HundrED Global Collection 2023 — from hundred.org
Meet the 100 most impactful innovations that are changing the face of education in a post-COVID world.

Excerpt:
The year 2022 has been a year to look to the future, as the global education conversation moves again toward themes of education transformation and the futures of education. The 100 innovations selected for this year’s global collection are impacting the lives of over 95 million students worldwide. The collection highlights the important role of teachers in education innovation; the continued need for students to develop 21st century skills, including social and emotional learning; an increasing focus on student wellbeing and mental health; and equity in education.
For more information, download the full Global Collection 2023 report.
You can also browse the innovation pages of the selected innovators here.
.
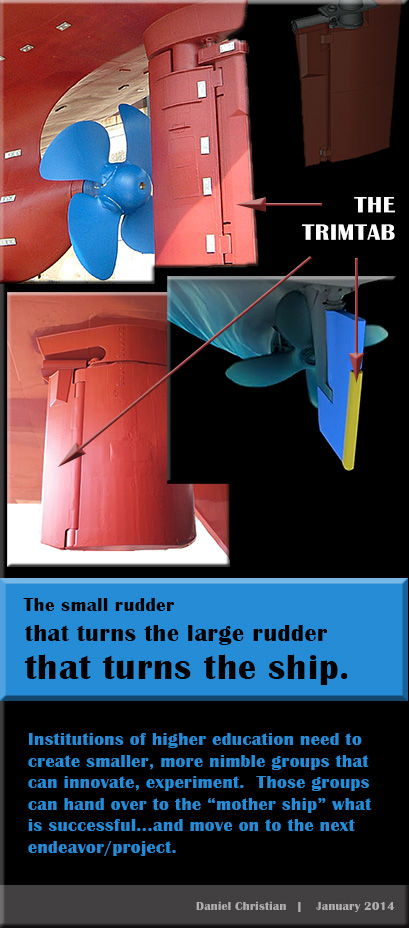
From DSC:
Here’s an excerpt of the email I received today from EducationHQ out of Australia — though I think it applies here in the United States as well:
 .
.
Amplify and value teachers’ voice in education policymaking: researchers — from educationhq.com
Amplify and value teachers’ voice in education policymaking: researchers

