‘The Dangers of Fluent Lectures’ — from insidehighered.com by Colleen Flaherty
A study says smooth-talking professors can lull students into thinking they’ve learned more than they actually have — potentially at the expense of active learning.
Excerpt:
The paper also provides important insight into why active learning hasn’t taken deeper root in academe, despite the many studies that have previously identified its effectiveness as compared to more passive approaches (namely the lecture). In a word: students. That is, while professors are often seen as the biggest impediments to innovative teaching, the study describes an “inherent student bias against active learning that can limit its effectiveness and may hinder the wide adoption of these methods.”
Compared with students in traditional lectures, students in active classes perceived that they learned less, while in reality they learned more. Students also rated the quality of instruction in passive lectures more highly, and expressed a preference to have “all of their physics classes taught this way,” despite their lower test scores.
…
In some ways, he said, “the study confirms what we have suspected anecdotally for a long time — that students feel more comfortable in a lecture environment and believe that they are learning more because of the expectations they have for a college learning environment.” But, in fact, he said, they’re “actually learning more in the environments where they are actively engaged in building knowledge about key concepts.”
From DSC:
The part about the students feeling more comfortable in a lecture environment and believing that they are learning more reminded me of this research/paper (which the graphics below reference and link to as well), where they mention the practices of highlighting and re-reading some text. Students feel like they are really learning the content more thoroughly when they are doing these things (and this is what I did in college as well). But the evidence shows that the utility of these methods is low. Instead, practice testing — which involves retrieval practice, as well as distributed practice and interleaved practice produce stronger results.
So what students feel and what’s actually occurring can be different…as Colleen’s article from insidehighered.com points out.
That said — and as the article asserted as well — is that some lecturing is fine to do:
At the same time, Eyler stressed that existing literature shows that some limited lecturing is “definitely OK,” as “students need to know content in order to engage in higher order thinking.”

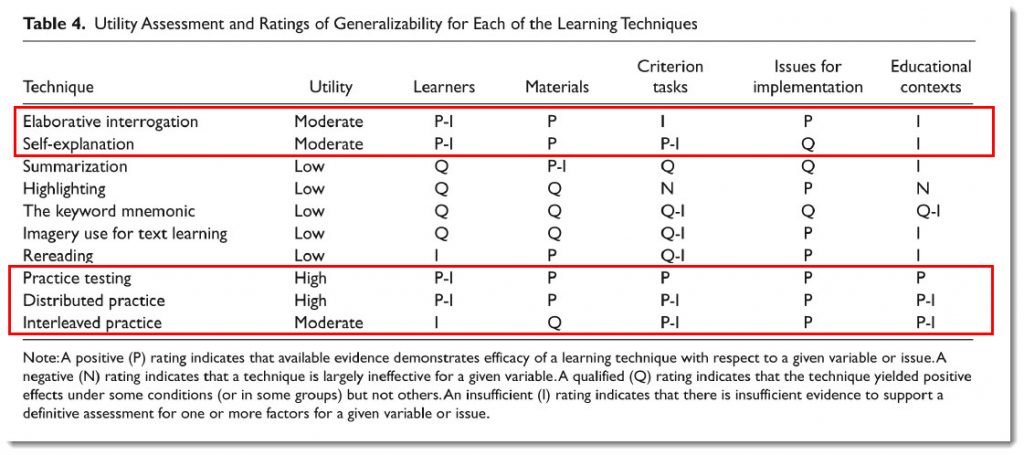
Addendum on 9/14/19: