180 Degree Turn: NYC District Goes From Banning ChatGPT to Exploring AI’s Potential — from edweek.org by Alyson Klein (behind paywall)
New York City Public Schools will launch an Artificial Intelligence Policy Lab to guide the nation’s largest school district’s approach to this rapidly evolving technology.
The Leader’s Blindspot: How to Prepare for the Real Future — from preview.mailerlite.io by the AIEducator
The Commonly Held Belief: AI Will Automate Only Boring, Repetitive Tasks First
The Days of Task-Based Views on AI Are Numbered
The winds of change are sweeping across the educational landscape (emphasis DSC):
- Multifaceted AI: AI technologies are not one-trick ponies; they are evolving into complex systems that can handle a variety of tasks.
- Rising Expectations: As technology becomes integral to our lives, the expectations for personalised, efficient education are soaring.
- Skill Transformation: Future job markets will demand a different skill set, one that is symbiotic with AI capabilities.
Teaching: How to help students better understand generative AI — from chronicle.com by Beth McMurtrie
Beth describes ways professors have used ChatGPT to bolster critical thinking in writing-intensive courses
Kevin McCullen, an associate professor of computer science at the State University of New York at Plattsburgh, teaches a freshman seminar about AI and robotics. As part of the course, students read Machines of Loving Grace: The Quest for Common Ground Between Humans and Robots, by John Markoff. McCullen had the students work in groups to outline and summarize the first three chapters. Then he showed them what ChatGPT had produced in an outline.
“Their version and ChatGPT’s version seemed to be from two different books,” McCullen wrote. “ChatGPT’s version was essentially a ‘laundry list’ of events. Their version was narratives of what they found interesting. The students had focused on what the story was telling them, while ChatGPT focused on who did what in what year.” The chatbot also introduced false information, such as wrong chapter names.
The students, he wrote, found the writing “soulless.”
7 Questions with Dr. Cristi Ford, VP of Academic Affairs at D2L — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
In the Wild West of generative AI, educators and institutions are working out how best to use the technology for learning. How can institutions define AI guidelines that allow for experimentation while providing students with consistent guidance on appropriate use of AI tools?
To find out, we spoke with Dr. Cristi Ford, vice president of academic affairs at D2L. With more than two decades of educational experience in nonprofit, higher education, and K-12 institutions, Ford works with D2L’s institutional partners to elevate best practices in teaching, learning, and student support. Here, she shares her advice on setting and communicating AI policies that are consistent and future-ready.
AI Platform Built by Teachers, for Teachers, Class Companion Raises $4 Million to Tap Into the Power of Practice — from prweb.com
“If we want to use AI to improve education, we need more teachers at the table,” said Avery Pan, Class Companion co-founder and CEO. “Class Companion is designed by teachers, for teachers, to harness the most sophisticated AI and improve their classroom experience. Developing technologies specifically for teachers is imperative to supporting our next generation of students and education system.”
7 Questions on Generative AI in Learning Design — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
Open LMS Adoption and Education Specialist Michael Vaughn on the challenges and possibilities of using artificial intelligence to move teaching and learning forward.
The potential for artificial intelligence tools to speed up course design could be an attractive prospect for overworked faculty and spread-thin instructional designers. Generative AI can shine, for example, in tasks such as reworking assessment question sets, writing course outlines and learning objectives, and generating subtitles for audio and video clips. The key, says Michael Vaughn, adoption and education specialist at learning platform Open LMS, is treating AI like an intern who can be guided and molded along the way, and whose work is then vetted by a human expert.
We spoke with Vaughn about how best to utilize generative AI in learning design, ethical issues to consider, and how to formulate an institution-wide policy that can guide AI use today and in the future.
