FuturePod gathers voices from the international field of Futures and Foresight. Through a series of podcast interviews, the founders of the field and emerging leaders share their stories, tools and experiences. The Futures and Foresight community comprises a remarkable and diverse group of individuals who span, academic, commercial and social interests.
AI and smart campuses are among higher ed tech to watch in 2020 — from edtechmagazine.com by Adam Stone
Early adopters tap emerging tools to achieve cost savings and improve learning outcomes.
Excerpt:
In parallel with the rise of municipal smart cities, higher education continues to push toward the smart campus, a vision of a digitally interconnected learning space in which data and devices combine to enhance the student experience. Colleges need to get smart to stay competitive.
Below is an excerpt from Deloitte’s report — Smart campus: The next-generation connected campus — which the above article links to.
Innovations used in smart banking, smart retail, smart digital workplaces, and smart venues like hospitals and stadiums could be extended to higher education campuses. These smart environments are enabling an easy and seamless experience by leveraging the most advanced and next-generation technologies available to them. And more importantly, they continually
modernize and adjust their practices to meet the needs of their constituents. To stay sustainable and relevant, institutions should employ technology and analytics-based insights to enhance the well-being of the communities in which they are rooted.
OPINION: The odds are still stacked against low-income college students; here are some ways to expand the possibilities — from hechingerreport-org by Aimee Eubanks-Davis; with thanks to Joseline Hardrick at the WMU-Cooley Law School for posting this on LinkedIn
Excerpts:
Unfortunately, the odds for low-income students are still stacked against them. In fact, only one in four will graduate with a strong first job or enter graduate school. There is no safety net for these students. In fact, for their families, they are the safety net. They’ll start college expecting to leave with good-paying jobs with benefits that allow them to pay back loans, help their parents or other family members financially, and lead a self-sustaining life. Instead, the jobs that college graduates from low-income backgrounds do eventually land set them on an incongruent path to earn 66 cents on the dollar compared to their more affluent peers.
When we help provide low-income and first-generation college students the tools to overcome gaps in skills, assist them in getting a foot in the door at a top internship and connect them with professionals in the field, they will blow us away every time. I, for one, am excited to see a world in which extraordinary diverse leaders can emerge truly from anywhere and everywhere.
Why AI is a threat to democracy – and what we can do to stop it — from asumetech.com by Lawrence Cole
Excerpts:
In the US, however, we also have a tragic lack of foresight. Instead of creating a grand strategy for AI or for our long-term futures, the federal government has removed the financing of scientific and technical research. The money must therefore come from the private sector. But investors also expect a certain return. That is a problem. You cannot plan your R&D breakthroughs when working on fundamental technology and research. It would be great if the big tech companies had the luxury of working very hard without having to organize an annual conference to show off their newest and best whiz bang thing. Instead, we now have countless examples of bad decisions made by someone in the G-MAFIA, probably because they worked quickly. We begin to see the negative effects of the tension between doing research that is in the interest of humanity and making investors happy.
…
The problem is that our technology has become increasingly sophisticated, but our thinking about what free speech is and what a free market economy looks like has not become that advanced. We tend to resort to very basic interpretations: free speech means that all speech is free, unless it conflicts with defamation laws, and that’s the end of the story. That is not the end of the story. We need to start a more sophisticated and intelligent conversation about our current laws, our emerging technology, and how we can make the two meet halfway.
So I absolutely believe that there is a way forward. But we have to come together and bridge the gap between Silicon Valley and DC, so that we can all steer the boat in the same direction.
— Amy Webb, futurist, NYU professor, founder of the Future Today Institute
Also see:
“FRONTLINE investigates the promise and perils of artificial intelligence, from fears about work and privacy to rivalry between the U.S. and China. The documentary traces a new industrial revolution that will reshape and disrupt our lives, our jobs and our world, and allow the emergence of the surveillance society.”
