DC: I agree that we neeed those smart glasses to free up our hands. For example, if #AR was a tool used by technical communicators to show us how to put a piece of furniture together, we need our hands free to do so.https://t.co/yKU0q7yUkv
— Daniel Christian (@dchristian5) February 16, 2019
From DSC:
In a next generation learning system, it would be sharp/beneficial to have a Netflix-like interface to check out potential functionalities that you could turn on and off (at will) — as one component of your learning ecosystem that could feature a setup located in your living room or office.
For example, put a Netflix-like interface to the apps out at eduappcenter.com (i.e., using a rolling interface at first, then going to a static page/listing of apps…again…similar to Netflix).
Google is bringing translation to its Home speakers — from businessinsider.com by Peter Newman
Excerpt:
Google has added real-time translation capabilities to its Google Home smart speakers, the Home Hub screened speaker, as well as other screened devices from third parties, according to Android Police.
Also see:
- Google Assistant is now your multilingual interpreter — from androidpolice.com by Hagop Kavafian
Why Facebook’s banned “Research” app was so invasive — from wired.com by Louise Matsakislo
Excerpts:
Facebook reportedly paid users between the ages of 13 and 35 $20 a month to download the app through beta-testing companies like Applause, BetaBound, and uTest.
…
Apple typically doesn’t allow app developers to go around the App Store, but its enterprise program is one exception. It’s what allows companies to create custom apps not meant to be downloaded publicly, like an iPad app for signing guests into a corporate office. But Facebook used this program for a consumer research app, which Apple says violates its rules. “Facebook has been using their membership to distribute a data-collecting app to consumers, which is a clear breach of their agreement with Apple,” a spokesperson said in a statement. “Any developer using their enterprise certificates to distribute apps to consumers will have their certificates revoked, which is what we did in this case to protect our users and their data.” Facebook didn’t respond to a request for comment.
Facebook needed to bypass Apple’s usual policies because its Research app is particularly invasive. First, it requires users to install what is known as a “root certificate.” This lets Facebook look at much of your browsing history and other network data, even if it’s encrypted. The certificate is like a shape-shifting passport—with it, Facebook can pretend to be almost anyone it wants.
To use a nondigital analogy, Facebook not only intercepted every letter participants sent and received, it also had the ability to open and read them. All for $20 a month!
Facebook’s latest privacy scandal is a good reminder to be wary of mobile apps that aren’t available for download in official app stores. It’s easy to overlook how much of your information might be collected, or to accidentally install a malicious version of Fortnite, for instance. VPNs can be great privacy tools, but many free ones sell their users’ data in order to make money. Before downloading anything, especially an app that promises to earn you some extra cash, it’s always worth taking another look at the risks involved.
AI bias: 9 questions leaders should ask — from enterprisersproject.com by Kevin Casey
Artificial intelligence bias can create problems ranging from bad business decisions to injustice. Use these questions to fight off potential biases in your AI systems.
Excerpt:
People questions to ask about AI bias
1. Who is building the algorithms?
2. Do your AI & ML teams take responsibility for how their work will be used?
3. Who should lead an organization’s effort to identify bias in its AI systems?
4. How is my training data constructed?
Data questions to ask about AI bias
5. Is the data set comprehensive?
6. Do you have multiple sources of data?
Management questions to ask about AI bias
7. What proportion of resources is appropriate for an organization to devote to assessing potential bias?
8. Have you thought deeply about what metrics you use to evaluate your work?
9. How can we test for bias in training data?
Amazon is pushing facial technology that a study says could be biased — from nytimes.com by Natasha Singer
In new tests, Amazon’s system had more difficulty identifying the gender of female and darker-skinned faces than similar services from IBM and Microsoft.
Excerpt:
Over the last two years, Amazon has aggressively marketed its facial recognition technology to police departments and federal agencies as a service to help law enforcement identify suspects more quickly. It has done so as another tech giant, Microsoft, has called on Congress to regulate the technology, arguing that it is too risky for companies to oversee on their own.
Now a new study from researchers at the M.I.T. Media Lab has found that Amazon’s system, Rekognition, had much more difficulty in telling the gender of female faces and of darker-skinned faces in photos than similar services from IBM and Microsoft. The results raise questions about potential bias that could hamper Amazon’s drive to popularize the technology.
A landmark ruling gives new power to sue tech giants for privacy harms — from fastcompany.com by Katharine Schwab
Excerpt:
A unanimous ruling by the Illinois Supreme Court says that companies that improperly gather people’s data can be sued for damages even without proof of concrete injuries, opening the door to legal challenges that Facebook, Google, and other businesses have resisted.
UIX: When the future comes to West Michigan, will we be ready? — from rapidgrowthmedia.com by Matthew Russell
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
“Here in the United States, if we were to personify things a bit, it’s almost like society is anxiously calling out to an older sibling (i.e., emerging technologies), ‘Heh! Wait up!!!'” Christian says. “This trend has numerous ramifications.”
