Why Aren’t Professors Taught to Teach? — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
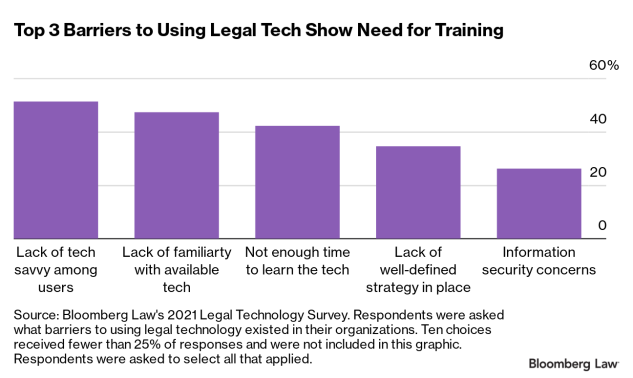
Professors are experts in their subject matters but many have limited training in actually teaching their students.
Excerpt:
“A lot of faculty are just modeling their instruction after the instruction they’ve received as an undergraduate or graduate student,” says Tanya Joosten, senior scientist and director of digital learning at University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee and the lead of the National Research Center for Distance Education and Technological Advancements.
As a perpetually short-on-time adjunct professor, I understand those who worry about mandatory training and required course reviews, but Pelletier stresses that she’s advocating for a more organic shift and that a top-down approach isn’t best. “That’s not as collaborative and generative as really just embracing that we have these two different kinds of experts, one type of expert is an expert in their subject, and the other expert is an expert in teaching and learning,” she says. More attention is needed to meld these two kinds of expertise.
From DSC:
It’s not just that colleges and universities are big business — if you have any remaining doubts about that perspective, take a moment to look at this new, interactive database to see what I mean. But it’s also that this type of business often rewards research, not teaching. And yet the students over the last several decades have continued to pay ever-increasing prices for skilled researchers, instead of increasingly skilled teachers.
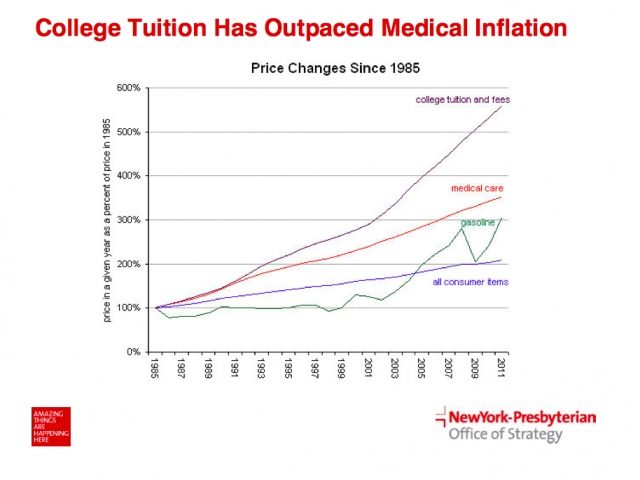
Would people put up with this with other types of purchases? I don’t think so. I wouldn’t want to…would you? Would we like to pay for something that we aren’t getting — like paying for all the extra options on a new car, but not getting them?
What goes around, comes around.
But by allowing this to have occurred, a backlash against the value of higher education has been building for years now. In many learners’ minds, they are questioning whether it’s worth taking on (potentially) decades’ worth of debt. At a minimum, the higher the price of obtaining degrees and/or other credentials becomes, the less Return on Investment (ROI) is realized by the learners (i.e., the purchasers of these goods and services). So while getting a degree is often still worth it, the ROI is going down. And this doesn’t address how relevant/up-to-date the educations are that these learners are receiving, which the employers out there will take issue with.