The film has five distinct messages about:
1. China’s AI Plan
2. The Promise of AI
3. The Future of Work
4. Surveillance Capitalism
5. The Surveillance State
Colleges see equity success with adaptive learning systems — from edtechmagazine.com by Shailaja Neelakantan
Powered by advanced algorithms, adaptive learning technologies boost completion rates and give students confidence.
“I used to teach one class of 100 students, but now I teach 100 classes of one student each,” said Doug Williams, the adaptive learning coordinator at Arizona State University, in the white paper, describing the effect of using such a technology-driven system to improve learning outcomes.
From DSC:
I post this item because I believe that this is the type of thing that will be a piece of our future learning ecosystems. Learning agents. Systems that accommodate each individual’s learning preferences. Real-time formative assessments…that impact what you see and experience next. Intelligent systems. Intelligent tutoring.
People demonstrate mastery at different times — let that be part of our futures — versus this one-size fits all, hop-on-board-or-you-miss-the-train…a train that stops for no one.
Report: College leaders not confident they can beat new competition — from educationdive.com by Hallie Busta, with thanks to Ray Schroeder for posting this out on LinkedIn
Excerpt:
While they say their institutions are prepared to meet students’ changing needs, they are less confident in their ability to address new forms of competition or change how the public views higher ed.
…
The report comes as higher ed stares down potentially fewer traditional students, more competition online, less state funding, and concerns over public perceptions of higher ed. These pressures have made smaller public and private institutions vulnerable to consolidation and even closure.
FTI 2020 Trend Report for Entertainment, Media, & Technology — from futuretodayinstitute.com
Our 3rd annual industry report on emerging entertainment, media and technology trends is now available.
- 157 trends
- 28 optimistic, pragmatic and catastrophic scenarios
- 10 non-technical primers and glossaries
- Overview of what events to anticipate in 2020
- Actionable insights to use within your organization
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Synthetic media offers new opportunities and challenges.
- Authenticating content is becoming more difficult.
- Regulation is coming.
- We’ve entered the post-fixed screen era.
- Voice Search Optimization (VSO) is the new Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
- Digital subscription models aren’t working.
- Advancements in AI will mean greater efficiencies.
Welcome to the future! The future of work is… — from gettingsmart.com
Excerpt:
The future of work is here, and with it, new challenges — so what does this mean for teaching and learning? It means more contribution and young people learning how to make a difference. In our exploration of the #futureofwork, sponsored by eduInnovation and powered by Getting Smart, we dive into what’s happening, what’s coming and how schools might prepare.
Are smart cities the pathway to blockchain and cryptocurrency adoption? — from forbes.com by Chrissa McFarlane
Excerpts:
At the recent Blockchain LIVE 2019 hosted annually in London, I had the pleasure of giving a talk on Next Generation Infrastructure: Building a Future for Smart Cities. What exactly is a “smart city?” The term refers to an overall blueprint for city designs of the future. Already half the world’s population lives in a city, which is expected to grow to sixty-five percent in the next five years. Tackling that growth takes more than just simple urban planning. The goal of smart cities is to incorporate technology as an infrastructure to alleviate many of these complexities. Green energy, forms of transportation, water and pollution management, universal identification (ID), wireless Internet systems, and promotion of local commerce are examples of current of smart city initiatives.
What’s most important to a smart city, however, is integration. None of the services mentioned above exist in a vacuum; they need to be put into a single system. Blockchain provides the technology to unite them into a single system that can track all aspects combined.
From DSC:
There are many examples of the efforts/goals of creating smart cities (throughout the globe) in the above article. Also see the article below.
DC: Some solid points to consider.
“As cities around the world become increasingly ‘smart’, I argue that – amid the optimised encounters and experiences – there also need to be slow moments, when people can mindfully engage with and enjoy the city.” https://t.co/NhzWIKgFOU
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) October 24, 2019
Delivering learning across a lifetime: Higher education’s new paradigm — from evolllution.com with thanks to Mr. Amrit Ahluwalia for his work on this
Excerpt:
Higher education is no longer a single engagement in an individual’s life, or a stop-off point between high school and a career.