10 Ways Technology Leaders Can Step Up and Into the Generative AI Discussion in Higher Ed — from er.educause.edu by Lance Eaton and Stan Waddell
- Offer Short Primers on Generative AI
- Explain How to Get Started
- Suggest Best Practices for Engaging with Generative AI
- Give Recommendations for Different Groups
- Recommend Tools
- Explain the Closed vs. Open-Source Divide
- Avoid Pitfalls
- Conduct Workshops and Events
- Spot the Fake
- Provide Proper Guidance on the Limitations of AI Detectors











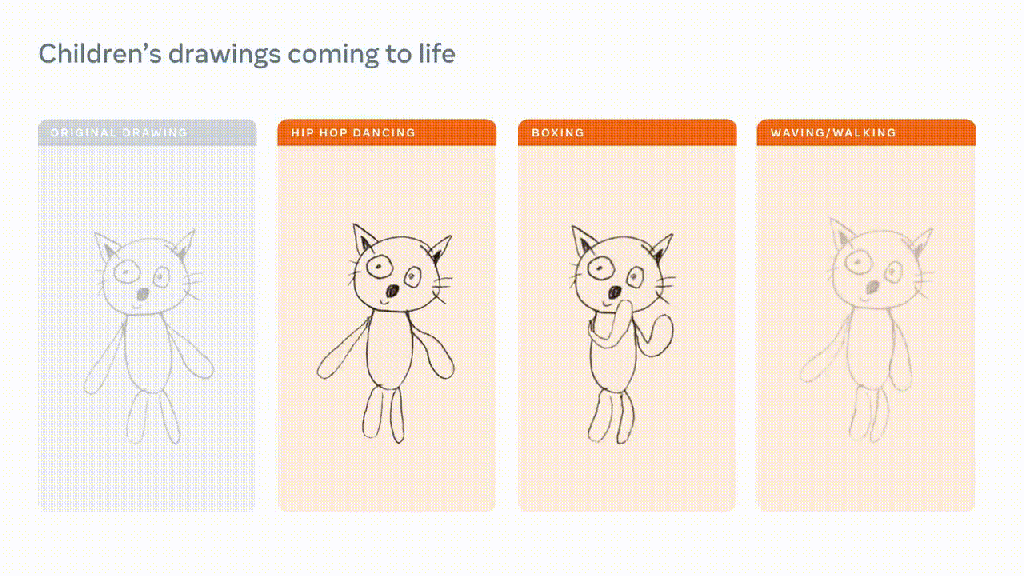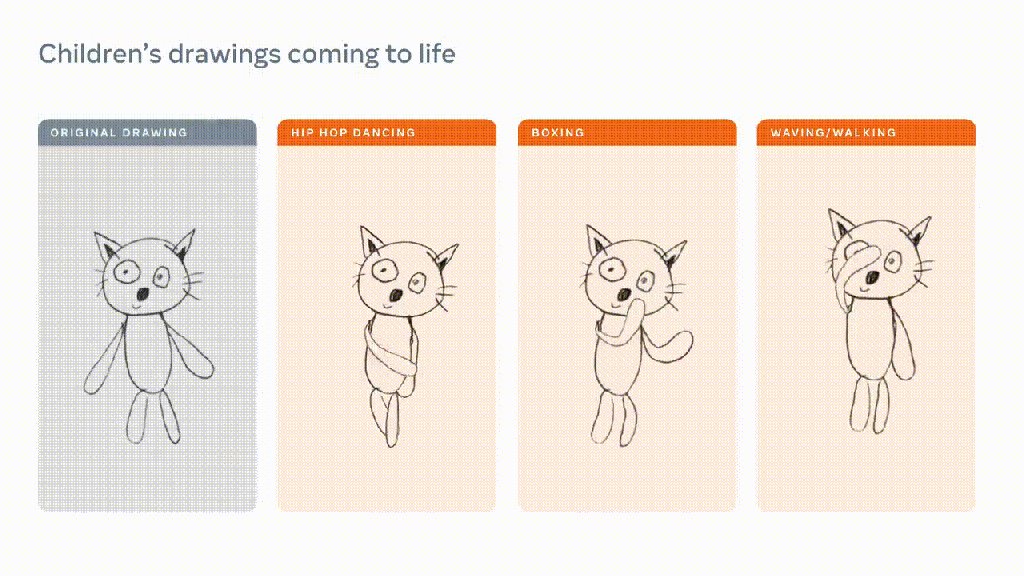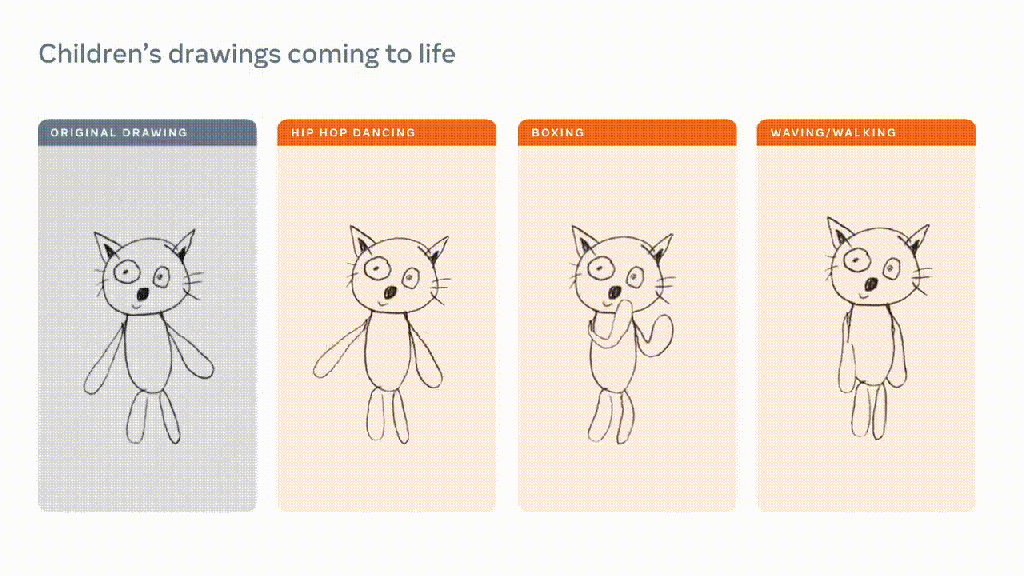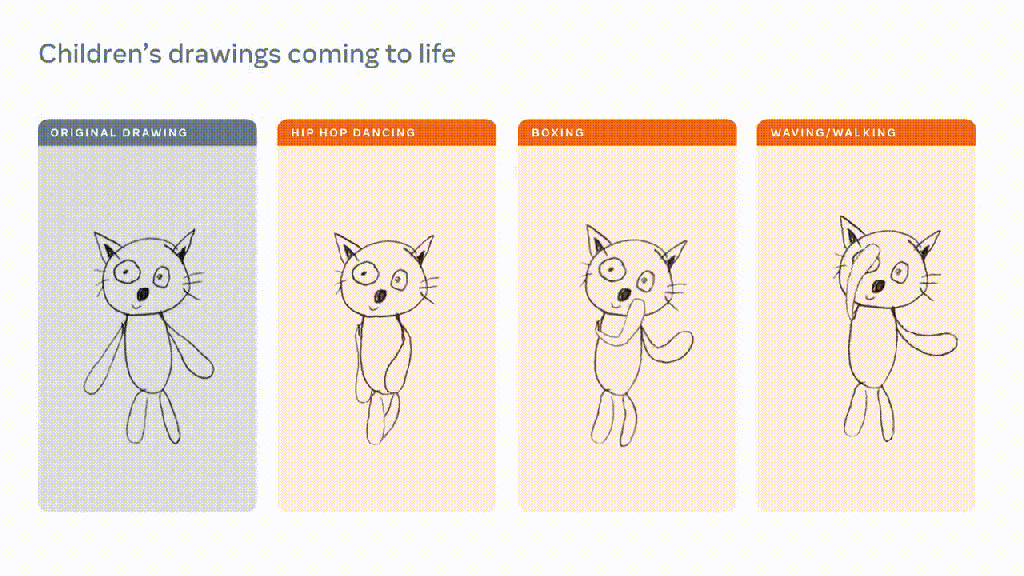





:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24976021/Canva_Magic_Studio.png)
