With a passion for helping #highered leverage #edtech, @dchristian5 is a 2017 Must-Read! https://t.co/e7cqFqynBW
— EdTech Higher Ed (@EdTech_HigherEd) June 22, 2017
From DSC:
Below is a great quote from David Koetje, Professor of Biology at Calvin College:
I think teaching and learning are a bit like dancing: We can say that one has to lead and the other has to follow. But in reality, each has to constantly pay close attention to the other. For the dance to be beautiful, both have to practice together diligently. If one dancer tries to do it all, then there’s no dance. It takes two to tango.
The 2017 Dean’s List: EdTech’s 50 Must-Read Higher Ed Blogs — from edtechmagazine.com by Meghan Bogardus Cortez
These administrative all-stars, IT gurus, teachers and community experts understand how the latest technology is changing the nature of education.
Excerpt:
With summer break almost here, we’ve got an idea for how you can use some of your spare time. Take a look at the Dean’s List, our compilation of the must-read blogs that seek to make sense of higher education in today’s digital world.
Follow these education trailblazers for not-to-be-missed analyses of the trends, challenges and opportunities that technology can provide.
If you’d like to check out the Must-Read IT blogs from previous years, view our lists from 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
From DSC:
I would like to thank Tara Buck, Meghan Bogardus Cortez, D. Frank Smith, Meg Conlan, and Jimmy Daly and the rest of the staff at EdTech Magazine for their support of this Learning Ecosystems blog through the years — I really appreciate it.
Thanks all for your encouragement through the years!
From DSC and Adobe — for faculty members and teachers out there:
Do your students an enormous favor by assigning them a digital communications project. Such a project could include images, infographics, illustrations, animations, videos, websites, blogs (with RSS feeds), podcasts, videocasts, mobile apps and more. Such outlets offer powerful means of communicating and demonstrating knowledge of a particular topic.
As Adobe mentions, when you teach your students how to create these types of media projects, you prepare them to be flexible and effective digital communicators. I would also add that these new forms and tools can be highly engaging, while at the same time, they can foster students’ creativity. Building new media literacy skills will pay off big time for your students. It will land them jobs. It will help them communicate to a global audience. Students can build upon these skills to powerfully communicate numerous kinds of messages in the future. They can be their own radio station. They can be their own TV station.
For more information, see this page out at Adobe.com.
From DSC:
This is where we may need more team-based approaches…because one person may not be able to create and grade/assess such assignments.
Microsoft Announces New Laptops and OS Perfect for 21st-Century Students — from edtechmagazine.com by Meghan Bogardus Cortez
Windows 10 S, Surface Laptop and other updates are coming to classrooms in the fall.
Excerpt:
Surface Laptop Introduces Seamless Technology
Perhaps the biggest cheers from the crowd came from the announcement of the new Surface Laptop, which will be available in June 2017.
…
The laptop checks in at 2.76 pounds with a 13.5-inch PixelSense display and 3:2 aspect ratio. Equipped with a fabric overlay on the backlit keyboard, the laptop is so seamless it doesn’t even have speaker grills. Instead, Panay says users can be immersed in sound while working on things like video. With a Surface Pen and the laptop’s LCD touch module, annotation is easy, even on videos.
Microsoft Debuts Surface Laptops, Windows 10 S for Education, Teams for Office 365 for Education — from campustechnology.com by David Nagel
Excerpt:
Microsoft has unveiled several new offerings for education, including the forthcoming Surface Laptop and a new version of Windows 10 designed for school environments — Windows 10 S.
Also see:
Also see:
From Mixed Reality to New Minecraft and OS, Microsoft Unleashes a Flurry of EDU Upgrades — from edsurge.com by Jenny AbamuMay
Excerpt:
“How can technology create more opportunity, not for a few but for all,” asked Nadella, noting how his own grandfather was not able to go to school because of the limited resources his family had. “Democratizing education must be something that is for everyone and not just for a select few, this is something that is deeply personal.”
His passionate and personal plea set the tone for the flurry of announcements and updates that followed. By the end of the whirlwind showcase, educators were weary but excited about future possibilities.