Today, and into the future, higher education’s role is ongoing as the demands of the future labor market will require individuals to continuously up-skill and re-skill to remain relevant. As such, while the traditional two- or four-year postsecondary model will continue to play an important role, colleges and universities must expand their repertoire to consciously deliver learning across individuals’ lifetimes.
Read on to learn how the 100 Year Life is changing the fundamental learning needs of individuals across the labor market, and to understand how postsecondary institutions can evolve to fulfil their missions within this new paradigm.
From DSC:
This important perspective/trend reminds me of the graphic below…

Also see:

The employee of the future, he added, “typically will have a new job every five years, probably for 60 to 80 years, and probably every one of those will require skills you did not learn in college.”
IT laggards could lose up to $20 billion in revenue over the next 5 years, says Accenture — from zdnet.com by Larry Dignan
Accenture’s leaders see enterprise technologies as a system compared to independent fixes and bet on cloud, AI, big data analytics and IoT.
Excerpt:
Companies that fail to scale innovation may lose up to $20 billion in revenue over the next five years as enterprises thrive or dive based on information technology decisions, according to Accenture.
Accenture’s report was based on a survey of more than 8,300 companies across 20 industries and 22 countries. Accenture scored companies on technology adoption, depth of technology adoption and cultural readiness. From there, Accenture segmented companies into leaders, defined as the top 10%, and laggards, which represent the bottom 25%.
Also see:
- Digital transformation: 3 change management mistakes to avoid — from enterprisersproject.com by Peter Bendor-Samuel
The degree of change and the pace of change both pick up during a digital transformation. Don’t let these common change management mistakes trip you up
up
The 7 biggest technology trends in 2020 everyone must get ready for now — from forbes.com by Bernard Marr
Excerpts:
- AI-as-a-service
- 5G data networks
- Autonomous Driving
- Personalized and predictive medicine
- Computer Vision
- Extended Reality
- Blockchain Technology
From DSC:
I appreciate this list from Bernard. I would also add voice-enabled interfaces/products (NLP) to this list, as well as more integration of AI into learning-related applications and services.
For the federal agencies, state representatives, senators, law schools, students in law school, lawyers, legislators, CIO’s, and CEO’s etc. out there: Are you/we ready for these? Given the pace of exponential change, how are you seeking to keep a pulse-check on these types of emerging technologies and their impacts on our society? How are you/we guiding the development of these emerging technologies?
From DSC:
The two postings below show the need for more collaboration and the use of teams:
The future of law and computational technologies: Two sides of the same coin — from legaltechlever.com by Daniel Linna Jr.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
An increasing number of lawyers today work with allied professionals to improve processes, better manage projects, embrace data-driven methods, and leverage technology to improve legal services and systems. Legal-services and lawyer regulations are evolving. And basic technologies and AI are slowly making their way into the legal industry, from legal aid organizations and courts to large law firms, corporate legal departments, and governments.
If we are to realize the potential to improve society with computational technologies, law, regulation, and ethical principles must be front and center at every stage, from problem definition, design, data collection, and data cleaning to training, deployment, and monitoring and maintenance of products and systems. To achieve this, technologists and lawyers must collaborate and share a common vocabulary. Lawyers must learn about technology, and technologists must learn about law. Multidisciplinary teams with a shared commitment to law, regulation, and ethics can proactively address today’s AI challenges, and advance our collaborative problem-solving capabilities to address tomorrow’s increasingly complex problems. Lawyers and technologists must work together to create a better future for everyone.
