence, robotics, algorithms, and automation continue to impact the workplace.
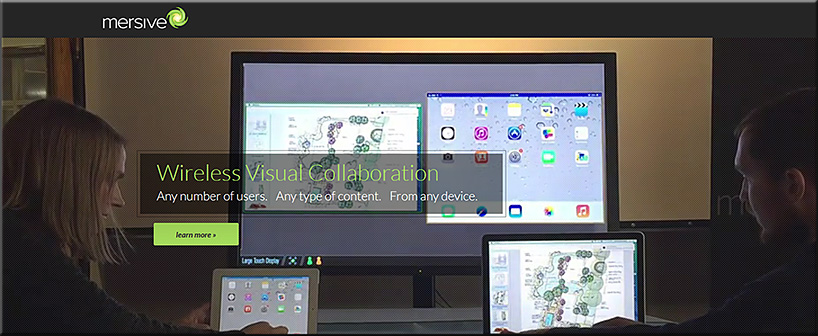
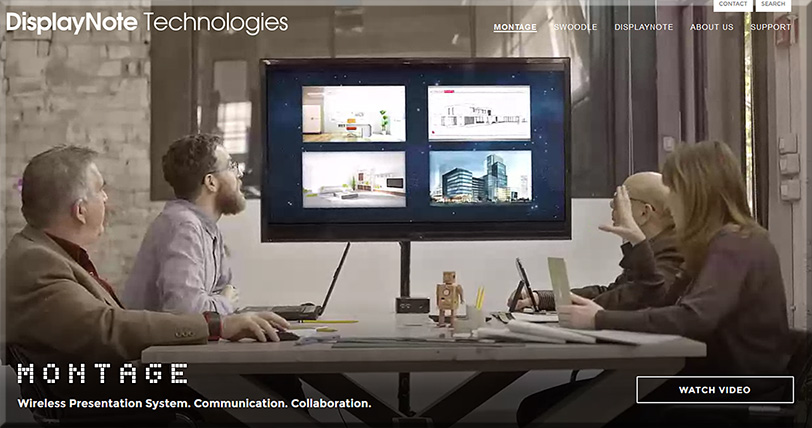
![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)
Learning from the Living [Class] Room:
A global, powerful, next generation learning platform
What does the vision entail?
- A new, global, collaborative learning platform that offers more choice, more control to learners of all ages – 24×7 – and could become the organization that futurist Thomas Frey discusses here with Business Insider:
“I’ve been predicting that by 2030 the largest company on the internet is going to be an education-based company that we haven’t heard of yet,” Frey, the senior futurist at the DaVinci Institute think tank, tells Business Insider.
- A learner-centered platform that is enabled by – and reliant upon – human beings but is backed up by a powerful suite of technologies that work together in order to help people reinvent themselves quickly, conveniently, and extremely cost-effectively
- An AI-backed system of analyzing employment trends and opportunities will highlight those courses and “streams of content” that will help someone obtain the most in-demand skills
- A system that tracks learning and, via Blockchain-based technologies, feeds all completed learning modules/courses into learners’ web-based learner profiles
- A learning platform that provides customized, personalized recommendation lists – based upon the learner’s goals
- A platform that delivers customized, personalized learning within a self-directed course (meant for those content creators who want to deliver more sophisticated courses/modules while moving people through the relevant Zones of Proximal Development)
- Notifications and/or inspirational quotes will be available upon request to help provide motivation, encouragement, and accountability – helping learners establish habits of continual, lifelong-based learning
- (Potentially) An online-based marketplace, matching learners with teachers, professors, and other such Subject Matter Experts (SMEs)
- (Potentially) Direct access to popular job search sites
- (Potentially) Direct access to resources that describe what other companies do/provide and descriptions of any particular company’s culture (as described by current and former employees and freelancers)
Further details:
While basic courses will be accessible via mobile devices, the optimal learning experience will leverage two or more displays/devices. So while smaller smartphones, laptops, and/or desktop workstations will be used to communicate synchronously or asynchronously with other learners, the larger displays will deliver an excellent learning environment for times when there is:
- A Subject Matter Expert (SME) giving a talk or making a presentation on any given topic
- A need to display multiple things going on at once, such as:
- The SME(s)
- An application or multiple applications that the SME(s) are using
- Content/resources that learners are submitting in real-time (think Bluescape, T1V, Prysm, other)
- The ability to annotate on top of the application(s) and point to things w/in the app(s)
- Media being used to support the presentation such as pictures, graphics, graphs, videos, simulations, animations, audio, links to other resources, GPS coordinates for an app such as Google Earth, other
- Other attendees (think Google Hangouts, Skype, Polycom, or other videoconferencing tools)
- An (optional) representation of the Personal Assistant (such as today’s Alexa, Siri, M, Google Assistant, etc.) that’s being employed via the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
This new learning platform will also feature:
- Voice-based commands to drive the system (via Natural Language Processing (NLP))
- Language translation (using techs similar to what’s being used in Translate One2One, an earpiece powered by IBM Watson)
- Speech-to-text capabilities for use w/ chatbots, messaging, inserting discussion board postings
- Text-to-speech capabilities as an assistive technology and also for everyone to be able to be mobile while listening to what’s been typed
- Chatbots
- For learning how to use the system
- For asking questions of – and addressing any issues with – the organization owning the system (credentials, payments, obtaining technical support, etc.)
- For asking questions within a course
- As many profiles as needed per household
- (Optional) Machine-to-machine-based communications to automatically launch the correct profile when the system is initiated (from one’s smartphone, laptop, workstation, and/or tablet to a receiver for the system)
- (Optional) Voice recognition to efficiently launch the desired profile
- (Optional) Facial recognition to efficiently launch the desired profile
- (Optional) Upon system launch, to immediately return to where the learner previously left off
- The capability of the webcam to recognize objects and bring up relevant resources for that object
- A built in RSS feed aggregator – or a similar technology – to enable learners to tap into the relevant “streams of content” that are constantly flowing by them
- Social media dashboards/portals – providing quick access to multiple sources of content and whereby learners can contribute their own “streams of content”
In the future, new forms of Human Computer Interaction (HCI) such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) will be integrated into this new learning environment – providing entirely new means of collaborating with one another.
Likely players:
- Amazon – personal assistance via Alexa
- Apple – personal assistance via Siri
- Google – personal assistance via Google Assistant; language translation
- Facebook — personal assistance via M
- Microsoft – personal assistance via Cortana; language translation
- IBM Watson – cognitive computing; language translation
- Polycom – videoconferencing
- Blackboard – videoconferencing, application sharing, chat, interactive whiteboard
- T1V, Prsym, and/or Bluescape – submitting content to a digital canvas/workspace
- Samsung, Sharp, LCD, and others – for large displays with integrated microphones, speakers, webcams, etc.
- Feedly – RSS aggregator
- _________ – for providing backchannels
- _________ – for tools to create videocasts and interactive videos
- _________ – for blogs, wikis, podcasts, journals
- _________ – for quizzes/assessments
- _________ – for discussion boards/forums
- _________ – for creating AR, MR, and/or VR-based content