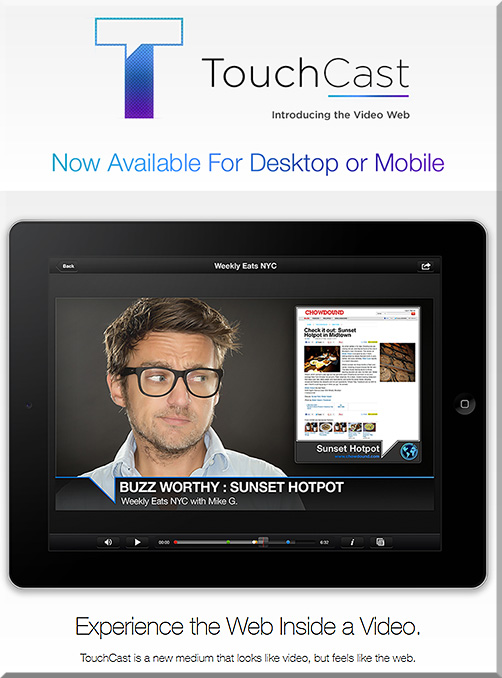
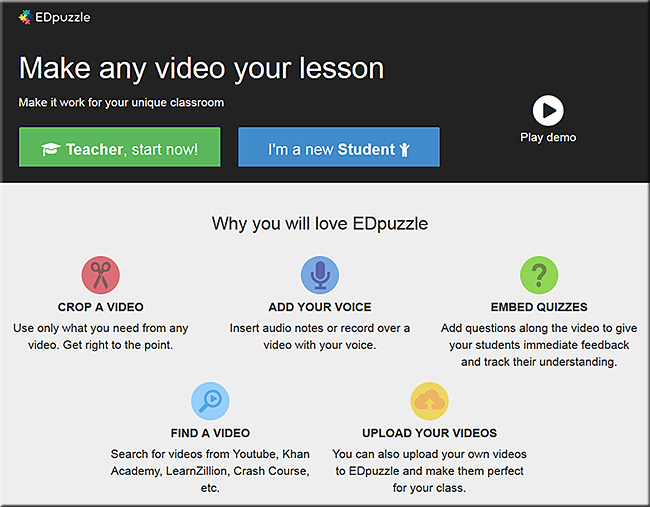
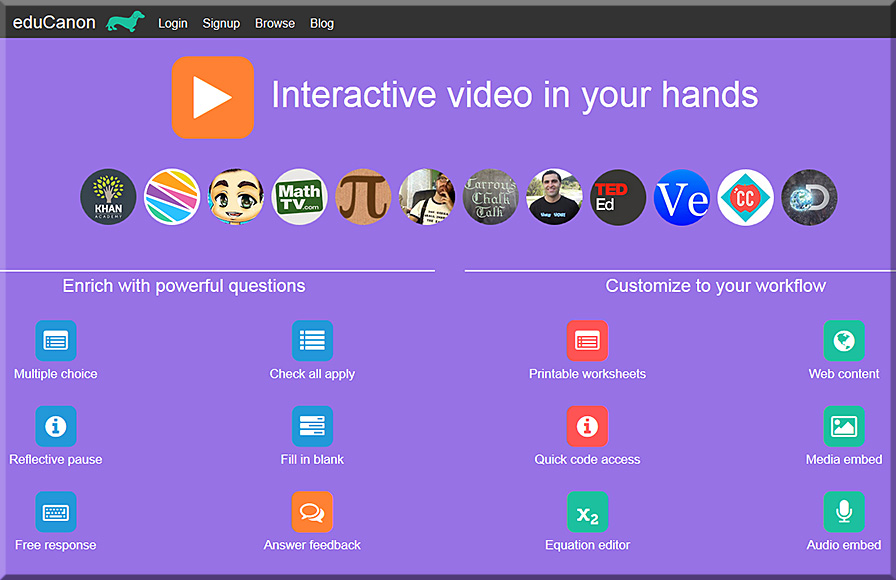
We’ve got to stop meeting like this! – Guest post by Jay Cross — from litmos.com
Excerpt:
You can re-jigger your meetings to make them relevant, challenging, and fun by adopting an approach that is revolutionizing secondary school learning.
It’s called Flipping the Meeting. Flipped meetings focus people’s face-to-face time on working with one another to solve problems. You prepare in advance at your own pace with resources framing the business issue. When people convene, they spend their time collaborating to solve a problem. Conversations cross-fertilize ideas and fuel learning. In the flipped meeting, you focus on making the decision before the bell goes off.
Two teachers pioneered the philosophy of flip starting back in 2007. Students read their homework before class and use the classroom for discussion, not presentation. Grades go up, as does retention. Millions of students have signed up for flipped instruction through The Khan Academy. This is the same philosophy that underlies the Flipped Meeting. Be prepared to be inspired and listen to the founders of the flip…
From DSC:
Piggybacking on what Jay is saying in that piece re: “Flipping the Meeting”, I wonder if tools like VoiceThread could also help obtain peoples’ thoughts and perspectives prior to holding a meeting — and to do so per what works for each individual’s schedule.
VoiceThread is a cloud application, so there is no software to install. The only system requirement is an up-to-date version of Adobe Flash. VoiceThread will work in any modern web browser and on almost any internet connection.
Creating
Upload, share and discuss documents, presentations, images, audio files and videos. Over 50 different types of media can be used in a VoiceThread.
Commenting
Comment on VoiceThread slides using one of five powerful commenting options: microphone, webcam, text, phone, and audio-file upload.
Sharing
Keep a VoiceThread private, share it with specific people, or open it up to the entire world. Learn more about sharing VoiceThreads.













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)