The above was from Jane’s posting 10 Trends for Digital Learning in 2018 — from modernworkplacelearning.com by Jane Hart
Excerpt:
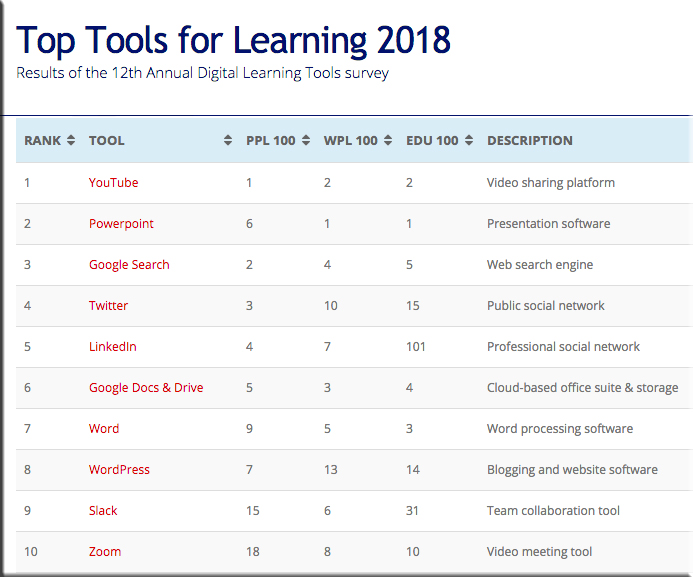
[On 9/24/18], I released the Top Tools for Learning 2018 , which I compiled from the results of the 12th Annual Digital Learning Tools Survey.
I have also categorised the tools into 30 different areas, and produced 3 sub-lists that provide some context to how the tools are being used:
- Top 100 Tools for Personal & Professional Learning 2018 (PPL100): the digital tools used by individuals for their own self-improvement, learning and development – both inside and outside the workplace.
- Top 100 Tools for Workplace Learning (WPL100): the digital tools used to design, deliver, enable and/or support learning in the workplace.
- Top 100 Tools for Education (EDU100): the digital tools used by educators and students in schools, colleges, universities, adult education etc.
3 – Web courses are increasing in popularity.
Although Coursera is still the most popular web course platform, there are, in fact, now 12 web course platforms on the list. New additions this year include Udacity and Highbrow (the latter provides daily micro-lessons). It is clear that people like these platforms because they can chose what they want to study as well as how they want to study, ie. they can dip in and out if they want to and no-one is going to tell them off – which is unlike most corporate online courses which have a prescribed path through them and their use is heavily monitored.
5 – Learning at work is becoming personal and continuous.
The most significant feature of the list this year is the huge leap up the list that Degreed has made – up 86 places to 47th place – the biggest increase by any tool this year. Degreed is a lifelong learning platform and provides the opportunity for individuals to own their expertise and development through a continuous learning approach. And, interestingly, Degreed appears both on the PPL100 (at 30) and WPL100 (at 52). This suggests that some organisations are beginning to see the importance of personal, continuous learning at work. Indeed, another platform that underpins this, has also moved up the list significantly this year, too. Anders Pink is a smart curation platform available for both individuals and teams which delivers daily curated resources on specified topics. Non-traditional learning platforms are therefore coming to the forefront, as the next point further shows.
From DSC:
Perhaps some foreshadowing of the presence of a powerful, online-based, next generation learning platform…?