The biggest things that happened in AI this year — from superhuman.ai by Zain Kahn
- Microsoft raises eyebrows with a huge $10 Billion investment in OpenAI.
- Meta launches Llama 2, their open-source rival to OpenAI’s models.
- OpenAI announces ChatGPT Plus, a paid version of their chatbot.
- Microsoft announces a new AI-powered Bing Search.
- OpenAI announces the powerful GPT-4 model, still considered to be the gold standard.
- Midjourney releases V5, which brings AI-powered image generation one step closer to reality.
- Microsoft launches Copilot for Microsoft 365.
- Google launches Bard, its rival to ChatGPT.
…and more
AI 2023: A Year in Review — from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard
2023 developments in AI and a hint of what they are building toward
Some of the items that Stefan includes in his posting include:
- ChatGPT and other language models that generate text.
- Image generators.
- Video generators.
- AI models that that can read, hear, and speak.
- AI models that can see.
- Improving models.
- “Multimodal” models.
- Training on specific content.
- Reasoning & planning.
- …and several others
The Dictionary.com Word of the Year is “hallucinate.” — from content.dictionary.com by Nick Norlen and Grant Barrett; via The Rundown AI
hallucinate
[ huh–loo-suh-neyt ]
verb
(of artificial intelligence) to produce false information contrary to the intent of the user and present it as if true and factual. Example: When chatbots hallucinate, the result is often not just inaccurate but completely fabricated.
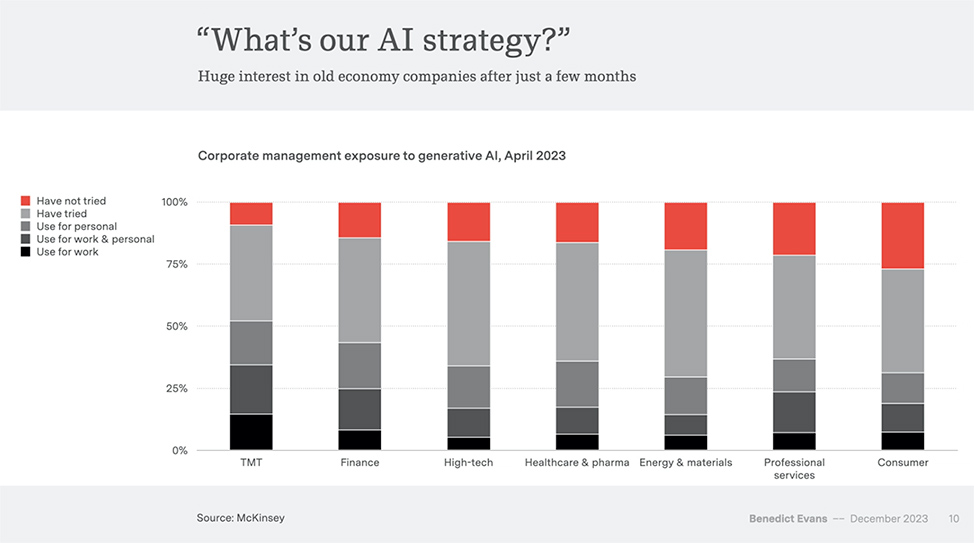
Soon, every employee will be both AI builder and AI consumer — from zdnet.com by Joe McKendrick, via Robert Gibson on LinkedIn
“Standardized tools and platforms as well as advanced low- or no-code tech may enable all employees to become low-level engineers,” suggests a recent report.
The time could be ripe for a blurring of the lines between developers and end-users, a recent report out of Deloitte suggests. It makes more business sense to focus on bringing in citizen developers for ground-level programming, versus seeking superstar software engineers, the report’s authors argue, or — as they put it — “instead of transforming from a 1x to a 10x engineer, employees outside the tech division could be going from zero to one.”
Along these lines, see:
- TECH TRENDS 2024 — from deloitte.com
Six emerging technology trends demonstrate that in an age of generative machines, it’s more important than ever for organizations to maintain an integrated business strategy, a solid technology foundation, and a creative workforce.
UK Supreme Court rules AI is not an inventor — from theverge.com by Emilia David
The ruling follows a similar decision denying patent registrations naming AI as creators.
The UK Supreme Court ruled that AI cannot get patents, declaring it cannot be named as an inventor of new products because the law considers only humans or companies to be creators.
The Times Sues OpenAI and Microsoft Over A.I. Use of Copyrighted Work — from nytimes.com by Michael M. Grynbaum and Ryan Mac
The New York Times sued OpenAI and Microsoft for copyright infringement on Wednesday, opening a new front in the increasingly intense legal battle over the unauthorized use of published work to train artificial intelligence technologies.
…
The suit does not include an exact monetary demand. But it says the defendants should be held responsible for “billions of dollars in statutory and actual damages” related to the “unlawful copying and use of The Times’s uniquely valuable works.” It also calls for the companies to destroy any chatbot models and training data that use copyrighted material from The Times.
On this same topic, also see:
Apple’s iPhone Design Chief Enlisted by Jony Ive, Sam Altman to Work on AI Devices — from bloomberg.com by Mark Gurman (behind paywall)
- Design executive Tang Tan is set to leave Apple in February
- Tan will join Ive’s LoveFrom design studio, work on AI project
AI 2023: Chatbots Spark New Tools — from heatherbcooper.substack.com by Jeather Cooper
ChatGPT and Other Chatbots
The arrival of ChatGPT sparked tons of new AI tools and changed the way we thought about using a chatbot in our daily lives.
Chatbots like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Bing Chat can help content creators by quickly generating ideas, outlines, drafts, and full pieces of content, allowing creators to produce more high-quality content in less time.
