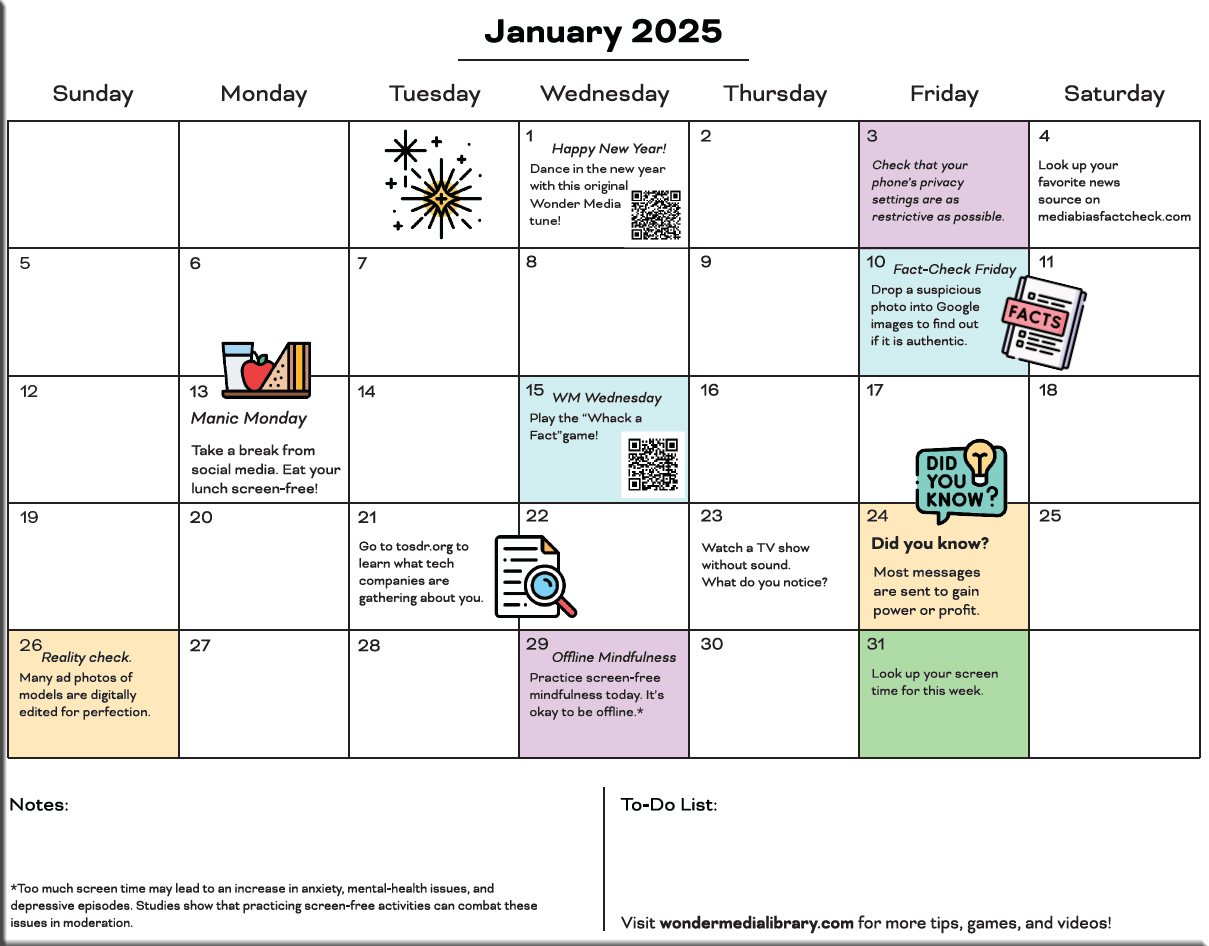
Here are my favorite back-to-school activities to strengthen learning — from retrievalpractice.org by Pooja K. Agarwal, Ph.D.
Welcome back to school! For most of us (myself included), the whirlwind of lesson prep, meetings, professional development—and of course, teaching—is here. Keep reading for my favorite back-to-school activities to engage students with retrieval practice during the first week of class.
…
It may (or may not) surprise you to know that my first day of class is full of retrieval practice. Even if you haven’t introduced content yet, use retrieval practice the first day or week of class. Here’s how, with quick activities you can adapt for K–12 students, higher ed courses, and all content areas:
How to Teach a Good First Day of Class — by James Lang; via Dr. Pooja Agarwal’s posting above
What you can expect to find here:
- I’ll start, as we academics so love to do, with a little bit of theory — specifically, four core principles that can help shape your planning for the first day of your course.
- Next, I’ll cover the logistics of a successful first day, including managing the space and technology as well as getting to know your students.
- To show you how to put the principles and the logistics into practice, I will provide examples of what a good set of first-day activities might look like in four disciplines.
