The Year TV Leaped Into The Future — from protocol.com by Janko Roettgers
The lockdowns this year have transformed our homes into offices, schools, concert halls, movie theaters and gyms. Our homes are working harder for us, but so is our technology. The device that is working the hardest is perhaps the TV—becoming our lifeline to a far more virtual world.
Addendums:
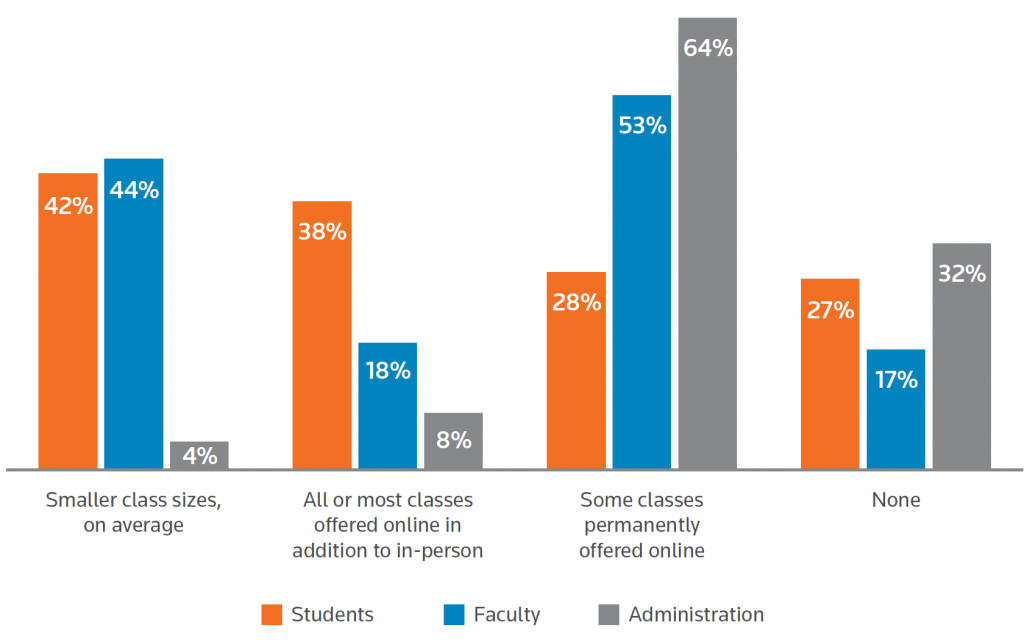
The Second Year of The MOOC: 2020 Saw a Rush to Large-Scale Online Courses — from edsurge.com by Dhawal Shah
Excerpt:
This was the year that more people learned what a MOOC is.
As millions suddenly found themselves with free time on their hands during the pandemic, many turned to online courses—especially, to free courses known as MOOCs, or Massive Open Online Courses. This phenomenon was compounded by media worldwide compiling lists of “free things to do during lockdown,” which tended to include MOOCs.
Within two months, Class Central had received over 10 million visits and sent over six million clicks to MOOC providers. These learners also turned out to be more engaged than usual. In April 2020, MOOC providers Coursera, edX and FutureLearn attracted as many new users in a single month as they did in the entirety of 2019.
.
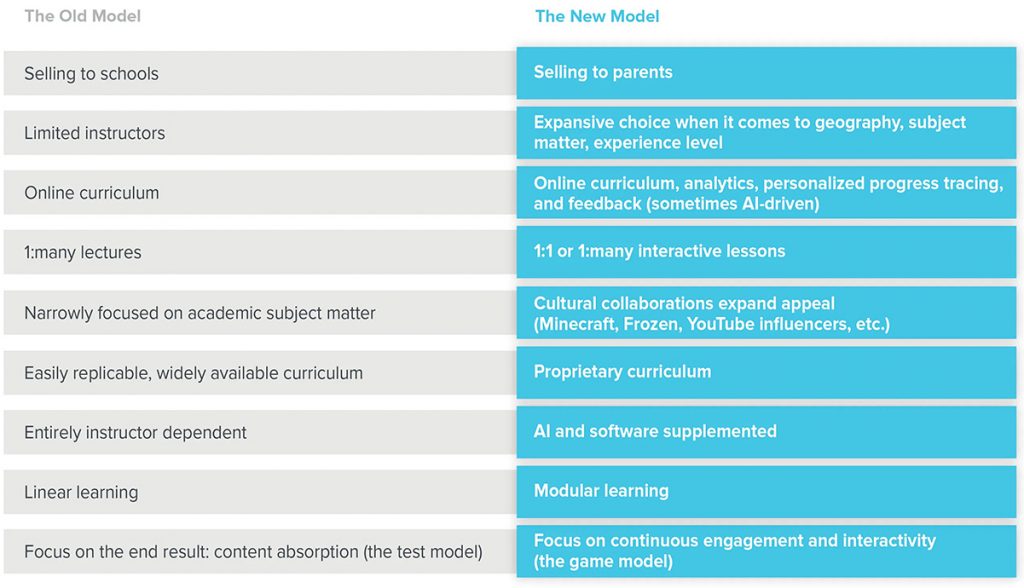
From DSC:
The pieces continue to come together…
...team-based content creation and delivery will dominate in the future (at least for the masses). It will offer engaging, personalized learning and the AI-based systems will be constantly scanning for the required/sought-after skills and competencies. The systems will then present a listing of items that will help people obtain those skills and competencies.
#AI #LearningProfiles #Cloud #LearningFromTheLivingClassRoom #LearningEcosystems #LearningSpaces #21stCentury #24x7x365 #Reinvent #Surviving #StayingRelevant #LifeLongLearning and many more tags/categories are applicable here.









![The Year TV Leaped Into The Future [Roettgers]](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/BigTrendsStreaming-2020-Janko-Roettgers.jpg)