The Good, the Bad, & the Unknown of AI — from aiedusimplified.substack.com by Lance Eaton
A recent talk at University of Massachusetts, Boston
.

…the text, slides, and prompt-guide can be found in this resource.
The Good, the Bad, & the Unknown of AI — from aiedusimplified.substack.com by Lance Eaton
A recent talk at University of Massachusetts, Boston
.

…the text, slides, and prompt-guide can be found in this resource.
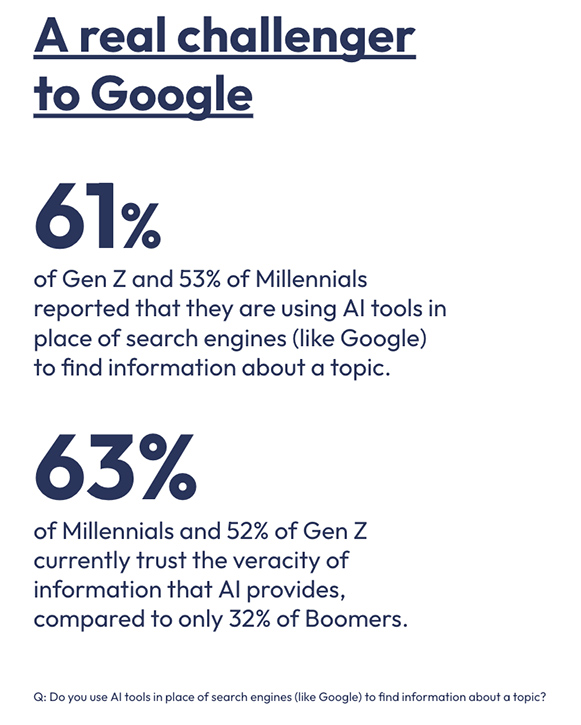
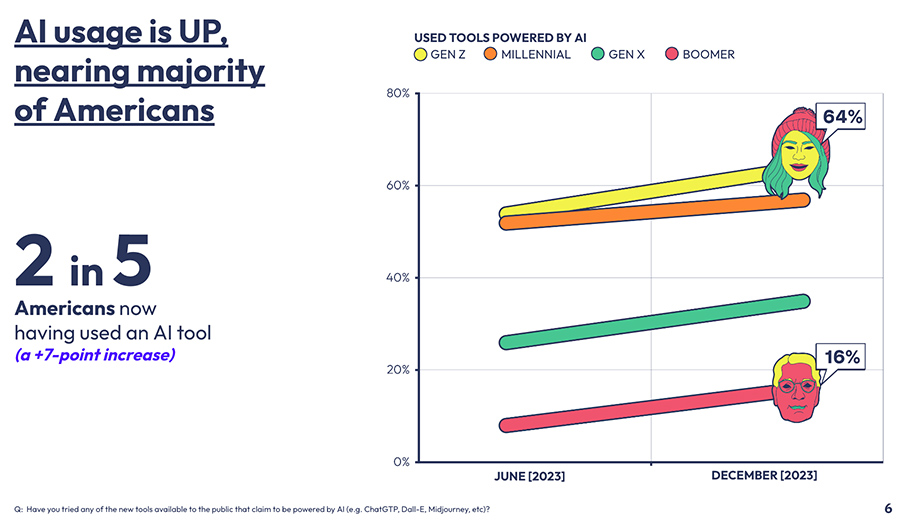
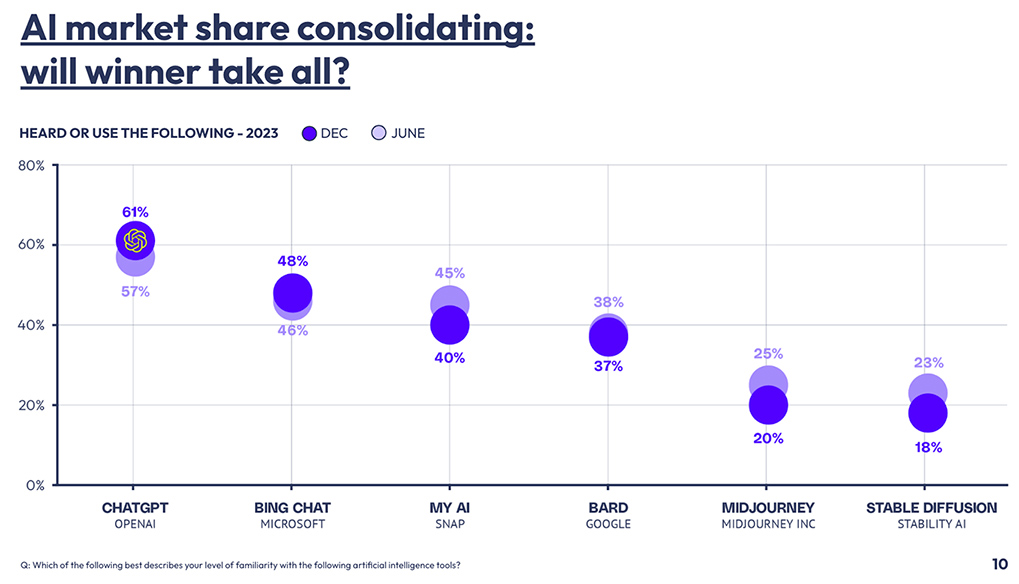
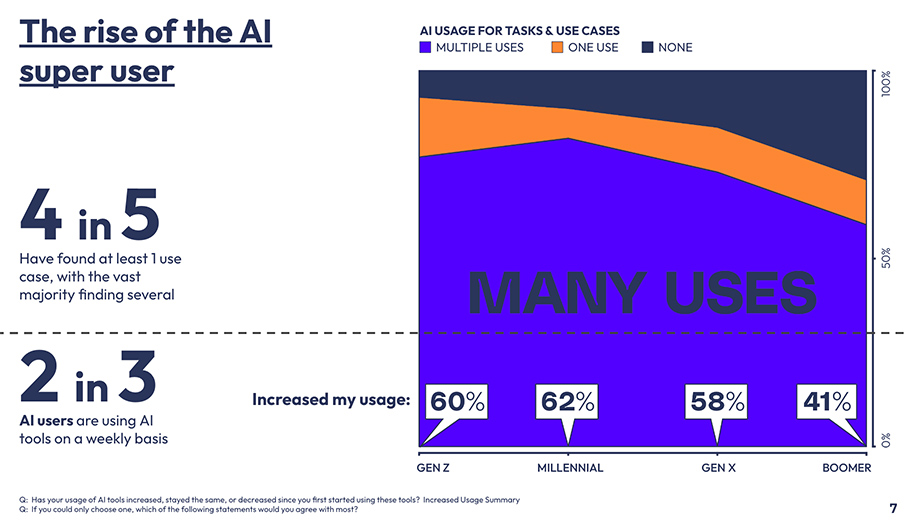
The Verge | What’s Next With AI | February 2024 | Consumer Survey

DC: Just because we can doesn’t mean we should.
It brings to mind #AI and #robotics and the #military — hmmmm…. https://t.co/1J4XKiHRUl
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) April 25, 2024
Microsoft AI creates talking deepfakes from single photo — from inavateonthenet.net
The Great Hall – where now with AI? It is not ‘Human Connection V Innovative Technology’ but ‘Human Connection + Innovative Technology’ — from donaldclarkplanb.blogspot.com by Donald Clark
The theme of the day was Human Connection V Innovative Technology. I see this a lot at conferences, setting up the human connection (social) against the machine (AI). I think this is ALL wrong. It is, and has always been a dialectic, human connection (social) PLUS the machine. Everyone had a smartphone, most use it for work, comms and social media. The binary between human and tech has long disappeared.