Also see:
Microsoft Unveils K-12 Operating System, Tools to Challenge Google — from edweek.org by Sean Cavanagh
Excerpt:
Microsoft unveiled a new, streamlined operating system, a slim laptop and a bevy of classroom tools, a group of products that in design and spirit seem aimed at competing with ascendant Chromebooks and other Google offerings in the school market.
At a product announcement on Tuesday crowded with company employees and tech journalists, Microsoft executives repeatedly touted a theme in describing the new operating system, Windows 10 S, and the accompanying products: simplicity.
The goal is “simplify to magnify,” Terry Myerson, Microsoft’s executive vice president of the Windows and devices group, told the assembled crowd. “Simplicity is power.”
“Technology should help, not hinder, teachers’ work in the classroom,” Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella said. It should make educators’ jobs easier, and “spark students’ creativity.”
New Google Earth has exciting features for teachers — from thejournal.com by Richard Chang
Excerpt:
Google has recently released a brand new version of Google Earth for both Chrome and Android. This new version has come with a slew of nifty features teachers can use for educational purposes with students in class. Following is a quick overview of the most fascinating features…
From DSC:
After seeing the postings below, it made me wonder:
- Will Starbucks, Apple Stores, etc. be “learning hubs” of the future?
i.e., places that aren’t really what we think of as a school, college, or university, but where people can go to learn something with others in the same physical space; such locations will likely tie into online or blended-based means of learning as well.
“Today at Apple” bringing new experiences to every Apple Store
Excerpt:
Cupertino, California — Apple today announced plans to launch dozens of new educational sessions next month in all 495 Apple stores ranging in topics from photo and video to music, coding, art and design and more. The hands-on sessions, collectively called “Today at Apple,” will be led by highly-trained team members, and in select cities world-class artists, photographers and musicians, teaching sessions from basics and how-to lessons to professional-level programs.
…
Apple will also offer special programs for families and educators. Teachers can come together for Teacher Tuesday to learn new ways to incorporate technology into their classrooms, or aspiring coders of all ages can learn how to code in Swift, Apple’s programming language for iOS and Mac apps. Families can join weekend Kids Hour sessions ranging from music making to coding with robots. Small business owners can engage with global and local entrepreneurs in the new Business Circuits program.
We’re creating a modern-day town square, where everyone is welcome in a space where the best of Apple comes together to connect with one another, discover a new passion, or take their skill to the next level.
Apple wants kids to hang out at Apple stores — from qz.com by Mike Murphy
Excerpt:
If you’ve just gotten out of school for the day and want to hang out with your friends before you head home, where would you go? In the US, there’s a near-infinite selection of chain restaurants, coffee shops, diners, bookstores, movie theaters, and comic book stores to choose from. But Angela Ahrendts, Apple’s head of retail, wants the answer to be an Apple store.
Apple is in the process of revamping the look and feel of its retail outlets across the world, and to highlight some of the recent changes (including rebranding the “Genius Bar” to the “Genius Grove” and adding foliage everywhere), Ahrendts gave an interview to CBS This Morning, this morning. Ahrendts told CBS that she will see her work as a success when Generation Z, the catchall term for the generation behind the equally amorphous Millennials, decides of their own volition to hang out at Apple stores. As CBS reported…
Lifeliqe Piloting Mixed Reality on Microsoft HoloLens for Grade 6-12 Classrooms — from thejournal.com by Richard Chang
Excerpt:
Using interactive 3D models and lesson plans from its app, Lifeliqe (pronounced “life like”) is now delivering educational content on two major immersive hardware platforms (Microsoft HoloLens and HTC Vive) as well as software platforms (Windows and iOS).
Students and teachers at Renton Prep Christian School in Washington state and Castro Valley Unified College in California participated in the pilot and were the first ever to try out Lifeliqe’s educational content on HoloLens during a science lesson (see video).
“The excitement we witnessed during the pilot shows us the great potential mixed reality has in sparking lightbulb moments.”
