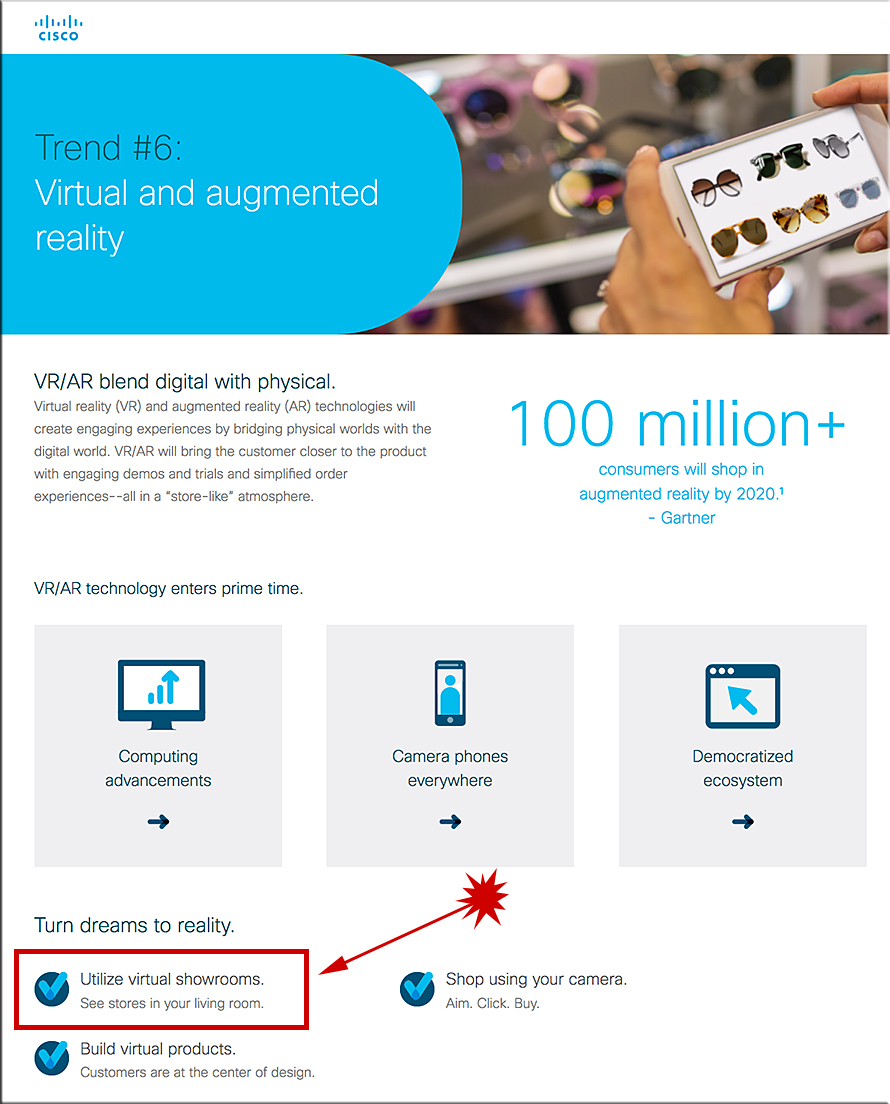
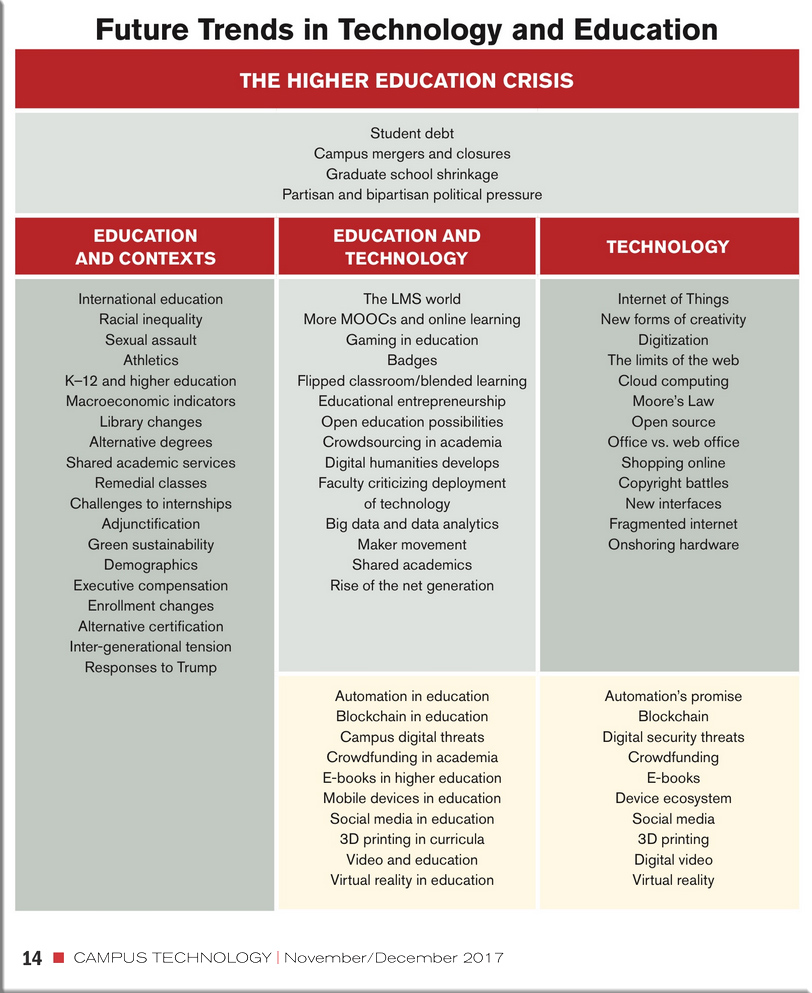
Virtual reality technology enters a Chinese courtroom — from supchina.com by Jiayun Feng
Excerpt:
The introduction of VR technology is part of a “courtroom evidence visualization system” developed by the local court. The system also includes a newly developed computer program that allows lawyers to present evidence with higher quality and efficiency, which will replace a traditional PowerPoint slideshow.