Techno-Social Engineering: Why the Future May Not Be Human, TikTok’s Powerful ForYou Algorithm, & More — from by Misha Da Vinci
Things to consider as you dive into this edition:
It’s been an insane week for AI (part 2)
Here are 14 most impressive reveals from this week:
1/ China just released OpenAI’s Sora rival “Vidu” which can create realistic clips in seconds.pic.twitter.com/MnTv9Wxpef
— Barsee ? (@heyBarsee) April 27, 2024
Addressing equity and ethics in artificial intelligence — from apa.org by Zara Abrams
Algorithms and humans both contribute to bias in AI, but AI may also hold the power to correct or reverse inequities among humans
“The conversation about AI bias is broadening,” said psychologist Tara Behrend, PhD, a professor at Michigan State University’s School of Human Resources and Labor Relations who studies human-technology interaction and spoke at CES about AI and privacy. “Agencies and various academic stakeholders are really taking the role of psychology seriously.”
NY State Bar Association Joins Florida and California on AI Ethics Guidance – Suggests Some Surprising Implications — from natlawreview.com by James G. Gatto
The NY State Bar Association (NYSBA) Task Force on Artificial Intelligence has issued a nearly 80 page report (Report) and recommendations on the legal, social and ethical impact of artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI on the legal profession. This detailed Report also reviews AI-based software, generative AI technology and other machine learning tools that may enhance the profession, but which also pose risks for individual attorneys’ understanding of new, unfamiliar technology, as well as courts’ concerns about the integrity of the judicial process. It also makes recommendations for NYSBA adoption, including proposed guidelines for responsible AI use. This Report is perhaps the most comprehensive report to date by a state bar association. It is likely this Report will stimulate much discussion.
For those of you who want the “Cliff Notes” version of this report, here is a table that summarizes by topic the various rules mentioned and a concise summary of the associated guidance.
The Report includes four primary recommendations:
Do We Need Emotionally Intelligent AI? — from marcwatkins.substack.com by Marc Watkins
We keep breaking new ground in AI capabilities, and there seems little interest in asking if we should build the next model to be more life-like. You can now go to Hume.AI and have a conversation with an Empathetic Voice Interface. EVI is groundbreaking and extremely unnerving, but it is no more capable of genuine empathy than your toaster oven.
…
From DSC:
Marc offers some solid thoughts that should make us all pause and reflect on what he’s saying.
We can endlessly rationalize away the reasons why machines possessing such traits can be helpful, but where is the line that developers and users of such systems refuse to cross in this race to make machines more like us?
Marc Watkins
Along these lines, also see:

How AI Is Already Transforming the News Business — from politico.com by Jack Shafer
An expert explains the promise and peril of artificial intelligence.
The early vibrations of AI have already been shaking the newsroom. One downside of the new technology surfaced at CNET and Sports Illustrated, where editors let AI run amok with disastrous results. Elsewhere in news media, AI is already writing headlines, managing paywalls to increase subscriptions, performing transcriptions, turning stories in audio feeds, discovering emerging stories, fact checking, copy editing and more.
Felix M. Simon, a doctoral candidate at Oxford, recently published a white paper about AI’s journalistic future that eclipses many early studies. Swinging a bat from a crouch that is neither doomer nor Utopian, Simon heralds both the downsides and promise of AI’s introduction into the newsroom and the publisher’s suite.
Unlike earlier technological revolutions, AI is poised to change the business at every level. It will become — if it already isn’t — the beginning of most story assignments and will become, for some, the new assignment editor. Used effectively, it promises to make news more accurate and timely. Used frivolously, it will spawn an ocean of spam. Wherever the production and distribution of news can be automated or made “smarter,” AI will surely step up. But the future has not yet been written, Simon counsels. AI in the newsroom will be only as bad or good as its developers and users make it.
Also see:
Artificial Intelligence in the News: How AI Retools, Rationalizes, and Reshapes Journalism and the Public Arena — from cjr.org by Felix Simon
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Nvidia just launched Chat with RTX
It leaves ChatGPT in the dust.