Out of those ramifications, Christian names three main points that society will have to address to fully understand, make use of, and make practical, future technologies.
- The need for the legal/legislative side of the world to close the gap between what’s possible and what’s legal
- The need for lifelong learning and to reinvent oneself
- The need to make pulse-checking/futurism an essential tool in the toolbox of every member of the workforce today and in the future
Photos by Adam Bird
From DSC:
The key thing that I was trying to relay in my contribution towards Matthew’s helpful article was that we are now on an exponential trajectory of technological change. This trend has ramifications for numerous societies around the globe, and it involves the legal realm as well. Hopefully, all of us in the workforce are coming to realize our need to be constantly pulse-checking the relevant landscapes around us. To help make that happen, each of us needs to be tapping into the appropriate “streams of content” that are relevant to our careers so that our knowledgebases are as up-to-date as possible. We’re all into lifelong learning now, right?
Along these lines, increasingly there is a need for futurism to hit the mainstream. That is, when the world is moving at 120+mph, the skills and methods that futurists follow must be better taught and understood, or many people will be broadsided by the changes brought about by emerging technologies. We need to better pulse-check the relevant landscapes, anticipate the oncoming changes, develop potential scenarios, and then design the strategies to respond to those potential scenarios.
6 key trends to 21st century teaching — from edsurge.com
Excerpt:
It’s popular these days to complain that college teaching hasn’t changed in hundreds of years. And sure, it’s possible to find some professors on any campus holding yellowed lecture notes, or clinging to dusty chalk. But the reality is that the internet and digital technologies have already brought profound changes to instructional styles and tools in higher education.
So what are the new teaching approaches catching on at today’s campuses? And what are the broader cultural changes around college teaching?
We set out to answer those questions over the past year, with a series of articles and interviews exploring what teaching in the 21st century looks like. Some show the nuances of the challenges of teaching with technology by telling stories of innovative professors, including how a water agency official who teaches an online community college course got started in creating open educational resources when her class was incorporated into a zero-cost textbook degree program. Others dive into research on the culture of teaching, like a talk with an anthropologist studying how professors react to (and sometimes resist) research on teaching practices.
Amazon has 10,000 employees dedicated to Alexa — here are some of the areas they’re working on — from businessinsider.com by Avery Hartmans
Summary (emphasis DSC):
- Amazon’s vice president of Alexa, Steve Rabuchin, has confirmed that yes, there really are 10,000 Amazon employees working on Alexa and the Echo.
- Those employees are focused on things like machine learning and making Alexa more knowledgeable.
- Some employees are working on giving Alexa a personality, too.
From DSC:
How might this trend impact learning spaces? For example, I am interested in using voice to intuitively “drive” smart classroom control systems:
- “Alexa, turn on the projector”
- “Alexa, dim the lights by 50%”
- “Alexa, open Canvas and launch my Constitutional Law I class”
What is 5G? Everything you need to know — from techradar.com by Mike Moore
The latest news, views and developments in the exciting world of 5G networks.
Excerpt:
What is 5G?
5G networks are the next generation of mobile internet connectivity, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections on smartphones and other devices than ever before.
Combining cutting-edge network technology and the very latest research, 5G should offer connections that are multitudes faster than current connections, with average download speeds of around 1GBps expected to soon be the norm.
The networks will help power a huge rise in Internet of Things technology, providing the infrastructure needed to carry huge amounts of data, allowing for a smarter and more connected world.
With development well underway, 5G networks are expected to launch across the world by 2020, working alongside existing 3G and 4G technology to provide speedier connections that stay online no matter where you are.
So with only a matter of months to go until 5G networks are set to go live, here’s our run-down of all the latest news and updates.
From DSC:
I wonder…
- What will Human Computer Interaction (HCI) look like when ~1GBps average download speeds are the norm?
- What will the Internet of Things (IoT) turn into (for better or for worse)?
- How will Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communications be impacted?
- What will that kind of bandwidth mean for XR-related technologies (AR VR MR)?
Gartner survey shows 37% of organizations have implemented AI in some form — from gartner.com
Despite talent shortages, the percentage of enterprises employing AI grew 270% over the past four years
Excerpt:
The number of enterprises implementing artificial intelligence (AI) grew 270 percent in the past four years and tripled in the past year, according to the Gartner, Inc. 2019 CIO Survey. Results showed that organizations across all industries use AI in a variety of applications, but struggle with acute talent shortages.
The deployment of AI has tripled in the past year — rising from 25 percent in 2018 to 37 percent today. The reasons for this big jump is that AI capabilities have matured significantly and thus enterprises are more willing to implement the technology. “We still remain far from general AI that can wholly take over complex tasks, but we have now entered the realm of AI-augmented work and decision science — what we call ‘augmented intelligence,’” Mr. Howard added.
