From DSC:
Yesterday, I attended the Michigan Virtual University (MVU) Online Learning Symposium on the campus of Michigan State University. I would like to send a shout out to MVU for putting this event together and to MSU for hosting a solid event, as well as to all of the speakers and presenters throughout the day.

Some key points/themes:
- Online-based learning within K-12 in Michigan continues to increase:
- Over 91,000 Michigan K-12 students took one or more virtual courses during the 2014-15 school year. This number is up over 15,000 students compared to the number reported last year (increase of 20%).
- Michigan K-12 students accounted for approximately 446,000 virtual course enrollments in 2014-15, surpassing the 2013-14 figure by more than 126,000 enrollments (increase of 40%).
- A side note from DSC:
Given this growth in online learning in the K-12 space…
Given the emphasis in K-12 to provide more CHOICE to students…
Given the emphasis to turn over the ownership of learning to students…….those colleges and universities who will carry on these students’ educations must realize that the K-12 student is changing…their expectations are changing. They want MORE CHOICE. MORE CONTROL. If you only offer a face-to-face delivery approach, that likely won’t cut it in the future.

- Technology will continue to play a strategic role in the quest to provide greater degrees of personalization as well as provide the data to aid in learning success
An insert, dated 4/14/16 from:
We’re already seeing such changing expectations, as identified in the following article from 4/11/16:
“What Gen Z Thinks About Ed Tech in College” — edtechmagazine.com
A report on digital natives sheds light on their learning preferences.
Excerpt:
A survey of the collegiate educational-technology expectations of 1.300 middle and high school students from 49 states was captured by Barnes and Noble. The survey, Getting to Know Gen Z, includes feedback on the students’ expectations for higher education.
“These initial insights are a springboard for colleges and universities to begin understanding the mindset of Gen Z as they prepare for their future, focusing specifically on their aspirations, college expectations and use of educational technology for their academic journey ahead,” states the survey’s introduction.
Like the millennials before them, Generation Z grew up as digital natives, with devices a fixture in the learning experience. According to the survey results, these students want “engaging, interactive learning experiences” and want to be “empowered to make their own decisions.” In addition, the students “expect technology to play an instrumental role in their educational experience.”
Keynotes/speakers (with some notes on their presentations included):
Buddy Berry
Superintendent of Eminence Independent Schools
Eminence, Kentucky
Also see:
School on FIRE (Framework of Innovation for Reinventing Education)
Woven throughout all we do is the concept of Surprise and Delight. We want each student, staff, and stakeholder to be continually amazed and engaged each and every day. We want to create and foster an environment where creativity and customer service abound in all aspects of our school. Whether great or small, the element of “Surprise and Delight” is the essence of our organization.
Buddy gave an emotional, powerful keynote address — even while cooking up a delicious dish.

Photo from Eric Kunnen at GVSU
The aromas spread throughout the room, even if only a handful of people were actually going to eat the dish (a lesson is in there for education reform as well). Buddy thinks outside the box and wants those in the Eminence Independent School system to start thinking differently as well. He seeks to have their schools surprise and delight students — awesome! As an example of this, he wouldn’t accept no to some things re: providing WiFi to their students. So he had their buses outfitted with WiFi, then saw to it that those buses were parked overnight in the areas where their students didn’t have access to WiFi. Students within 100 yards of those buses now have WiFi.
As a result of a tragic accident involving one of his former football players, Buddy is truly driven to change the world. He thinks big. He is on a mission, backed up by vast amounts of energy and determination.
Their School on FIRE document mentions the following bullet points re: personalized learning:
- Student choice in electives
- Personalized student goals
- Personalized Learning Environment in all classes
- ICE (Interventions, Connections, and Enrichments) Model (K-12)
Brian J. Whiston
State Superintendent of Public Instruction
Brian:
- Mentioned Michigan’s Top 10 in 10 Years Program, striving to put Michigan in the nation’s top 10 performers for education within the next 10 years
- Mentioned Governor Snyder’s recently introduced 21st Century Education Commission, created to prepare students for the global economy (see the full text of Executive Order 2016-6) which states that “the Commission shall act in an advisory capacity to the Governor and the state of Michigan, and shall do all of the following:”
- Analyze top performing states and nations to determine how their systems of education (structure, governance, funding, and accountability) have led to academic and career success for students pre-school through career credentialing/post-secondary education.
- Determine, for top performing states and nations, the similarities and differences between their demographic, cultural and economic realities and Michigan’s demographic, cultural, and economic realities.
- Based on this analysis of top performing states and nations, identify the structural (configuration of schools,) governance, funding, and accountability enablers and inhibitors impacting the academic success and career preparedness for Michigan students and residents, including distinct demographic and geographic variances as appropriate.
- Recommend changes to restructure, as necessary, the configuration, governance, funding, and accountability of Michigan’s education system to significantly improve student achievement and career preparedness, and ensure the high quality of all education options available to parents and students.
- Prioritize the Commission’s recommendations for implementation.
.
(The report/recommendations are due by 11/30/16.)
- Asserted that students should lead/own their own learning — that students set and pursue their own goals
(From DSC: I love that goal, as it will serve the students well in their futures; lifelong learning is now required and each of us has to own our own learning.)
- Suggested that teacher preparation programs should be more akin to what medical schools do — and have student teachers work with kids earlier on in the process; be able to learn something, then immediately apply it. Teacher prep programs need to become more nimble.
(From DSC: In another panel, it was asked what teacher preparation programs are doing to train future teachers on how to teach online…? A solid, necessary question — at least for the foreseeable future.)
Joe Freidhoff
Vice President of Research, Policy & Professional Learning, MVU
Joe shared numerous pieces of data from the report that he authored:
Freidhoff, J.R. (2016). Michigan’s K-12 virtual learning effectiveness report 2014-15. Lansing, MI: Michigan Virtual University. Retrieved from http://media.mivu.org/institute/pdf/er_2015.pdf.