Here are 7 incredible things RTX can do: pic.twitter.com/H6K4oJtNcH
— Poonam Soni (@CodeByPoonam) March 2, 2024
EMO: Emote Portrait Alive – Generating Expressive Portrait Videos with Audio2Video Diffusion Model under Weak Conditions — from humanaigc.github.io Linrui Tian, Qi Wang, Bang Zhang, and Liefeng Bo
We proposed EMO, an expressive audio-driven portrait-video generation framework. Input a single reference image and the vocal audio, e.g. talking and singing, our method can generate vocal avatar videos with expressive facial expressions, and various head poses, meanwhile, we can generate videos with any duration depending on the length of input video.
Adobe previews new cutting-edge generative AI tools for crafting and editing custom audio — from blog.adobe.com by the Adobe Research Team
New experimental work from Adobe Research is set to change how people create and edit custom audio and music. An early-stage generative AI music generation and editing tool, Project Music GenAI Control allows creators to generate music from text prompts, and then have fine-grained control to edit that audio for their precise needs.
“With Project Music GenAI Control, generative AI becomes your co-creator. It helps people craft music for their projects, whether they’re broadcasters, or podcasters, or anyone else who needs audio that’s just the right mood, tone, and length,” says Nicholas Bryan, Senior Research Scientist at Adobe Research and one of the creators of the technologies.
How AI copyright lawsuits could make the whole industry go extinct — from theverge.com by Nilay Patel
The New York Times’ lawsuit against OpenAI is part of a broader, industry-shaking copyright challenge that could define the future of AI.
There’s a lot going on in the world of generative AI, but maybe the biggest is the increasing number of copyright lawsuits being filed against AI companies like OpenAI and Stability AI. So for this episode, we brought on Verge features editor Sarah Jeong, who’s a former lawyer just like me, and we’re going to talk about those cases and the main defense the AI companies are relying on in those copyright cases: an idea called fair use.
FCC officially declares AI-voiced robocalls illegal — from techcrunch.com by Devom Coldewey
The FCC’s war on robocalls has gained a new weapon in its arsenal with the declaration of AI-generated voices as “artificial” and therefore definitely against the law when used in automated calling scams. It may not stop the flood of fake Joe Bidens that will almost certainly trouble our phones this election season, but it won’t hurt, either.
