We’re not talking about chemtrails, HAARP (High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program) or other weather warfare that has been featured in science fiction movies; the concerns were raised not a conspiracy theorist, but by climate scientist, geoengineering specialist and Rutgers University Professor Alan Robock. He “called on secretive government agencies to be open about their interest in radical work that explores how to alter the world’s climate.” If emerging climate-altering technologies can effectively alter the weather, Robock is “worried about who would control such climate-altering technologies.”

From DSC:
I say this is an illustrative posting because if the inventor/programmer of this sort of drone wanted to poison someone, they surely could do so. I’m not even sure that this drone exists or not; it doesn’t matter, as we’re quickly heading that way anyway. So potentially, this kind of thing is very scary stuff.
We need people who care about other people.
Or see:
Five useful ideas from the World Cup of Drones — from dezeen.com
The article mentions some beneficial purposes of drones, such as for search and rescue missions or for assessing water quality. Some positive intentions, to be sure.
But again, it doesn’t take too much thought to come up with some rather frightening counter-examples.
GENE-RELATED RESEARCH
Or another example re: gene research/applications; an excerpt from:
Turning On Genes, Systematically, with CRISPR/Cas9 — from by genengnews.com
Scientists based at MIT assert that they can reliably turn on any gene of their choosing in living cells.
Excerpt:
It was also suggested that large-scale screens such as the one demonstrated in the current study could help researchers discover new cancer drugs that prevent tumors from becoming resistant.
From DSC:
Sounds like there could be some excellent, useful, positive uses for this technology. But who is to say which genes should be turned on and under what circumstances? In the wrong hands, there could be some dangerous uses involved in such concepts as well. Again, it goes back to those involved with designing, developing, selling, using these technologies and services.
ROBOTICS
Will robots be used for positive or negative applications?
The mechanized future of warfare — from theweek.com
OR
Atlas Unplugged: The six-foot-two humanoid robot that might just save your life — from zdnet.com
Summary:From the people who brought you the internet, the latest version of the Atlas robot will be used in its disaster-fighting robotic challenge.
AUTONOMOUS CARS
How Uber’s autonomous cars will destroy 10 million jobs and reshape the economy by 2025 — from sanfrancisco.cbslocal.com by
Excerpt:
Autonomous cars will be commonplace by 2025 and have a near monopoly by 2030, and the sweeping change they bring will eclipse every other innovation our society has experienced. They will cause unprecedented job loss and a fundamental restructuring of our economy, solve large portions of our environmental problems, prevent tens of thousands of deaths per year, save millions of hours with increased productivity, and create entire new industries that we cannot even imagine from our current vantage point.
One can see the potential for good and for bad from the above excerpt alone.
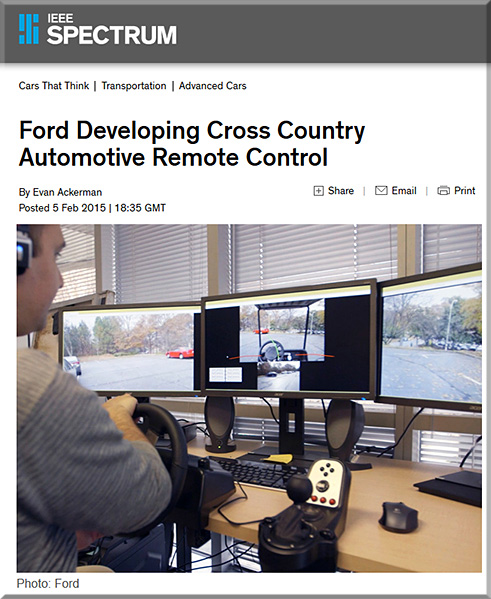
Or Ford developing cross country automotive remote control — from spectrum.ieee.org
Or Germany has approved the use of self driving cars on Autobahn A9 Route — from wtvox.com
While the above items list mostly positive elements, there are those who fear that autonomous cars could be used by terrorists. That is, could a terrorist organization make some adjustments to such self-driving cars and load them up with explosives, then remotely control them in order to drive them to a certain building or event and cause them to explode?
Again, it depends upon whether the designers and users of a system care about other people.
BIG DATA / AI / COGNITIVE COMPUTING
The rise of machines that learn — from infoworld.com by Eric Knorr; with thanks to Oliver Hansen for his tweet on this
A new big data analytics startup, Adatao, reminds us that we’re just at the beginning of a new phase of computing when systems become much, much smarter
Excerpt:
“Our warm and creepy future,” is how Miko refers to the first-order effect of applying machine learning to big data. In other words, through artificially intelligent analysis of whatever Internet data is available about us — including the much more detailed, personal stuff collected by mobile devices and wearables — websites and merchants of all kinds will become extraordinarily helpful. And it will give us the willies, because it will be the sort of personalized help that can come only from knowing us all too well.
Privacy is dead: How Twitter and Facebook are exposing you — from finance.yahoo.com
Excerpt:
They know who you are, what you like, and how you buy things. Researchers at MIT have matched up your Facebook (FB) likes, tweets, and social media activity with the products you buy. The results are a highly detailed and accurate profile of how much money you have, where you go to spend it and exactly who you are.
The study spanned three months and used the anonymous credit card data of 1.1 million people. After gathering the data, analysts would marry the findings to a person’s public online profile. By checking things like tweets and Facebook activity, researchers found out the anonymous person’s actual name 90% of the time.
iBeacon, video analysis top 2015 tech trends — from progressivegrocer.com
Excerpt:
Using digital to engage consumers will make the store a more interesting and – dare I say – fun place to shop. Such an enhanced in-store experience leads to more customer loyalty and a bigger basket at checkout. It also gives supermarkets a competitive edge over nearby stores not equipped with the latest technology.
Using video cameras in the ceilings of supermarkets to record shopper behavior is not new. But more retailers will analyze and use the resulting data this year. They will move displays around the store and perhaps deploy new traffic patterns that follow a shopper’s true path to purchase. The result will be increased sales.
Another interesting part of this video analysis that will become more important this year is facial recognition. The most sophisticated cameras are able to detect the approximate age and ethnicity of shoppers. Retailers will benefit from knowing, say, that their shopper base includes more Millennials and Hispanics than last year. Such valuable information will change product assortments.
Scientists join Elon Musk & Stephen Hawking, warn of dangerous AI — from rt.com
Excerpt:
Hundreds of leading scientists and technologists have joined Stephen Hawking and Elon Musk in warning of the potential dangers of sophisticated artificial intelligence, signing an open letter calling for research on how to avoid harming humanity.
The open letter, drafted by the Future of Life Institute and signed by hundreds of academics and technologists, calls on the artificial intelligence science community to not only invest in research into making good decisions and plans for the future, but to also thoroughly check how those advances might affect society.
SMART/ CONNECTED TVs
Though there are many other examples, I think you get the point.
That biblical idea of loving our neighbors as ourselves…well, as you can see,
that idea is as highly applicable, important, and relevant today as it ever was.
Jennifer A. Doudna, an inventor of a new genome-editing technique, in her office at the University of California, Berkeley. Dr. Doudna is the lead author of an article calling for a worldwide moratorium on the use of the new method, to give scientists, ethicists and the public time to fully understand the issues surrounding the breakthrough.
Credit Elizabeth D. Herman for The New York Times