Some excerpts from the Key Findings section:
- Over 91,000 Michigan K-12 students took one or more virtual courses during the 2014-15 school year. This number is up over 15,000 students compared to the number reported last year (increase of 20%). Three out of four students taking virtual courses came from the Local virtual learner subset, 15% came from cyber schools, and 10% from MVS
- Michigan K-12 students accounted for approximately 446,000 virtual course enrollments in 2014-15, surpassing the 2013-14 figure by more than 126,000 enrollments (increase of 40%). High school grade levels continued to account for the largest number of enrollments, though the elementary grade levels showed the largest year-over-year percentage increases. The Local virtual learner subset accounted for 63% of the virtual enrollments.
- Virtual enrollment patterns suggest that Michigan schools tend to enroll higher performing students in MVS courses, but rarely use MVS for lower performing students. In contrast, when Local schools provide their own virtual solution, they primarily enroll students who have failed several courses taken in the traditional classroom environment.
- As in past years, virtual enrollments were heaviest in the core subject areas, led by English Language and Literature (20%) and Mathematics (17%).
- Once again, males and females each accounted for roughly half of the virtual enrollments, and there was almost no difference in the percentage of males and females enrolling in core subjects.
- Over half (51%) of schools with virtual enrollments had 100 or more virtual enrollments in the 2014-15 school year, though the second most likely scenario was that they had less than 10 (19%). This “all” or “very few” phenomenon continues the trend observed over the past four years, despite the number of schools with virtual enrollments growing from 654 in 2010-11 to over 1,072 in 2014-15.
Joe also shared some items from “A Report to the Legislature” — from 12/1/15.

Other notes:
- Professional Development would be ideally experiential, sustained; and staffed by people who have actually done things. Those people would ideally be available to coach/support others.
- Support is key, as not everyone is highly proficient in using/applying technology.
- edupaths.org
EduPaths is a professional development portal for ALL Michigan Educators. EduPaths courses are aligned with school improvement framework, multi tiered systems of support, and designed to expand understanding on a wide variety of topics. Courses are available online and are completely self-paced. They are intended to help educators to personalize their own learning plan any time and any place. Another feature of EduPaths are the strategic partnerships with statewide educational organizations. Our goal is to “Help Educators Navigate their Professional Growth” through providing content and connecting content from our statewide partners.
- GenNET Online Learning
- LearnPort.org
Michigan LearnPort® provides online learning solutions for educators and the educational community. Through Michigan LearnPort, you can access high quality courses and resources, meet professional development requirements, earn State Continuing Education Clock Hours and more.
- micourses.org
- mischooldata.org
MI School Data is the State of Michigan’s official public portal for education data to help citizens, educators and policy makers make informed decisions that can lead to improved success for our students. The site offers multiple levels and views for statewide, intermediate school district, district, school, and college level information. Data are presented in graphs, charts, trend lines and downloadable spreadsheets to support meaningful evaluation and decision making.
- The culture of a community will be key in determining what happens with that community’s educational system.
- Several of the sessions dealt with the topic of quality, and some of the organizations/tools mentioned there include:
- MVU’s iEducator Program

Backchannel products/solutions I saw used:
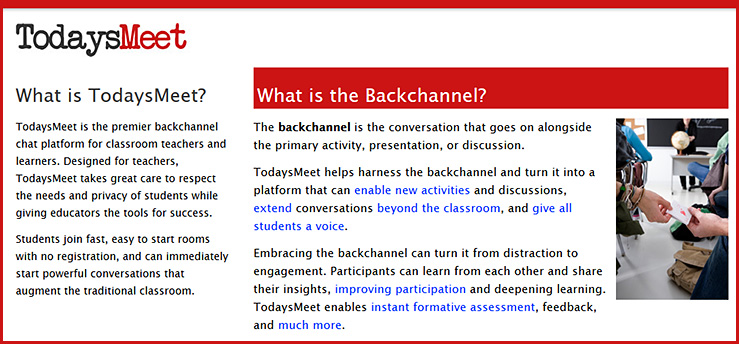
TodaysMeet.com
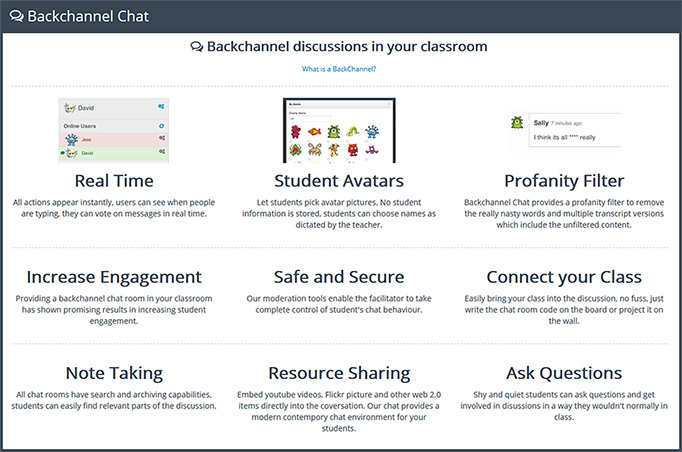
BackChannelChat.com











![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)