Lifeliqe is introducing pilots of mixed reality applications on Microsoft HoloLens — from lifeliqe.com
Excerpt:
Lifeliqe is thrilled to start piloting mixed reality educational scenarios for Microsoft HoloLens in grade 6-12 classrooms! The first two schools we are working with are Renton Prep in Seattle, WA and Castro Valley Unified College, CA. The students and teachers there were the first ever to try out Lifeliqe’s educational content on HoloLens during a Science lesson.
The 82 Hottest EdTech Tools of 2017 According to Education Experts — from tutora.co.uk by Giorgio Cassella
Excerpt:
If you work in education, you’ll know there’s a HUGE array of applications, services, products and tools created to serve a multitude of functions in education.
Tools for teaching and learning, parent-teacher communication apps, lesson planning software, home-tutoring websites, revision blogs, SEN education information, professional development qualifications and more.
There are so many companies creating new products for education, though, that it can be difficult to keep up – especially with the massive volumes of planning and marking teachers have to do, never mind finding the time to actually teach!
So how do you know which ones are the best?
Well, as a team of people passionate about education and learning, we decided to do a bit of research to help you out.
We’ve asked some of the best and brightest in education for their opinions on the hottest EdTech of 2017. These guys are the real deal – experts in education, teaching and new tech from all over the world from England to India, to New York and San Francisco.
They’ve given us a list of 82 amazing, tried and tested tools…
From DSC:
The ones that I mentioned that Giorgio included in his excellent article were:
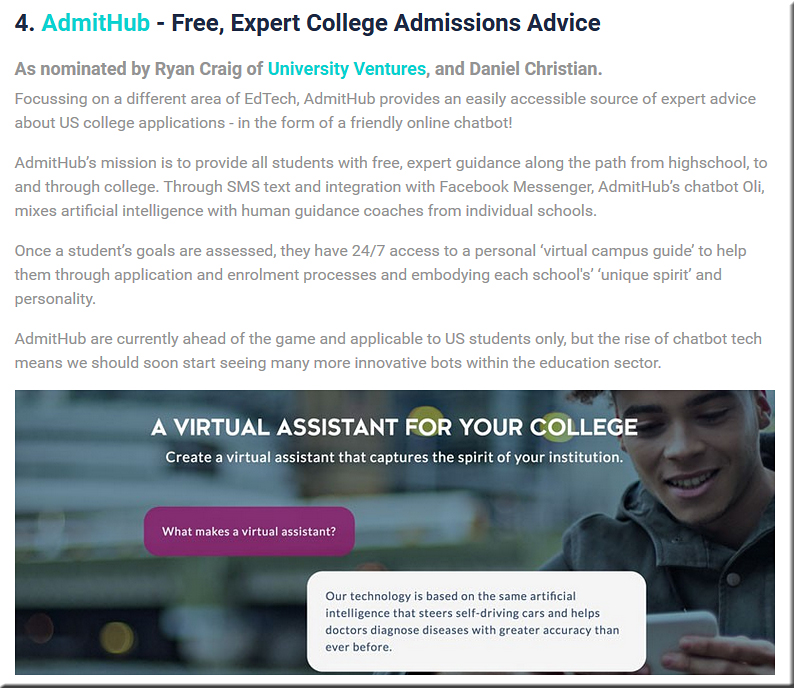
- AdmitHub – Free, Expert College Admissions Advice
- Labster – Empowering the Next Generation of Scientists to Change the World
- Unimersiv – Virtual Reality Educational Experiences
- Lifeliqe – Interactive 3D Models to Augment Classroom Learning
Perfect marriage between universities and K12 public schools — from huffingtonpost.com by Dr. Rod Berger
Excerpt:
I sat down with Dr. Jeanice Kerr Swift at this year’s AASA conference in New Orleans to learn about the unique advantage of running a public school district that resides alongside one of our nation’s most prominent universities. The University of Michigan provides the district of Ann Arbor with rich partnerships that lift the learning experiences of the children in the community. Kerr Swift is delighted to have the enthusiasm of not only the University but the business community in reaching out to the students of Ann Arbor.