Key Findings from the “2019 CIO Survey: CIOs Have Awoken to the Importance of AI”
-
The percentage of enterprises deploying artificial intelligence (AI) has tripled in the past year.
-
CIOs picked AI as the top game-changer technology.
-
Enterprises use AI in a wide variety of applications.
-
AI suffers from acute talent shortages.
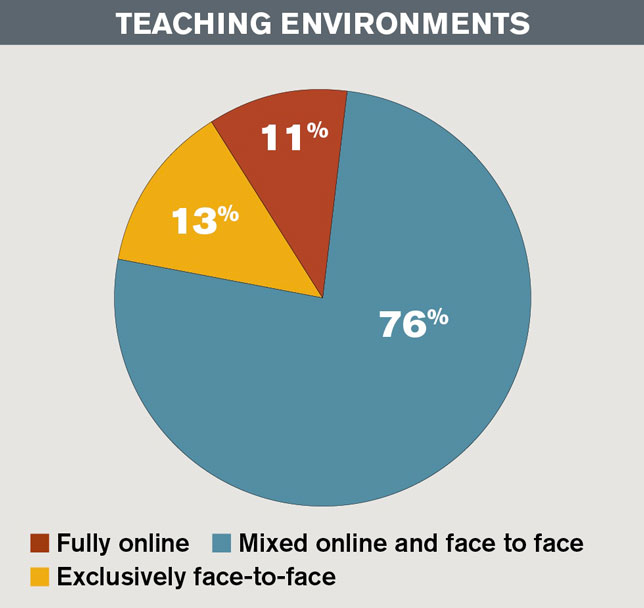
Survey: Online, Blended Dominate Today’s Learning Environments — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
In our latest Teaching with Technology Survey, the vast majority of faculty members said they teach in either a fully online or blended format.
However, that doesn’t mean those instructors blend every course. When we asked faculty how many of their classes are blended, 29 percent said they teach all blended classes, while 45 percent blend some of their classes. Six percent said they plan to use the blended model in the next year or are exploring the option.
From DSC:
In this posting, I discussed an idea for a new TV show — a program that would be both entertaining and educational. So I suppose that this posting is a Part II along those same lines.
The program that came to my mind at that time was a program that would focus on significant topics and issues within American society — offered up in a debate/presentation style format.
I had envisioned that you could have different individuals, groups, or organizations discuss the pros and cons of an issue or topic. The show would provide contact information for helpful resources, groups, organizations, legislators, etc. These contacts would be for learning more about a subject or getting involved with finding a solution for that problem.
OR
…as I revist that idea today…perhaps the show could feature humans versus an artificial intelligence such as IBM’s Project Debater:
Project Debater is the first AI system that can debate humans on complex topics. Project Debater digests massive texts, constructs a well-structured speech on a given topic, delivers it with clarity and purpose, and rebuts its opponent. Eventually, Project Debater will help people reason by providing compelling, evidence-based arguments and limiting the influence of emotion, bias, or ambiguity.
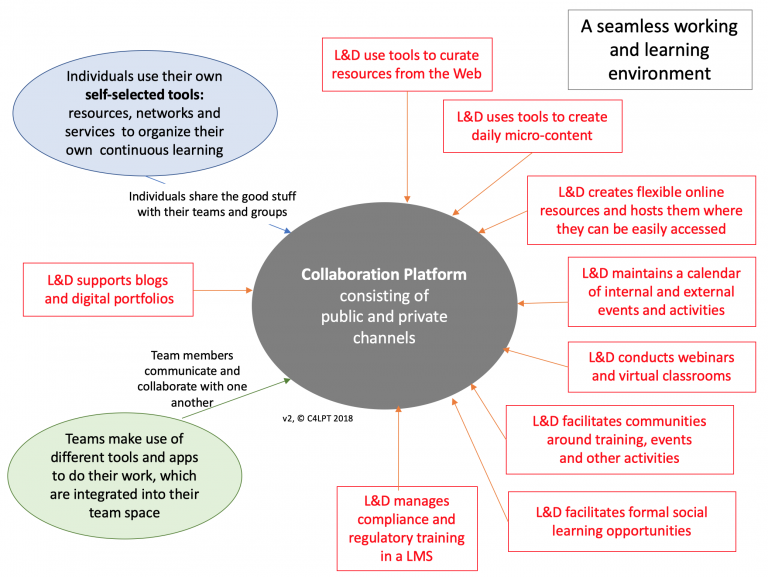
From DSC:
Below is a graphic from an article by Jane Hart that’s entitled, “A seamless working and learning environment“- to me, it’s another good example/graphic of a learning ecosystem. This one happens to belong to an organization, but each of us has our own learning ecosystem as well.