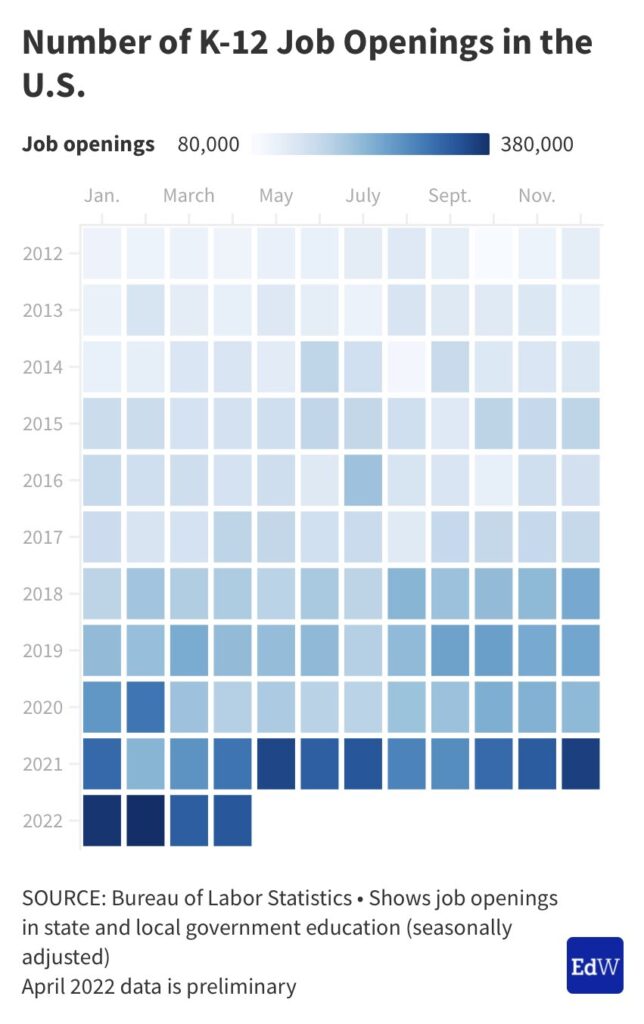
Yale Study: Vast Majority of High Schoolers Unhappy at School — from fee.org by Kerry McDonald
The Yale findings echo previous conclusions about young people’s attitudes toward school.
Excerpt:
Most high school students are not happy at school. A new study by Yale researchers finds that nearly three-quarters of high schoolers report negative feelings toward school. The study surveyed more than 20,000 high school students in all 50 US states and found widespread dissatisfaction at school across all demographic groups, with girls reporting slightly more negative emotions than boys. According to Yale co-author Zorana Ivcevic,
It was higher than we expected. We know from talking to students that they are feeling tired, stressed, and bored, but were surprised by how overwhelming it was.
From DSC:
If you were to have polled him during his ninth through eleventh-grade years, our son would have been one of the very disgruntled students going through high school. His senior year was spent doing exactly what he wanted to be doing — and he was much happier, more engaged, and more motivated to learn the material. He was also around an entirely different student body his senior year — where students were there because they wanted to be there and they were all pursuing their craft.
Fast forward a couple of years, and he actually enjoyed a good deal of his learning experiences this summer and he’s really looking forward to his film and acting classes this fall. It’s amazing the amount of energy and determination/interest that gets unleashed when the motivation is intrinsic.
.

Also from fee.org by Kerry McDonald:
.
9 Digital Etiquette Tips — from techlearning.com by Lisa Nielsen
Teaching proper digital etiquette to students starts with modeling it
Excerpt:
It’s undeniable that the pandemic changed the way we teach, learn, work, and live, but when some people returned to in-person learning and their schools, it seemed they could use some advice on digital etiquette for the new, and extremely connected, world in which we are now operating. This is a world where at any time you may be meeting or teaching in-person, via video, phone, or a combination thereof at the same time.
While adapting was easier for some, others could use a bit of help. For those people, you may want to share or discuss these tips with them.
A Guide To Design Thinking For Kids — from edtechreview.in by Saniya Khan
Excerpt:
The concept is active and inclusive. What’s more, children embrace design thinking with enthusiasm. Across the globe, schools are embracing design thinking as a new way to learn and increase student participation. It should be on our education agenda. Of course, this is more complicated than standard repackaged evaluations. However, conceptual thinking gives children golden opportunities for commitment and creativity, two prerequisites for true learning.
.

How Accredible Makes Learning Credible — from gettingsmart.com by Tom Vander Ark
Key Points
- To increase the value of credentials, Accredible launched Spotlight Directory.
- This allows issuers to provide a home base for people that hold their credentials.
Excerpts:
Learners store credentials in their Accredible wallet and can incorporate them into their LinkedIn profile.
To increase the value of credentials, Accredible launched Spotlight Directory which allows issuers to provide a home base for people that hold their credentials. For example, the Hootsuite Certified Professionals Directory showcases everyone that has earned a Hootsuite credential.
The faster the world of work changes, the more the transcripts lose signal value and the more we need finer grained and more dynamic ways of communicating capabilities.
Tom Vander Ark
Addendum on 8/22/22:
What parents should say to teachers (according to teachers) — from washingtonpost.com by Elizabeth Chang
Excerpt:
“Parents are often surprised by stories of other parents’ treatment of teachers,” wrote Margaret Flaherty, 42, a high school English teacher at a public school in Byfield, Mass. “When I share some of the things parents have said or written to me, mouths go agape. They can be mean. Very mean. And we are so tired. Start with assuming good intentions and take it from there.”