The implementation of real world projects matches University of Michigan scientists with teachers and students to enrich school learning environments. One example is the Woven Wind program that provides real life wind turbine applications. Students learn, and teachers have their classes bolstered by the input of advanced experimentation. Project Lead the Way is another example that is providing modules for classroom learning.
According to Jeanice Kerr Swift, technology should support and strengthen learning, not stand in the place of person-to-person engagement. Devices are there to serve and enhance, not replace teacher-student collaboration and critical thinking. Kerr Swift believes there is a balance of the “Cs” to consider: collaboration, connection, and community. If all the “Cs” are listening and working together, then a school district can thrive.
Jeanice Kerr Swift certainly makes the balance look easy and enviable in Ann Arbor Michigan.
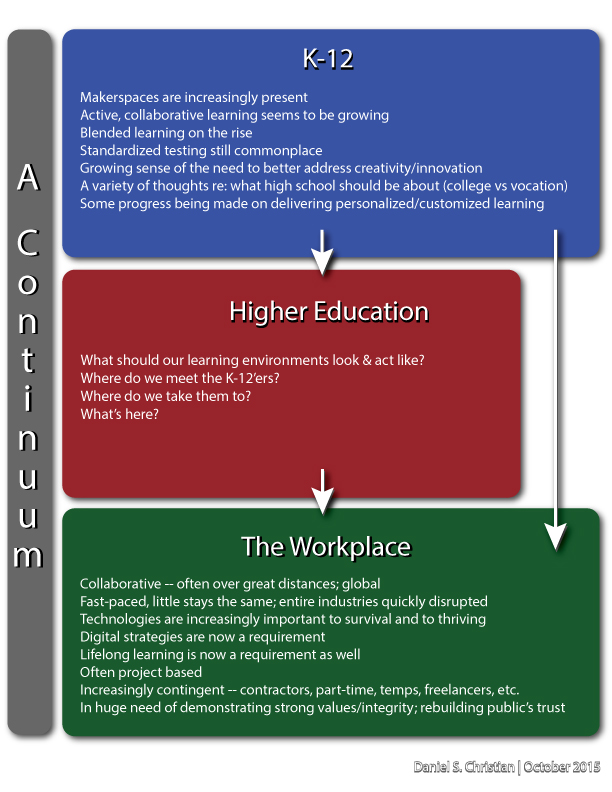
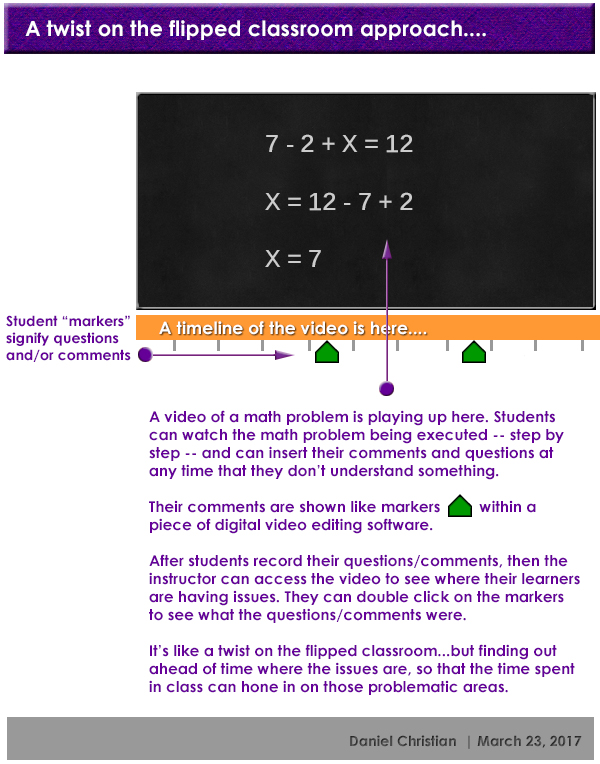
From DSC:
For you ed tech vendors, programmers, and/or entrepreneurs out there, would you please create the software to do this? By the way, for purposes of equal access, this could be done in class — it doesn’t have to be done outside of normal school hours.
