Key point from DSC:
Digitally-based means of learning are going to skyrocket!!! Far more than what we’ve seen so far! There are several trends that are occurring to make this so.
As background here, some of the keywords and phrases that are relevant to this posting include:
- Wireless content sharing
- Wireless collaboration solutions
- Active learning based classrooms
- Conference rooms
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
- Enterprise wireless display solutions
- Enterprise collaboration solutions
- Cross platform support: iOS, Android, Windows
- Personalized learning
- Learning analytics
Some of the relevant products in this area include:
- Bluescape
- Mezzanine from Oblong Industries
- Montage from DisplayNote Technologies
- ThinkHub and ViewHub from T1V
- Mersive Solstice
- Crestron AirMedia
- Barco Clickshare
- Haworth Workware Wireless
- Christi Brio
- AMX enzo
- NovoConnect from Vivitek
- Arrive MediaPoint
- Apple TV
- Chromecast
From DSC:
First of all, consider the following products and the functionalities they offer.
People who are in the same physical space can collaborate with people from all over the world — no matter if they are at home, in another office, on the road, etc.
For several of these products, remote employees/consultants/trainers/learners can contribute content to the discussions, just like someone in the same physical location can.
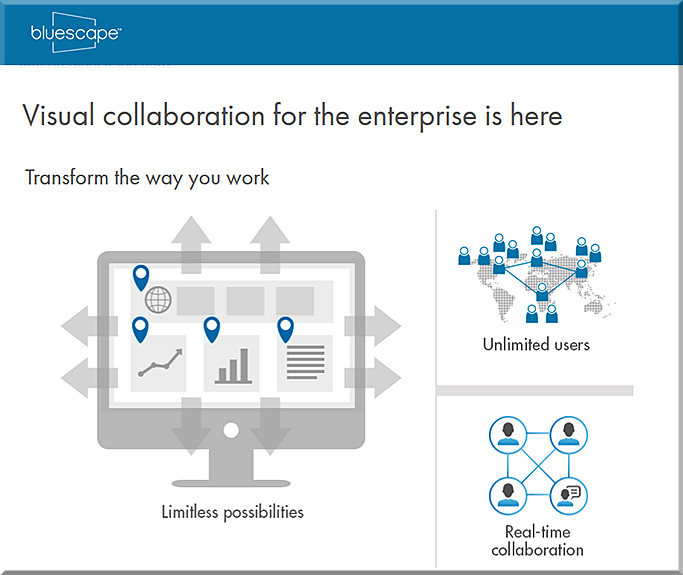

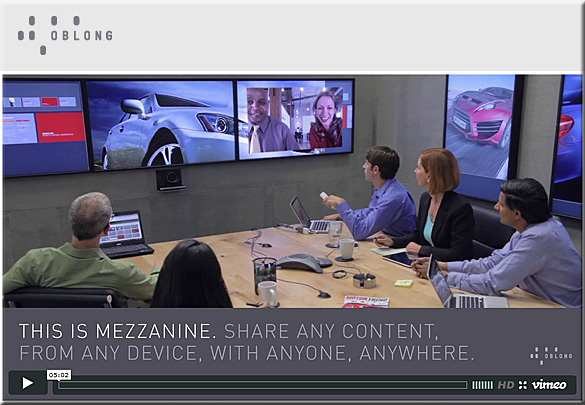


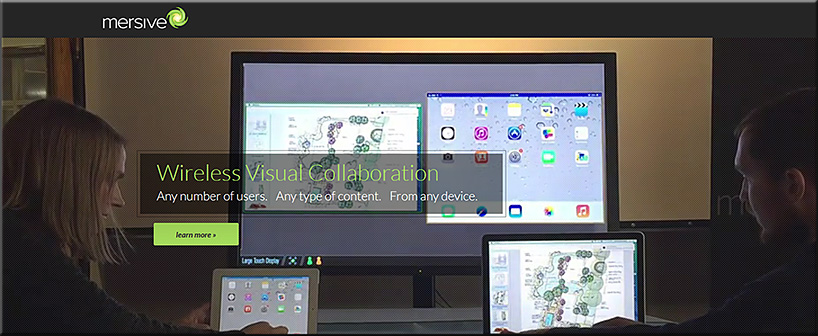
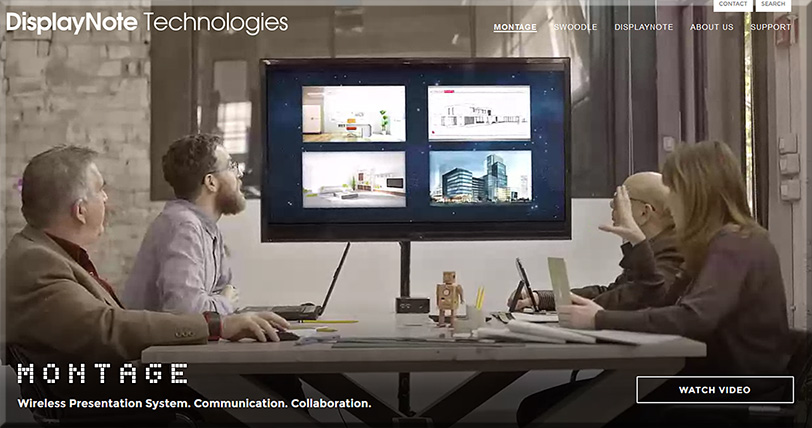