- I’ll finish with some suggestions for how to support the good work you have done on the first day with some follow-up activities.
7 Pieces of Advice for New Teachers — from edutopia.org by Brienne May
Focus on relationships with students and colleagues to make a good start to the year—and remember to ask for what you need.
Too often, teacher preparation programs are rich in theory but light on practical guidance. After working hard through my undergraduate classes, completing student teaching, and spending countless hours laminating and cutting, I still found myself on the first day of school, standing in front of a room full of expectant faces with eager eyes, and realized I had no idea what to do next. I didn’t know what to say to students in that moment, let alone how to survive the following 180 days. Twelve years later, I have collected a trove of advice I wish I could have shared with that fresh-faced teacher.
The Transient Information Effect: Why Great Explanations Don’t Always Stick — from scienceoflearning.substack.com by Nidhi Sachdeva and Jim Hewitt
In this post, Dr. John Sweller describes how the Transient Information Effect can overload student working memory and what teachers can do about it.
Highlights:
- The Transient Information Effect happens when important information disappears before learners can process and remember it.
- Dr. John Sweller, who first studied the Transient Information Effect, answers our questions about this overlooked learning challenge.
- Turning transient information into something students can revisit (like writing key steps on the board) can help explanations stick.
41 Elementary Classroom Jobs to Build Shared Responsibility and Community — from edutopia.org by Donna Paul
Classroom jobs help students feel seen, trusted, and excited to contribute to their classroom community.
Each fall, one of the first routines I introduce is our classroom job board. It’s more than a list of tasks—it helps students feel that they belong and have real roles in our shared space. Over the years, I’ve expanded beyond classic jobs like Line Leader and Pencil Sharpener to include creative roles with quirky titles that engage and resonate with students.
Here are the jobs that have helped my students feel seen, trusted, and excited to contribute.
Guiding Students to Overcome Learned Helplessness — from edutopia.org by Michelle Singh
New teachers can create an environment where students feel supported and understand that mistakes are part of the learning process.
Creating a Kid-Led Hall of Fame for Books — from edutopia.org by Eric Hall
Allowing elementary students to nominate and vote for their favorite books of the year can create a culture of celebration in the classroom.
When I started teaching, I remembered that conversation with my elementary school librarian. I thought, “Why should adults have all the fun?” I wanted my students to experience the excitement of recognizing books they thought were the best. And just like that, the Hallbery Awards were born and continued twice a year for over 15 years. (Why Hallbery? Because my last name is Hall.)
Understanding Diagnostic, Formative, and Summative Assessments — from edmentum.com
Today, we’re taking a look at the three primary forms of assessments—diagnostic, formative, and summative—with the goal of not only differentiating between them but also better understanding the purpose and potential power of each.
At their core, each of the three primary assessment types serves a distinct purpose. Diagnostic assessments are used before instruction to help identify where students are in their comprehension of academic content. Formative assessments are used while content is being taught to understand what students are picking up, to guide their learning, and to help teachers determine what to focus on moving forward. Summative assessments are used after instruction to evaluate the outcomes of student learning: what, or how much, they ultimately learned.
How one state revamped high school to reflect reality: Not everyone goes to college — from hechingerreport.org by Kavitha Cardoza
Indiana’s initial plan for revised graduation requirements was criticized for prioritizing workforce skills over academic preparedness. The state has tried to find a balance between the two
This story is part of Hechinger’s ongoing coverage about rethinking high school. Read about high school apprenticeships in Indiana, a new diploma in Alabama that trades chemistry for carpentry, and “career education for all” in Kentucky.
The “New Indiana Diploma” — which was signed into law in April and goes into effect for all incoming first-year students this academic year — gives students the option to earn different “seals” in addition to a basic diploma, depending on whether they plan to attend college, go straight to work or serve in the military. Jenner describes it as an effort to tailor the diploma to students’ interests, expose students to careers and recognize different forms of student achievement.
How Teachers in This District Pushed to Have Students Spend Less Time Testing — from edweek.org by Elizabeth Heubeck
Students in one Arizona district will take fewer standardized tests this school year, the result of an educator-led push to devote less time to testing.
The Tucson Education Association, backed by the school board and several parents, reached an agreement with the Tucson Unified school system in May to reduce the number of district-mandated standardized assessments students take annually starting in the 2025-26 academic year.
Just 25 percent of educators agreed that state-mandated tests provide useful information for the teachers in their school, according to a 2023 EdWeek Research Center survey of teachers, principals, and district leaders.
30 Ways to Bring Calm to a Noisy High School Classroom — from edutopia.org by Anne Noyes Saini
From ‘finding the lull’ to the magic of a dramatic whisper, these teacher-tested strategies quickly get high school students focused and back on track.
Approaching Experiential Learning as a Continuum — from edutopia.org by Bill Manchester
Teachers can consider 12 characteristics of experiential learning to make lessons more or less active for students.