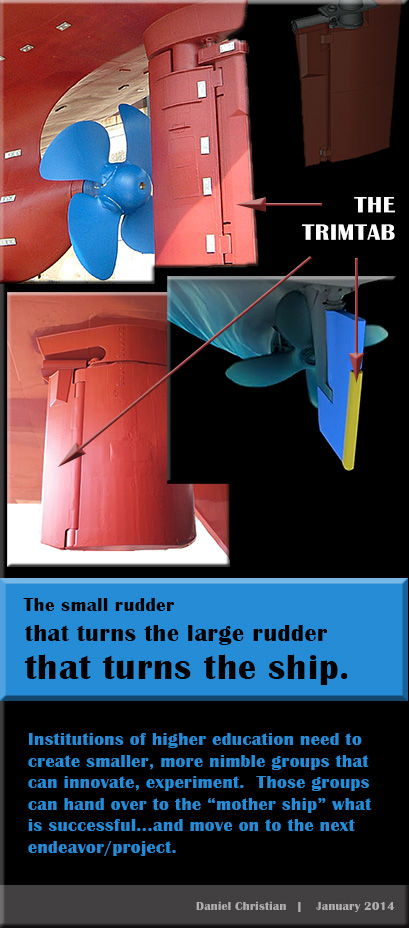
From DSC:
As with higher education in general, we need more team-based efforts in the legal realm as well as more TrimTab Groups.
- What’s a lawyer now? Law’s shift from practice to skill — from forbes.com by Mark Cohen
Excerpts:
Why does this distinction matter? Because law—like so many industries—is undergoing a tectonic shift. It is morphing from a lawyer dominated, practice-centric, labor-intensive guild to a tech-enabled, process and data-driven, multi-disciplinary global industry. The career paths, skills, and expectations of lawyers are changing. So too are how, when, and on what financial terms they are engaged; with whom and from what delivery models they work; their performance metrics, and the resources—human and machine—they collaborate with. Legal practice is shrinking and the business of delivering legal services is expanding rapidly.
Law is no longer the exclusive province of lawyers. Legal knowledge is not the sole element of legal delivery—business and technological competencies are equally important. It’s a new ballgame—one that most lawyers are unprepared for.
…
How did we get here and are legal careers for most a dead end? Spoiler alert: there’s tremendous opportunity in the legal industry. The caveat: all lawyers must have basic business and technological competency whether they pursue practice careers or leverage their legal knowledge as a skill in legal delivery and/or allied professional careers.
Upskilling the legal profession is already a key issue, a requisite for career success. Lawyers must learn new skills like project management, data analytics, deployment of technology, and process design to leverage their legal knowledge. Simply knowing the law will not cut it anymore.
From DSC:
I really appreciate the work of the above two men whose articles I’m highlighting here. I continue to learn a lot from them and am grateful for their work.
That said, just like it’s a lot to expect a faculty member (in higher ed) who teaches online to not only be a subject matter expert, but also to be skilled in teaching, web design, graphic design, navigation design, information design, audio design, video editing, etc…it’s a lot to expect for a lawyer to be a skilled lawyer, business person, and technician. I realize that Mark was only saying a basic level of competency…but even that can be difficult to achieve at times. Why? Because people have different skillsets, passions, and interests. One might be a good lawyer, but not a solid technician…or vice versa. One might be a solid professor, but isn’t very good with graphic design.
A momentous change in the legal industry garnering little attention — from forbes.com by Hendrik Pretorius
Excerpt:
The needed evolution in legal service delivery may receive a big push in the near future. Surprisingly, this issue seems to be flying under the radar for many in the legal industry.
The California Bar, through its Task Force on Access Through Innovation of Legal Services, created in 2018, seeks to “identify possible regulatory changes to enhance the delivery of, and access to, legal services through the use of technology, including artificial intelligence and online legal service delivery models.”
A report commissioned by this task force stated that “[m]odifying the ethics rules to facilitate greater collaboration across law and other disciplines will (1) drive down costs; (2) improve access; (3) increase predictability and transparency of legal services; (4) aid the growth of new businesses; and (5) elevate the reputation of the legal profession.”
Herein lies one of the fundamental challenges within the legal industry: viewing the law as the delivery of a legal product, and understanding that this delivery needs to revolve around the user, not the lawyer. There is a real and growing divide between the current model of legal service delivery put forth by a traditional law firm model and what the public wants. Consumers have raised the bar based on what they are experiencing in interacting with other businesses in other industries.
…
I love what many of these legal tech companies are doing: They are applying standards from outside the entrenched legal industry and changing entire delivery models. This should be a real wake-up call. But how can law firms truly compete and play a role?