[California] Governor Brown signs bills to provide free digital textbooks for students — from technapex.com by Caity Doyle
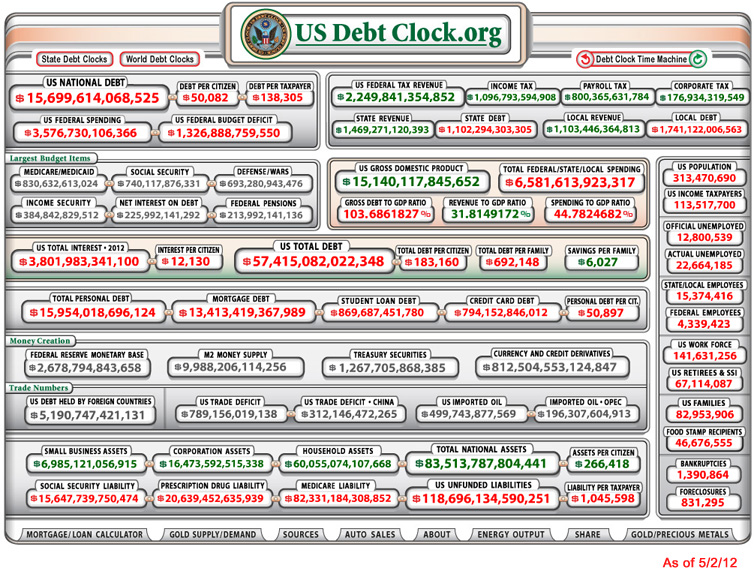
U.S. debt $417 billion below the debt ceiling — from CNN.com by Jeanne Sahadi
Excerpt:
The debt ceiling is currently set at $16.394 trillion. At the end of August, the amount of debt subject to that limit — which excludes certain types of debt — was $15.977 trillion, roughly $417 billion below the cap. Since the government typically borrows between $100 billion and $125 billion a month, that means it’s on track to hit the ceiling sometime in December. But the Treasury Department will likely be able to use “extraordinary measures” to keep the debt just below the legal limit for a couple of months.
Bottom line:
Congress will likely need to raise the ceiling in early 2013 or Treasury will risk defaulting on the country’s legal obligations by failing to pay all of its bills in full and on time.
From DSC:
At some point, if we don’t turn things around, the vast majority of our tax dollars will go to pay for interest on our debt…and. nothing. else.
Also see:
- A State-by-State Report Card on Public Postsecondary Education — from icw.uschamber.com
Excerpt:
But to reap these benefits fully, the nation clearly has a long way to go. Producing the additional degrees the United States needs would be a challenge in flush economic times; doing so in the current fiscal environment will require significant and difficult modifications.
. - A Sobering Look at College Affordability — from The Chronicle by Beckie Supiano
…and back from previous dates:
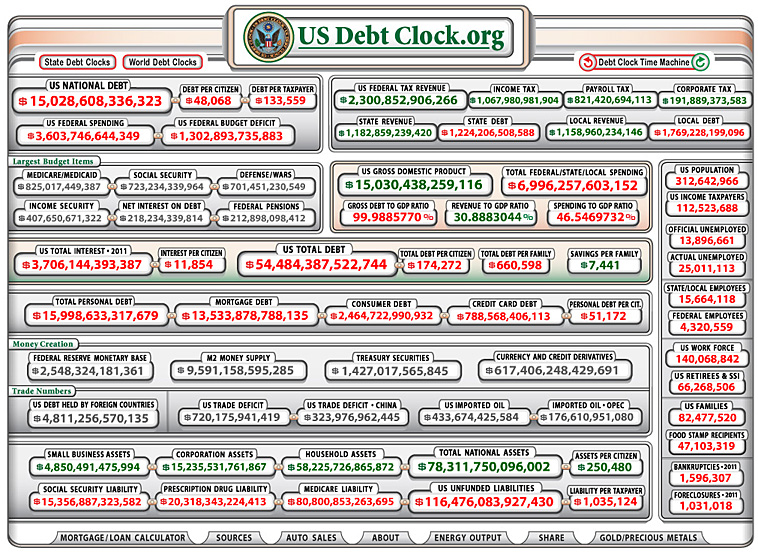
As of 11-20-11

As of 8-24-11
Also see:
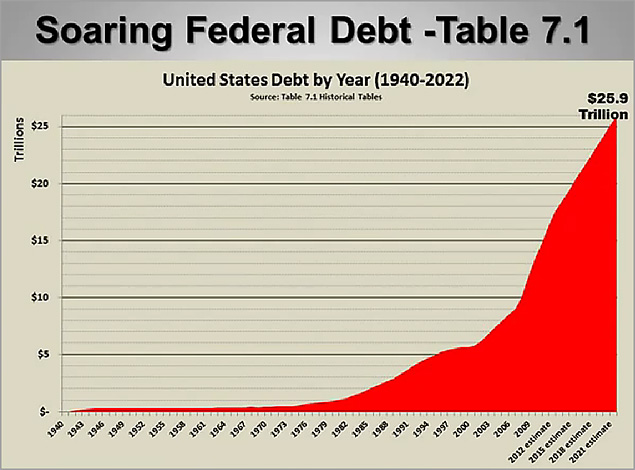
- United States Budget Dilemma.wmv — a soaring debt and a budget congress can’t balance!
Addendum on 5/7/12:
- Five political lies we must expose to save our children — from the HuffingtonPost.com by Gary Shapiro
Pentagon: You know what’s cool? A trillion-dollar fighter — from cnet.com by D. Terdiman