From DSC:
Many of these sorts of systems & software are aimed at helping people collaborate — again, regardless of where they are located. Remote learners/content contributors are working in tandem with a group of people in the same physical location. If this is true in business, why can’t it be true in the world of education?
So keep that in mind, as I’m now going to add on a few other thoughts and trends that build upon these sorts of digitally-based means of collaborating.
Q: Towards that end…ask yourself, what do the following trends and items have in common?
- The desire to capture and analyze learner data to maximize learning
- Colleges’ and universities’ need to increase productivity (which is also true in the corporate & K-12 worlds)
- The trend towards implementing more active learning-based environments
- The increasing use of leveraging students’ devices for their learning (i.e., the BYOD phenomenon)
- The continued growth and increasing sophistication of algorithms
A: All of these things may cause digitally-based means of learning to skyrocket!!!
To wrap up this line of thought, below are some excerpts from recent articles that illustrate what I’m trying to get at here.
Embrace the Power of Data
A continuous improvement mindset is important. Back-end learning analytics, for example, can reveal where large numbers of students are struggling, and may provide insights into questions that require new feedback or content areas that need more development. Data can also highlight how students are interacting with the content and illuminate things that are working well—students’ lightbulb moments.
— Five Principles for Your Learning Design Toolkit
from edsurge.com by Amanda Newlin
Mitchell gave the example of flight simulators, which not only provide students with a way to engage in the activity that they want to learn, but also have data systems that monitor students’ learning over time, providing them with structured feedback at just the right moment. This sort of data-centric assessment of learning is happening in more and more disciplines — and that opens the door to more innovation, he argued.
…
A promising example, said Thille, is the use of educational technology to create personalized and adaptive instruction. As students interact with adaptive technology, the system collects large amounts of data, models those data, and then makes predictions about each student based on their interactions, she explained. Those predictions are then used for pedagogical decision-making — either feeding information back into the system to give the student a personalized learning path, or providing insights to faculty to help them give students individualized support.
…
“We need the models and the data to be open, transparent, peer-reviewable and subject to academic scrutiny.”
…
“We began to actually examine what we could do differently — based not upon hunches and traditions, but upon what the data told us the problems were for the students we enroll,” said Renick. “We made a commitment not to raise our graduation rate through getting better students, but through getting better — and that gain meant looking in the mirror and making some significant changes.”
…
A 21st-century learning culture starts with digital content. In 2010, Jackson State University was looking for ways that technology could better address the needs of today’s learner. “We put together what we call our cyberlearning ecosystem,” said Robert Blaine, dean of undergraduate studies and cyberlearning. “What that means is that we’re building a 21st-century learning culture for all of our students, writ large across campus.” At the core of that ecosystem is digital content, delivered via university-supplied iPads.
— 7 Things Higher Education Innovators Want You to Know
from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
On Bennett’s wish list right now is an application that allows students to give feedback at specific points of the videos that they’re watching at home. This would help him pinpoint and fix any “problem” areas (e.g. insufficient instructions for difficult topics/tasks) and easily see where students are experiencing the most difficulties.
TechSmith’s now-retired “Ask3” video platform, for example, would have done the trick. It allowed users to watch a video and ask text-based questions at the point where playback was stopped. “I’d like to be able to look at my content and say, ‘Here’s a spot where there are a lot of questions and confusion,'” said Bennett, who also sees potential in an “I get it” button that would allow students to hit the button when everything clicks. “That would indicate the minimum viable video that I’d need to produce.” Learning Catalytics offers a similar product at a fee, Bennett said, “but I can’t charge my students $20 a year to use it.”
— 6 Flipped Learning Technologies To Watch in 2016
from thejournal.com by Bridget McCrea
All of these trends lend themselves to causing a major increase in the amount of learning that occurs via digitally-based means and methods.





















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)