The new rule, contemplated for months and telegraphed last week, isn’t actually a new rule — the FCC can’t just invent them with no due process. Robocalls are just a new term for something largely already prohibited under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act: artificial and pre-recorded messages being sent out willy-nilly to every number in the phone book (something that still existed when they drafted the law).
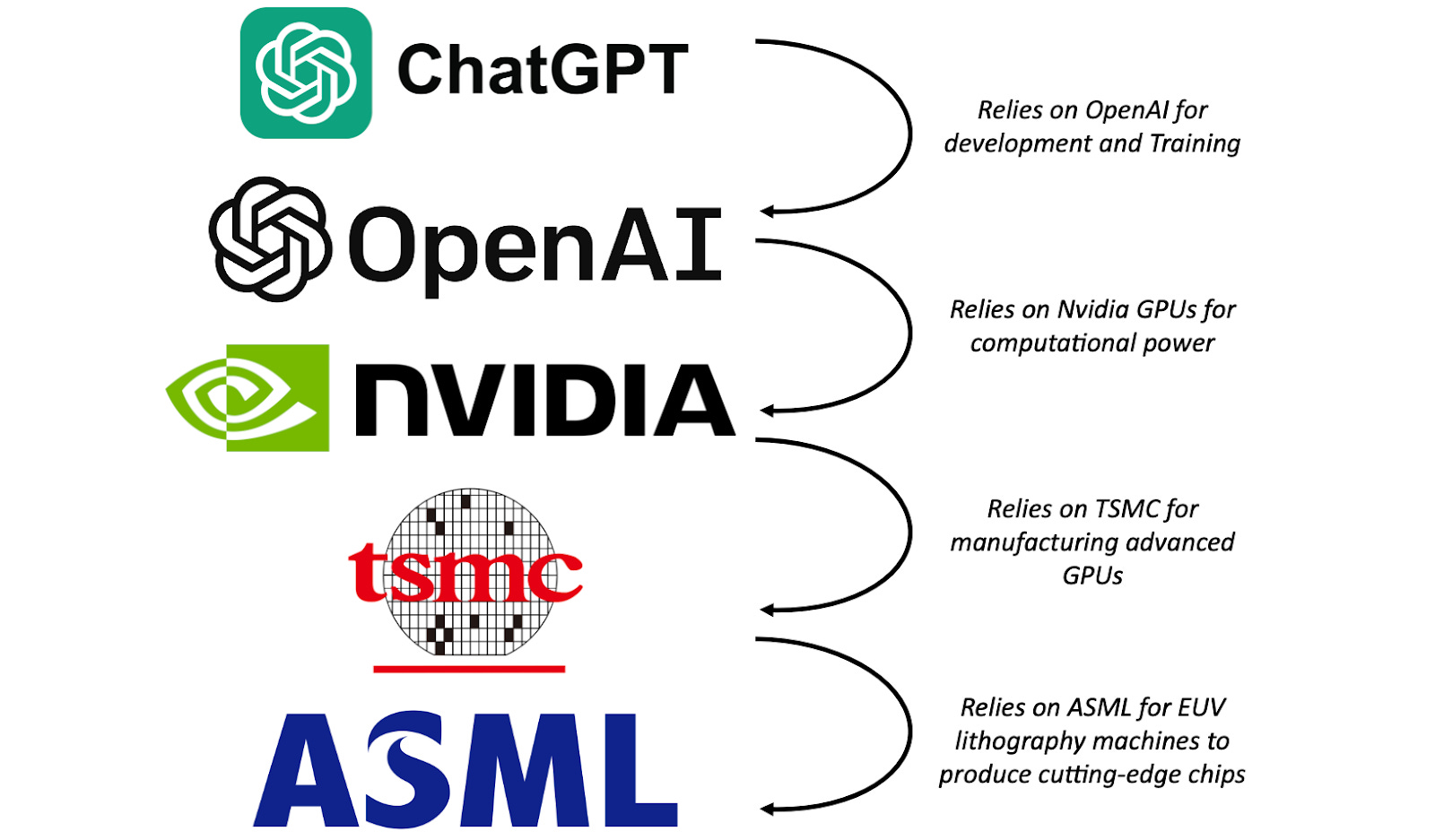
EIEIO…Chips Ahoy! — from dashmedia.co by Michael Moe, Brent Peus, and Owen Ritz
Here Come the AI Worms — from wired.com by Matt Burgess
Security researchers created an AI worm in a test environment that can automatically spread between generative AI agents—potentially stealing data and sending spam emails along the way.
Now, in a demonstration of the risks of connected, autonomous AI ecosystems, a group of researchers have created one of what they claim are the first generative AI worms—which can spread from one system to another, potentially stealing data or deploying malware in the process. “It basically means that now you have the ability to conduct or to perform a new kind of cyberattack that hasn’t been seen before,” says Ben Nassi, a Cornell Tech researcher behind the research.
Generative AI in a Nutshell – how to survive and thrive in the age of AI — from youtube.com by Henrik Kniberg; via Robert Gibson and Adam Garry on LinkedIn
Lawless superintelligence: Zero evidence that AI can be controlled — from earth.com by Eric Ralls
In the realm of technological advancements, artificial intelligence (AI) stands out as a beacon of immeasurable potential, yet also as a source of existential angst when considering that AI might already be beyond our ability to control.
Dr. Roman V. Yampolskiy, a leading figure in AI safety, shares his insights into this dual-natured beast in his thought-provoking work, “AI: Unexplainable, Unpredictable, Uncontrollable.”
His research underscores a chilling truth: our current understanding and control of AI are woefully inadequate, posing a threat that could either lead to unprecedented prosperity or catastrophic extinction.
From DSC:
This next item is for actors, actresses, and voiceover specialists:
Turn your voice into passive income. — from elevenlabs.io; via Ben’s Bites
Are you a professional voice actor? Sign up and share your voice today to start earning rewards every time it’s used.
