The economic potential of generative AI — from mckinsey.com; via Superhuman
.
DC: It should prove to be interesting & fun to watch how #AI and #XR related technologies will be integrated into games & the #gamification of #learning .https://t.co/HO2CftqNrs via @VRScout
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) June 23, 2023
.
On giving AI eyes and ears — from oneusefulthing.org by Ethan Mollick
AI can listen and see, with bigger implications than we might realize.
Excerpt:
But even this is just the beginning, and new modes of using AI are appearing, which further increases their capabilities. I want to show you some examples of this emerging world, which I think will soon introduce a new wave of AI use cases, and accompanying disruption.
We need to recognize that these capabilities will continue to grow, and AI will be able to play a more active role in the real world by observing and listening. The implications are likely to be profound, and we should start thinking through both the huge benefits and major concerns today.
Ethan Mollick
5 Steps to Transforming Images into Videos Using AI Tools — from heatherbcooper.substack.com by Heather Cooper
A simple guide to layering AI tools for quick video creation
.
‘Nobody wins in an academic-integrity arms race’ — from chonicle.com by Ian Wilhelm
How artificial intelligence is changing the way college thing about cheating
Even though generative AI is a new thing, it doesn’t change why students cheat. They’ve always cheated for the same reason: They don’t find the work meaningful, and they don’t think they can achieve it to their satisfaction. So we need to design assessments that students find meaning in.
Tricia Bertram Gallant
Caught off guard by AI — from chonicle.com by Beth McMurtrie and Beckie Supiano
Professor scrambled to react to ChatGPT this spring — and started planning for the fall
Excerpt:
Is it cheating to use AI to brainstorm, or should that distinction be reserved for writing that you pretend is yours? Should AI be banned from the classroom, or is that irresponsible, given how quickly it is seeping into everyday life? Should a student caught cheating with AI be punished because they passed work off as their own, or given a second chance, especially if different professors have different rules and students aren’t always sure what use is appropriate?
GPT-4 Can Use Tools Now—That’s a Big Deal — from every.to by Dan Shipper; resource via Sam DeBrule
What “function calling” is, how it works, and what it means
Excerpt:
…OpenAI built tool use right into the GPT API with an update called function calling. It’s a little like a child’s ability to ask their parents to help them with a task that they know they can’t do on their own. Except in this case, instead of parents, GPT can call out to external code, databases, or other APIs when it needs to.
Each function in function calling represents a tool that a GPT model can use when necessary, and GPT gets to decide which ones it wants to use and when. This instantly upgrades GPT capabilities—not because it can now do every task perfectly—but because it now knows how to ask for what it wants and get it.
.
.
How ChatGPT can help disrupt assessment overload — from timeshighereducation.com by David Carless
Advances in AI are not necessarily the enemy – in fact, they should prompt long overdue consideration of assessment types and frequency, says David Carless
Excerpt:
Reducing the assessment burden could support trust in students as individuals wanting to produce worthwhile, original work. Indeed, students can be co-opted as partners in designing their own assessment tasks, so they can produce something meaningful to them.
A strategic reduction in quantity of assessment would also facilitate a refocusing of assessment priorities on deep understanding more than just performance and carries potential to enhance feedback processes.
If we were to tackle assessment overload in these ways, it opens up various possibilities. Most significantly there is potential to revitalise feedback so that it becomes a core part of a learning cycle rather than an adjunct at its end. End-of-semester, product-oriented feedback, which comes after grades have already been awarded, fails to encourage the iterative loops and spirals typical of productive learning.
.
.
The full 12 uses are here: https://edgeoflearning.com/your-new-teaching-superpower-ai-tools/
The AI Tools in Education Database — from kiwi-path-612.notion.site by EdTech Insiders
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Since AI in education has been moving at the speed of light, we built this AI Tools in Education database to keep track of the most recent AI tools in education and the changes that are happening every day. This database is intended to be a community resource for educators, researchers, students, and other edtech specialists looking to stay up to date. This is a living document, so be sure to come back for regular updates.
.
.
Time for Class 2023 Study finds students are earlier adopters of generative AI tools than faculty, and majority (69%) of learners prefer hybrid, blended or online course formats — from globenewswire.com by Tyton Partners
.
AI Could Prevent Hiring Bias — Unless It Makes It Worse — from nerdwallet.com by Anna Helhoski
Advocates say AI can eliminate human biases in hiring. Skeptics point out that AI tools are trained by … humans.
Excerpt:
These claims conjure up the rosiest of images: human resource departments and their robot buddies solving discrimination in workplace hiring. It seems plausible, in theory, that AI could root out unconscious bias, but a growing body of research shows the opposite may be more likely.
…
Companies’ use of AI didn’t come out of nowhere: For example, automated applicant tracking systems have been used in hiring for decades. That means if you’ve applied for a job, your resume and cover letter were likely scanned by an automated system. You probably heard from a chatbot at some point in the process. Your interview might have been automatically scheduled and later even assessed by AI.
From DSC:
Here was my reflection on this:
DC: Along these lines, I wonder if Applicant Tracking Systems cause us to become like typecast actors and actresses — only thought of for certain roles. Pigeonholed.
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) June 23, 2023
Also related to AI in hiring, see:
4 in 10 Companies Will Be Using AI Interviews by 2024 — from resumebuilder.com
In June, ResumeBuilder.com surveyed more than 1,000 employees who are involved in hiring processes at their workplaces to find out about their companies’ use of AI interviews.
The results:
- 43% of companies already have or plan to adopt AI interviews by 2024
- Two-thirds of this group believe AI interviews will increase hiring efficiency
- 15% say that AI will be used to make decisions on candidates without any human input
- More than half believe AI will eventually replace human hiring managers
Watch OpenAI CEO Sam Altman on the Future of AI — from bloomberg.com
Sam Altman, CEO & Co-Founder, OpenAI discusses the explosive rise of OpenAI and its products and what an AI-laced future can look like with Bloomberg’s Emily Chang at the Bloomberg Technology Summit.
.
PowerSchool Announces Collaboration with Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service to Provide Personalized Learning at Scale in K-12 Education — from powerschool.com
Large-scale language models integrated within PowerSchool Performance Matters and PowerSchool LearningNav products will empower educators in delivering transformative personalized learning pathways
The implementation of generative AI within these products will dramatically improve educators’ ability to deliver personalized learning to students at scale by enabling the application of personalized assessments and learning pathways based on individual student needs and learning goals. K-12 educators will also benefit from access to OpenAI technology…
.
FETC 2023 Virtual Roundtable: How AI Will Transform K-12 Education
AI could be the great equalizer!
Holly Clark
Example screenshots:
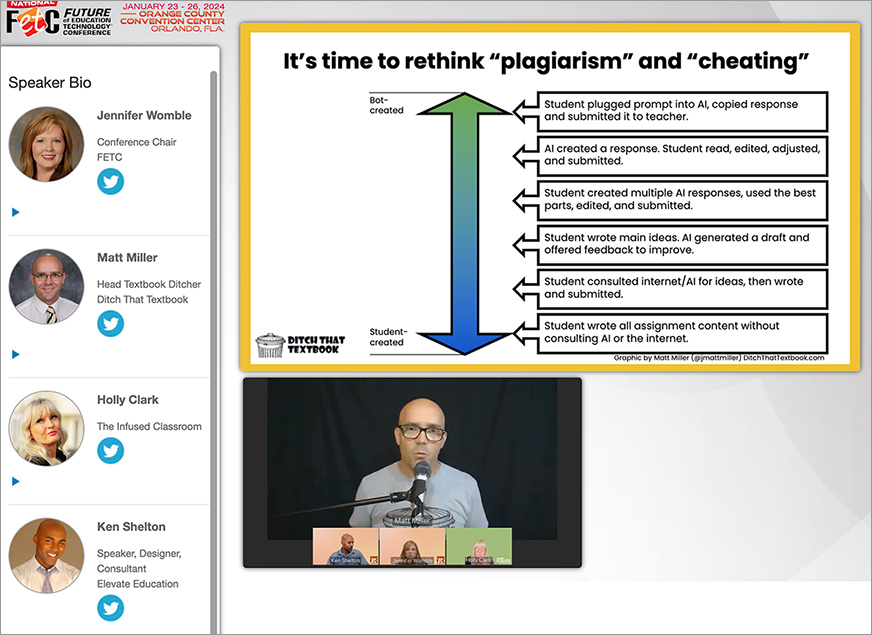














AI-assisted cheating isn’t a temptation if students have a reason to care about their own learning.
Yesterday I happened to listen to two different podcasts that ended up resonating with one another and with an idea that’s been rattling around inside my head with all of this moral uproar about generative AI:
** If we trust students – and earn their trust in return – then they will be far less motivated to cheat with AI or in any other way. **
First, the question of motivation. On the Intentional Teaching podcast, while interviewing James Lang and Michelle Miller on the impact of generative AI, Derek Bruff points out (drawing on Lang’s Cheating Lessons book) that if students have “real motivation to get some meaning out of [an] activity, then there’s far less motivation to just have ChatGPT write it for them.” Real motivation and real meaning FOR THE STUDENT translates into an investment in doing the work themselves.
…
Then I hopped over to one of my favorite podcasts – Teaching in Higher Ed – where Bonni Stachowiak was interviewing Cate Denial about a “pedagogy of kindness,” which is predicated on trusting students and not seeing them as adversaries in the work we’re doing.
So the second key element: being kind and trusting students, which builds a culture of mutual respect and care that again diminishes the likelihood that they will cheat.
…
Again, human-centered learning design seems to address so many of the concerns and challenges of the current moment in higher ed. Maybe it’s time to actually practice it more consistently. #aiineducation #higheredteaching #inclusiveteaching