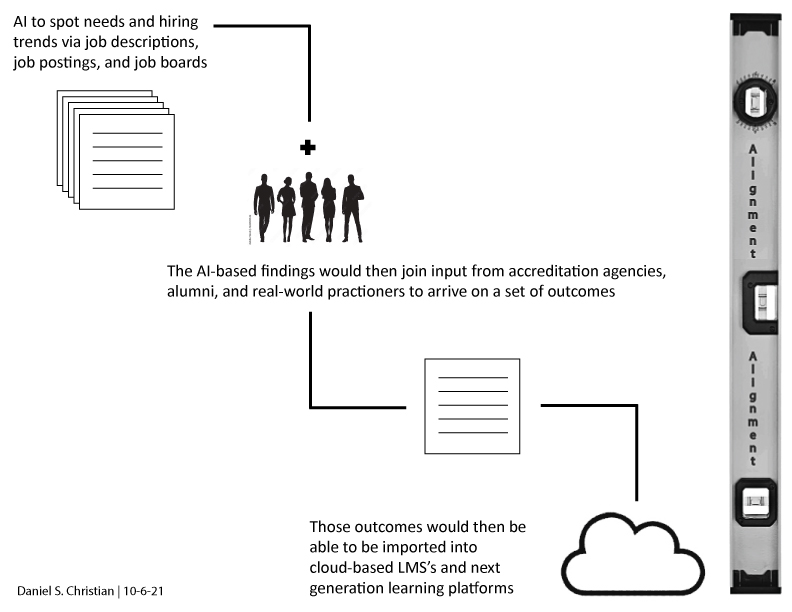
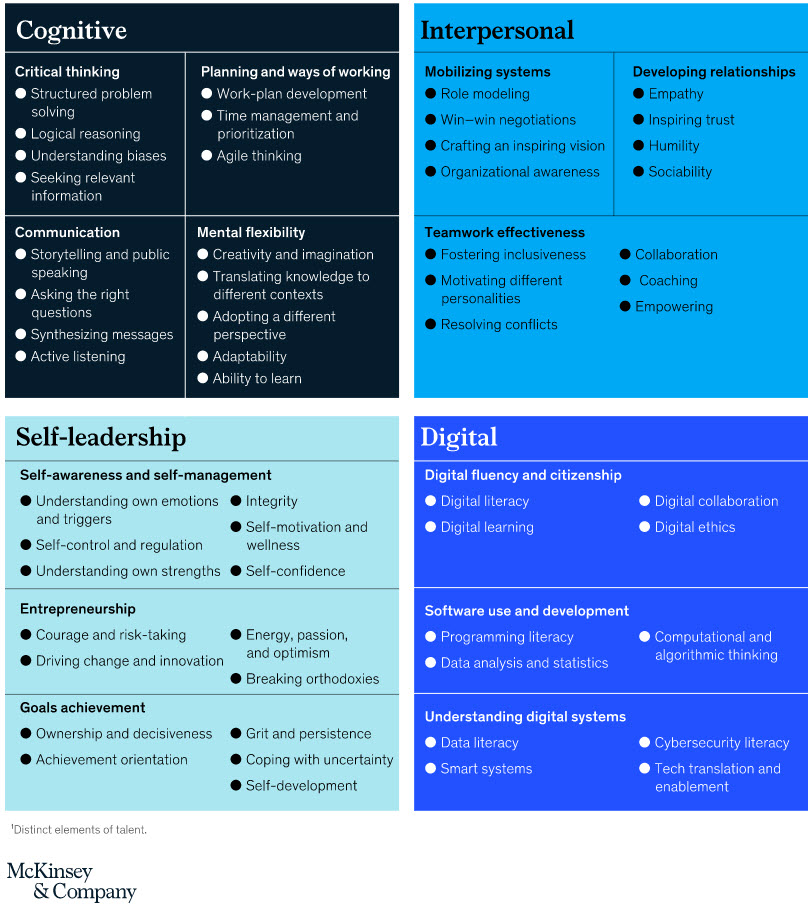
From an Instructional Designer’s perspective, it isn’t just time that’s the issue here. There continues to exist a tiered hierarchy within higher education. Faculty see themselves as more knowledgeable because they are teaching and because they are the Subject Matter Experts (SMEs). But they are not expert teachers. Many full-time faculty members don’t listen to people who are knowledgeable in the learning science world, and they often don’t value that expertise. (This can be true of administrators as well.) But when a fellow faculty member (i.e., their “true peer” from their perspective) suggests the same idea that Instructional Designers have been recommending for years, they suddenly open their eyes and ears to see and hear this seemingly new, wonderful approach.
Some possible scenarios
Thus, a wave has been building against traditional institutions of higher education — readers of this blog will have picked up on this years ago. Once alternatives significantly hit the radar — ones that get the learners solid, good-paying jobs — there could be a mass exodus out of what we think of as traditional higher education. At least that’s one potential scenario.
For example, if a next-generation learning platform comes along that offers teams and individuals the ability to deliver lifelong learning at 50% or more off the price of an average degree, then be on the lookout for massive change. If professors and/or teams of specialists — those who are skilled in instructional design and teaching — can go directly to their learners — it could be an interesting world indeed. (Outschool is like this, by the way.) In that scenario, below are two potential methods of providing what accreditation agencies used to provide:
- Obtaining the skills and competencies being requested from the workplace to “pass the tests” (whatever those assessments turn out to be)
- Voting a course up or down (i.e., providing crowd-sourced rating systems)
Other possible scenarios
Another scenario is that traditional institutions of higher education really kick their innovation efforts into high gear. They reward teaching. They develop less expensive methods of obtaining degrees. They truly begin delivering more cost-effective means of obtaining lifelong learning and development “channels” for educating people.
And there are other possible scenarios, some of which I could think of and many I would likely miss. But to even ask the solid and highly-relevant question as plainly stated in the article above — Why Aren’t Professors Taught to Teach? — that is something that must be dealt with. Those organizations that use a team-based approach are likely to be able to better answer and address that question.