The woman who thinks time has rendered Western education obsolete — from unlimited.world with thanks to Maree Conway for her tweet on this
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
For years, Finland has loitered in the upper echelons of global literacy and numeracy tables, leading politicians from other Western nations to see its education system as a model of inspiration. Why, then, is the Finnish government submitting it to a radical overhaul?
Dr. Marjo Kyllonen is the Education Manager for Helsinki. Having devised the blueprint for the future of Finland’s school system, she is playing a pivotal role in driving these changes through. She is doing so because she sees the structure and aims of current education systems in the West as increasingly irrelevant and obsolete, relics of an Industrial Age that we started to leave behind a long time ago. She argues that we need to rethink our entire relationship to education to equip future generations with the tools they need to face the challenges to come –challenges such as climate collapse, automated workforces, urbanisation and social division. The key to her blueprint is an emphasis on collaborative, holistic, “phenomenon” teaching – a routine that is less beholden to traditional subject-based learning and instead teaches pupils to work together to deal with problems they will face in their everyday lives, including those they encounter online and in the digital world.
Other:
- If schools were invented today, what would they be like?
- Instead of studying different subjects in isolation, learning should be anchored to real-life phenomena, things that kids see around them, so they see the connection between what they’re learning and real life. The traditional way of teaching isolated subjects with a teacher as the sole oracle of knowledge is widening the gap between the lives kids are living today and what they do at school.
- So we have to think, what skills will people need in 60 years? Life is not split into subjects, so why is learning? What is more crucial for future society is cross-disciplinary thinking; all the experts say that the big problems of tomorrow won’t be solved if you only have one approach.
From DSC:
Whether one agrees with Marjo or not, her assertions are very thought provoking. I really enjoyed reading this piece.
Report: Overtime, Low Wages Causing Educator Stress — from thejournal.com by Sri Ravipati
Excerpt:
As the role of the educator continues to evolve, it is necessary to take a look at some of the challenges they face day-to-day: What contributes to educators’ stress? Have the recent changes in the federal government added to their stress at all? How can technology help? To find out the answers to these questions, online learning company Course Hero polled educators about their economic satisfaction, work-related stress, classroom technology and even how the new Trump administration impacts them.
The company recently released its inaugural “State of the Educator Survey” report, which includes findings from a 68-question survey conducted in January. Course Hero polled 412 higher ed professors and 117 high school Advanced Placement (AP) teachers who work full-time and part-time in a variety of disciplines. As it turns out, all of the aforementioned topics have contributed to increased stress felt by nearly half of the survey participants. In fact, five times as many educators reported increased rather than decreased stress, with 42 percent responding that their job became more stressful in the last year (compared to 8 percent who reported a decrease). Exactly half of respondents said their stress level stayed the same.
From DSC:
Given the exponential pace of technological change that many societies throughout the globe are now on, we need some tools to help us pulse-check what’s going on in the relevant landscapes that we are trying to scan.
Below, I would like to suggest 2 methods/tools to do this. I have used both methods for years, and I have found them to be immensely helpful in pulse-checking the landscapes. Perhaps these tools will be helpful to you — or to your students or employees — as well. I vote for these 2 tools to be a part of all of our learning ecosystems. (And besides, they also encourage micro-learning while helping us spot emerging trends.)
What educators can learn about effective teaching from a Harvard prof — from ecampusnews.com by Alan November
Excerpt:
Harvard professor David Malan has managed to pull off a neat trick: His Computer Science 50 course is the most popular course at both Harvard and Yale. By examining his success, we can learn some important lessons about effective teaching.
CS50 assumes no prior knowledge or skill in computer programming, yet it’s extremely demanding. Despite its rigor, CS50 regularly attracts thousands of students each year. While some aspire to become software engineers, others enroll just to experience the course.
Why is Professor Malan’s course so popular, even with students who don’t plan a career in computer science—and even though it requires a lot of work? Here are three keys to Malan’s effective teaching that I think all schools everywhere should apply, from K-12 schools to colleges and universities.
- Strengthen the social side of learning.
- Teach students to self-assess.
- Provide a public audience to inspire students to invent.