Scammers trick company employee using video call filled with deepfakes of execs, steal $25 million — from techspot.com by Rob Thubron; via AI Valley
The victim was the only real person on the video conference call
The scammers used digitally recreated versions of an international company’s Chief Financial Officer and other employees to order $25 million in money transfers during a video conference call containing just one real person.
The victim, an employee at the Hong Kong branch of an unnamed multinational firm, was duped into taking part in a video conference call in which they were the only real person – the rest of the group were fake representations of real people, writes SCMP.
As we’ve seen in previous incidents where deepfakes were used to recreate someone without their permission, the scammers utilized publicly available video and audio footage to create these digital versions.
Letter from the YouTube CEO: 4 Big bets for 2024 — from blog.youtube by Neal Mohan, CEO, YouTube; via Ben’s Bites

.
#1: AI will empower human creativity.
#2: Creators should be recognized as next-generation studios.
#3: YouTube’s next frontier is the living room and subscriptions.
#4: Protecting the creator economy is foundational.
Viewers globally now watch more than 1 billion hours on average of YouTube content on their TVs every day.
Bard becomes Gemini: Try Ultra 1.0 and a new mobile app today — from blog.google by Sissie Hsiao; via Rundown AI
Bard is now known as Gemini, and we’re rolling out a mobile app and Gemini Advanced with Ultra 1.0.
Since we launched Bard last year, people all over the world have used it to collaborate with AI in a completely new way — to prepare for job interviews, debug code, brainstorm new business ideas or, as we announced last week, create captivating images.
Our mission with Bard has always been to give you direct access to our AI models, and Gemini represents our most capable family of models. To reflect this, Bard will now simply be known as Gemini.
A new way to discover places with generative AI in Maps — from blog.google by Miriam Daniel; via AI Valley
Here’s a look at how we’re bringing generative AI to Maps — rolling out this week to select Local Guides in the U.S.
Today, we’re introducing a new way to discover places with generative AI to help you do just that — no matter how specific, niche or broad your needs might be. Simply say what you’re looking for and our large-language models (LLMs) will analyze Maps’ detailed information about more than 250 million places and trusted insights from our community of over 300 million contributors to quickly make suggestions for where to go.
Starting in the U.S., this early access experiment launches this week to select Local Guides, who are some of the most active and passionate members of the Maps community. Their insights and valuable feedback will help us shape this feature so we can bring it to everyone over time.
Google Prepares for a Future Where Search Isn’t King — from wired.com by Lauren Goode
CEO Sundar Pichai tells WIRED that Google’s new, more powerful Gemini chatbot is an experiment in offering users a way to get things done without a search engine. It’s also a direct shot at ChatGPT.
Survey Results Predict Top Legal Technology Trends for 2024 — from jdsupra.com
In the 2023 Litigation Support Trend Survey, U.S. Legal Support asked lawyers and legal professionals what technology trends they observed in 2023, and how they expect their use of technology to change in 2024.
Now, the results are in—check out the findings below.
Topics included:
Speaking of legaltech and/or how emerging technologies are impacting the legal realm, also see:
? Voice Cloning in Law: ? A Brave New World of Sound!
In my latest blog, “The Deepfake Dilemma: Navigating Voice Cloning in the Legal System,” I tackle the complex challenges posed by voice cloning technology in the justice system. Discover the challenges, risks, and ethical… pic.twitter.com/Jj5u51u1Ia
— Judge Scott Schlegel (@Judgeschlegel) January 3, 2024
Animate Anyone — from theneurondaily.com by Noah Edelman & Pete Huang
Animate Anyone is a new project from Alibaba that can animate any image to move however you’d like.
While the technology is bonkers (duh), the demo video has stirred up mixed reactions.
…
I mean…just check out the (justified) fury on Twitter in response to this research.
To the researchers’ credit, they haven’t released a working demo yet, probably for this exact concern.
DC: Agreed. But don’t expect much help from the American Bar Association! It’s almost 2024 and the vast majority of law schools still can’t offer 100% online-based programs!!!
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) December 4, 2023