Excerpt:
Monash University’s Teachers’ Perceptions of their Work Survey has revealed teachers’ waning satisfaction in their role and highlighted their…
Also from educationhq.com
Teachers changed my life: Trauma-informed education shows kids they matter — from educationhq.com by Beck Thompson
.
Nonprofit Bringing Businesses to Life in the Classroom — to the Tune of $400,000 — from the74million.org by Tim Newcomb
Making candles out of crayons, building birdhouses, fashioning furniture: Real World Scholars has helped 50,000 students become entrepreneurs
Not much entices a second grader to skip out on recess to get back to schoolwork. But excitement around a classroom-run business can do just that, especially when it means creating candles out of crayons and selling them in the local community.
Students design their ideal urban home in My ArchiSchool exhibition — from dezeen.com
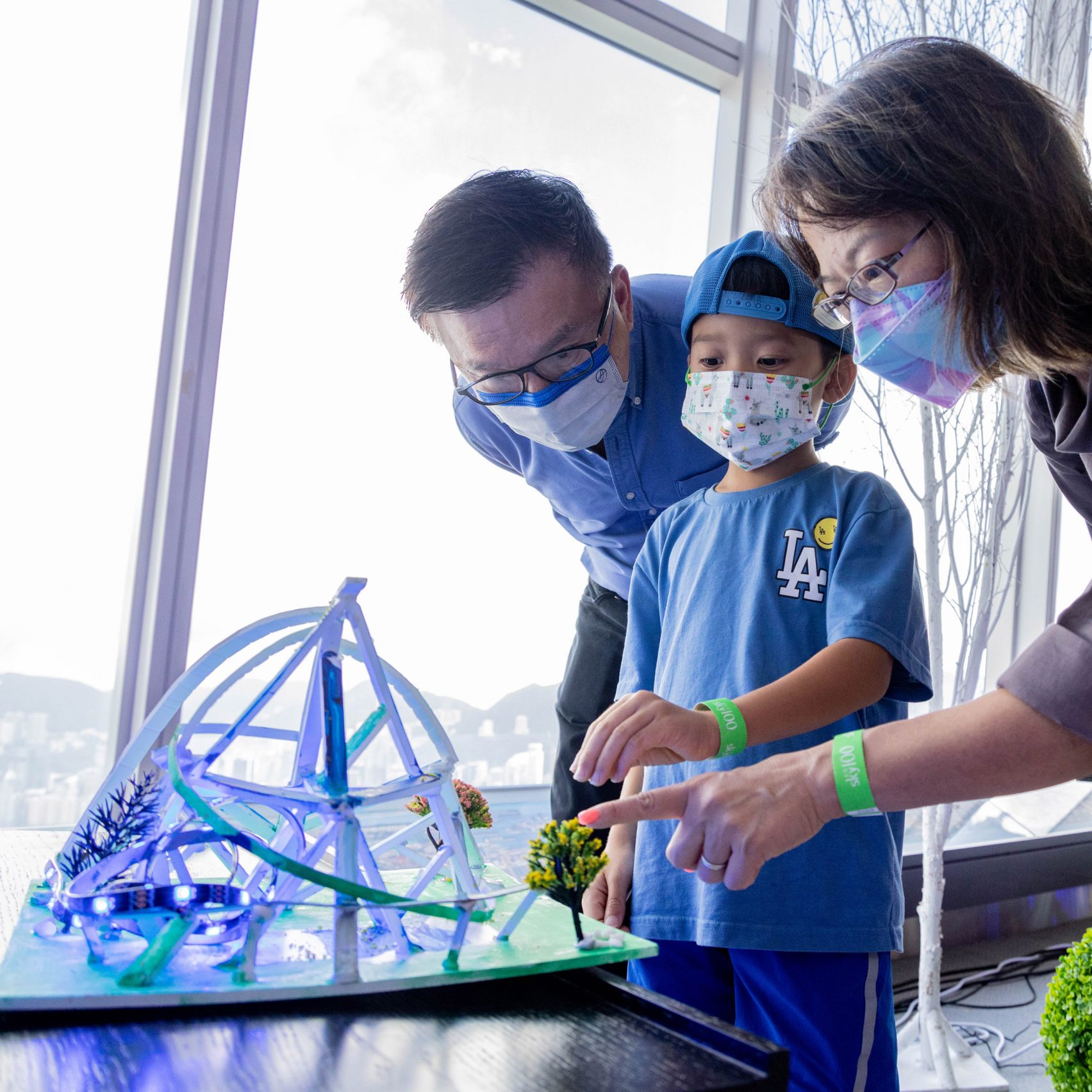

Excerpt:
Promotion: fifty-two students presented digital designs and architectural models of their ideal home as part of Hong Kong-based education institute My ArchiSchool’s latest exhibition. As part of the exhibition, My ArchiSchool students were asked to design their ideal home within an urban environment. The exhibition, which took place on 2 October 2022 at the Sky100 on the 100th floor of the International Commerce Centre in Hong Kong, showcased photomontages of digital designs presented alongside physical models.
5 Resources that help students become digital citizens — from rdene915.com by Rachelle Dene Poth
Excerpt:
We need to create opportunities for students to become more digitally aware and literate, and to be responsible when using technology. There are many ways to do this, depending on our content area and grade level. We can model best practices for our students, bring in a specific digital citizenship curriculum to guide them through their learning, or use digital tools and resources available to have students explore and create.
Helping students learn to safely navigate what has become a highly digital world is something that we are all responsible for. Students need to be aware of the impact of their posts online, how to create and manage social accounts and protect their information, and how to properly access and use resources they obtain through technology.
3 Reasons School and District Leaders Should Get on Social Media — from edweek.org by Marina Whiteleather
Excerpt:
School and district leaders can—and should—be using social media in their work.
That’s the message shared by Stephanie McConnell, a superintendent in the Hawkins Independent School District in Texas, and Salome Thomas-El, a K-8 principal in Delaware, during an Education Week K-12 Essentials forum on Oct. 13.
At the event, McConnell and Thomas-El provided insights and advice for school leaders who are hesitant to post on certain social platforms or unsure how to use them.