These AI tools boost efficiency and creativity in content production across formats like blog posts, social captions, newsletters, and more.
Microsoft’s next Surface laptops will reportedly be its first true ‘AI PCs’ — from theverge.com by Emma Roth
Next year’s Surface Laptop 6 and Surface Pro 10 will feature Arm and Intel options, according to Windows Central.
Microsoft is getting ready to upgrade its Surface lineup with new AI-enabled features, according to a report from Windows Central. Unnamed sources told the outlet the upcoming Surface Pro 10 and Surface Laptop 6 will come with a next-gen neural processing unit (NPU), along with Intel and Arm-based options.
How one of the world’s oldest newspapers is using AI to reinvent journalism — from theguardian.com by Alexandra Topping
Berrow’s Worcester Journal is one of several papers owned by the UK’s second biggest regional news publisher to hire ‘AI-assisted’ reporters
With the AI-assisted reporter churning out bread and butter content, other reporters in the newsroom are freed up to go to court, meet a councillor for a coffee or attend a village fete, says the Worcester News editor, Stephanie Preece.
“AI can’t be at the scene of a crash, in court, in a council meeting, it can’t visit a grieving family or look somebody in the eye and tell that they’re lying. All it does is free up the reporters to do more of that,” she says. “Instead of shying away from it, or being scared of it, we are saying AI is here to stay – so how can we harness it?”
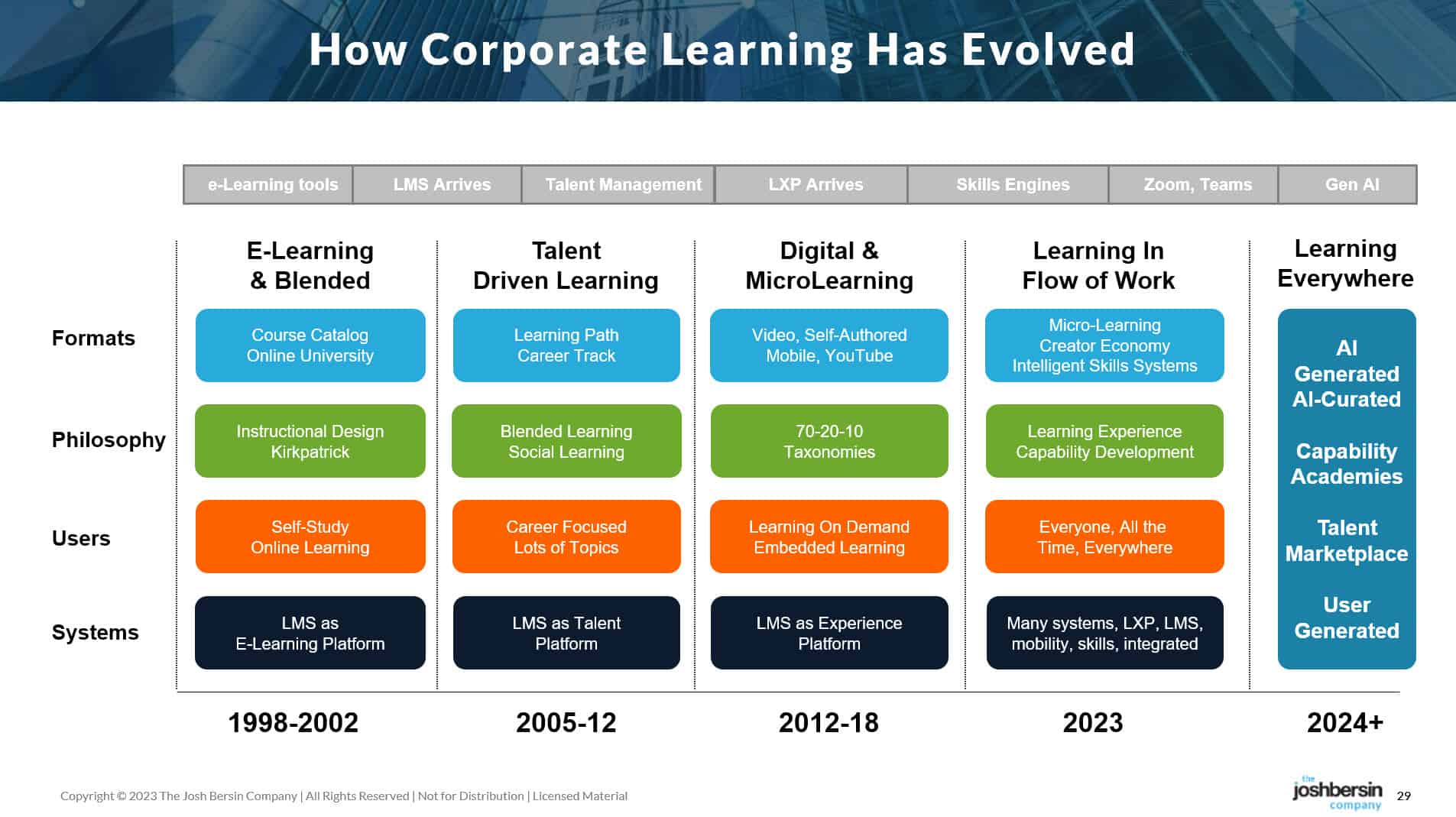
What to Expect in AI in 2024 — from hai.stanford.edu by
Seven Stanford HAI faculty and fellows predict the biggest stories for next year in artificial intelligence.
Topics include:
- White Collar Work Shifts
- Deepfake Proliferation
- GPUs Shortage
- More Helpful Agents
- Hopes for U.S. Regulation
- Asking Big Questions, Applying New Policies
- Companies Will Navigate Complicated Regulations
Addendum on 1/2/24: