Social strikes back — from a16z.com
Social Strikes Back is a series exploring the next generation of social networks and how they’re shaping the future of consumer tech. See more at a16z.com/social-strikes-back.
Excerpt:
Until recently, it was commonly accepted that “social” was done. The market had been fully saturated, the thinking went, dominated by the holy trinity of Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Turns out, rumors of social’s demise have been greatly exaggerated. Not only are we seeing the rise of innovative new social networks—from the earshare of Clubhouse to the seamless interactivity of cloud gaming—but having a social component has become a powerful acquisition and retention tool for every consumer product, across education, shopping, fitness, food, entertainment, and more. In this series, we reveal what new social looks like, the forces that are driving it, and how to build it.
Meet Me in the Metaverse — from a16z.com by Jonathan Lai
Excerpts:
There are many competing visions for how we’ll build the Metaverse: a persistent, infinitely-scaling virtual space with its own economy and identity system.
…
New social modalities will emerge in the Metaverse. Advances in cloud streaming and AI will enable new forms of engagement with friends—for example, the ability to pop into a persistent virtual world and discover new people and experiences together, entirely unplanned.
Live, Social, and Shoppable: The Future of Video — from a16z.com by Connie Chan
Excerpt:
Now, we’re about to enter a whole new era of video-first products that extend far beyond entertainment and gaming. If phase one of video was a laid-back experience, video 2.0 will be far more interactive and participatory, with users engaging with the platform, giving direct feedback on the content, and fundamentally shaping the experience in real time.
Also see:
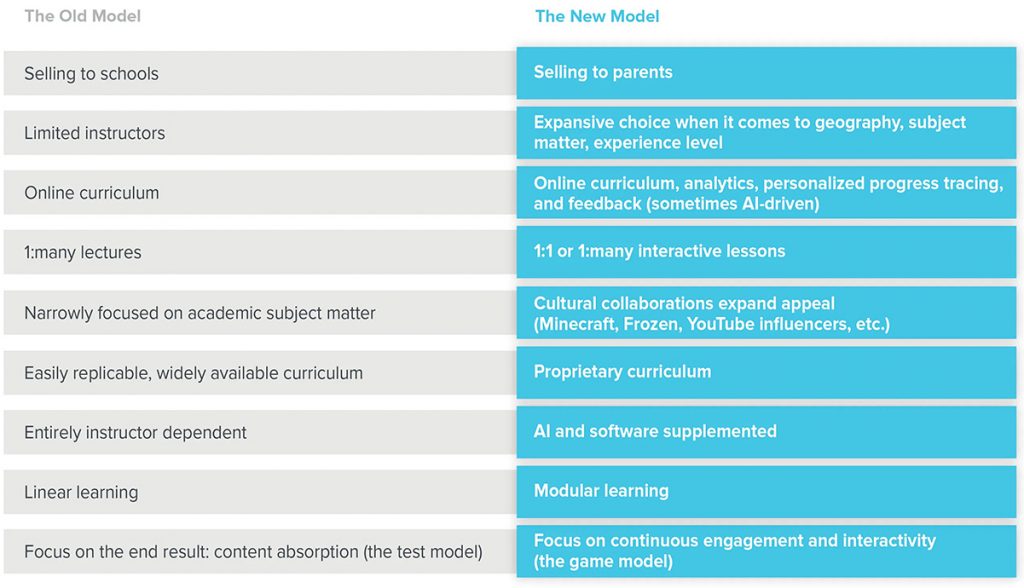
Edtech’s Answer to Remote Learning Burnout — from a16z.com by Anne Lee Skates and Connie Chan
Excerpt:
While previous generations of edtech largely focused on in-school content distribution, more recently founders have turned their attention to after-school and out-of-school education. There’s a lot left to build. We believe post-COVID online education will differ from the past in key ways.