From DSC:
Cool? Seriously?! Is this where we want to spend a trillion $$? On more instruments of death? Geez…
Instead, I wonder what the United States could contribute to the world by building multimedia-based, high-end, interactive, engaging, personalized/customized, online-based learning materials that are expensive to build, but inexpensive to access?
.
Also see:
Cap and gown learning on a shoestring budget — from timeshighereducation.co.uk by Jon Marcus
Excerpt:
With novel credentials being developed and employers seeing the value of low-cost study based on open courseware, Jon Marcus asks if the bricks-and-mortar elite will end up on the wrong side of history

Excerpt:
California is on the precipice of implementing the Common Core State Standards (CCSS), which were developed through an initiative of the National Governors Association and the Council of Chief State School Officers to reflect the knowledge and skills needed for success in college and careers. In California, one of 45 adopting states, the standards represent a significant shift in expectations for both teaching and learning, not just in English language arts (ELA) and mathematics, but also in literacy related to science and history/social science. The newly adopted standards call for a deep conceptual understanding of the content in ELA and mathematics and, also, for the ability to apply this content to other disciplines. New assessments aligned to the standards are due to be implemented in 2014-15. It all sounds good. But are teachers ready to teach to the new standards?
From DSC:
Due to my lack of knowledge, the jury is still out for me re: what I think about the Common Core State Standards. The crux of my struggle has to do with:
- Who determines which courses/topics are included in the standards — both now and in the future?
- How often will they be updated to insure the foundations are truly foundational to our students’ futures?
- Are such large swaths of standards helpful and effective or are they an extension of a one-size-fits all approach? (For example, I look back on some of the items that I took in K-12 — many of which I’ve forgotten and I never use — but I’ll bet are still in the standards. )
I would like to see some solid foundations being built as well — as I assume that’s what the standards seek to implement. I just hope we can provide places for students’ wide variety of passions to be identified, explored, and strongly nurtured as my economics training taught me that we all win when each of us does what we do best.
Can someone educate me on these standards? What are the upsides and downsides — the pros and cons — of these standards? Thanks!
Addendum on 3/2/12:
Below are the concluding paragraphs of Introducing Bennett Hypothesis 2.0 [by Andrew Gillen, Center for College Affordability and Productivity, with emphasis below from DSC)
Original Bennett Hypothesis + a couple refinements + Bowen’s Rule = Bennett Hypothesis 2.0.
The original Bennett Hypothesis held that increases in financial aid will lead to higher tuition, but the empirical evidence testing the hypothesis is inconclusive. The next generation of the concept, Bennett Hypothesis 2.0, adds three refinements.
1. All Aid is Not Created Equal
2. Selectivity, Tuition Caps, and Price Discrimination are Important
3. Don’t Ignore the Dynamic Story
These three refinements not only help explain the mixed empirical evidence, but also provide a better understanding of the relationship between financial aid and tuition. While the first two refinements weaken the link between the two (lessening our concern about Bennett Hypothesis 2.0), the third refinement strengthens the link, implying that we should almost always be concerned about financial aid leading to higher tuition.
Given the current structure of the higher education system, Bennett Hypothesis 2.0 implies that the government will always be fighting a losing battle to increase access to college or improve college affordability since “additional government [financial aid] funds keep providing revenues that, under the current incentive system, increase costs.”54 As higher financial aid pushes costs higher, it inevitably puts upward pressure on tuition. Higher tuition, of course, reduces college affordability, leading to calls for more financial aid, setting the vicious cycle in motion all over again.
Bennett Hypothesis 2.0 exacerbates rather than causes out of control spending by colleges, the ultimate cause of which is Bowen’s Rule. Nevertheless, that is no excuse for ill-designed financial aid programs to pour fuel the fire. As Bennett noted:
“Federal student aid policies do not cause college price inflation, but there is little doubt that they help make it possible.”55
Those words remain just as true today as they were a quarter century ago.
From DSC:
This report seems to show that the current system is only serving to expand the higher ed bubble even further; surely a pop will be heard in the future (if it hasn’t already at some individual colleges and universities). Such a financial aid system seems to be causing one of the elements of the perfect storm — the cost of higher ed — to mount its waves to an even higher level. (Keep in mind I created the image below in September 2010, but many of these forces are still with us today.)