It is reported that the system will soon be implemented in courtrooms across the city of Beijing.
Watch Waymo’s Virtual-Reality View of the World — from spectrum.ieee.org by Philip Ross
From DSC:
This is mind blowing. Now I see why Nvidia’s products/services are so valuable.
Along these same lines, also see this clip and/or this article entitled, This is why AR and Autonomous Driving are the Future of Cars:
The Legal Hazards of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality Apps — from spectrum.ieee.org by Tam Harbert
Liability and intellectual property issues are just two areas developers need to know about
Excerpt:
As virtual- and augmented-reality technologies mature, legal questions are emerging that could trip up VR and AR developers. One of the first lawyers to explore these questions is Robyn Chatwood, of the international law firm Dentons. “VR and AR are areas where the law is just not keeping up with [technology] developments,” she says. IEEE Spectrum contributing editor Tam Harbert talked with Chatwood about the legal challenges.
This VR Tool Could Make Kids A Lot Less Scared Of Medical Procedures — from fastcompany.com by Daniel Terdiman
The new app creates a personalized, explorable 3D model of a kid’s own body that makes it much easier for them to understand what’s going on inside.
Excerpt:
A new virtual reality app that’s designed to help kids suffering from conditions like Crohn’s disease understand their maladies immerses those children in a cartoon-like virtual reality tour through their body.
Called HealthVoyager, the tool, a collaboration between Boston Children’s Hospital and the health-tech company Klick Health, is being launched today at an event featuring former First Lady Michelle Obama.
A lot of kids are confused by doctors’ intricate explanations of complex procedures like a colonoscopy, and they, and their families, can feel much more engaged, and satisfied, if they really understand what’s going on. But that’s been hard to do in a way that really works and doesn’t get bogged down with a lot of meaningless jargon.
Augmented Reality in Education — from invisible.toys
The state of virtual reality — from furthermore.equinox.com by Rachael Schultz
How the latest advancements are optimizing performance, recovery, and injury prevention
Excerpt:
Virtual reality is increasingly used to enhance everything from museum exhibits to fitness classes. Elite athletes are using VR goggles to refine their skills, sports rehabilitation clinics are incorporating it into recovery regimes, and others are using it to improve focus and memory.
Here, some of the most exciting things happening with virtual reality, as well as what’s to come.
Augmented Reality takes 3-D printing to next level — from rtoz.org
Excerpt:
Cornell researchers are taking 3-D printing and 3-D modeling to a new level by using augmented reality (AR) to allow designers to design in physical space while a robotic arm rapidly prints the work. To use the Robotic Modeling Assistant (RoMA), a designer wears an AR headset with hand controllers. As soon as a design feature is completed, the robotic arm prints the new feature.
From DSC:
How might the types of technologies being developed and used by Kazendi’s Holomeeting be used for building/enhancing learning spaces?
AR and Blockchain: A Match Made in The AR Cloud — from medium.com by Ori Inbar
Excerpt:
In my introduction to the AR Cloud I argued that in order to reach mass adoption, AR experiences need to persist in the real world across space, time, and devices.
To achieve that, we will need a persistent realtime spatial map of the world that enables sharing and collaboration of AR Experiences among many users.
And according to AR industry insiders, it’s poised to become:
“the most important software infrastructure in computing”
aka: The AR Cloud.

















![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)