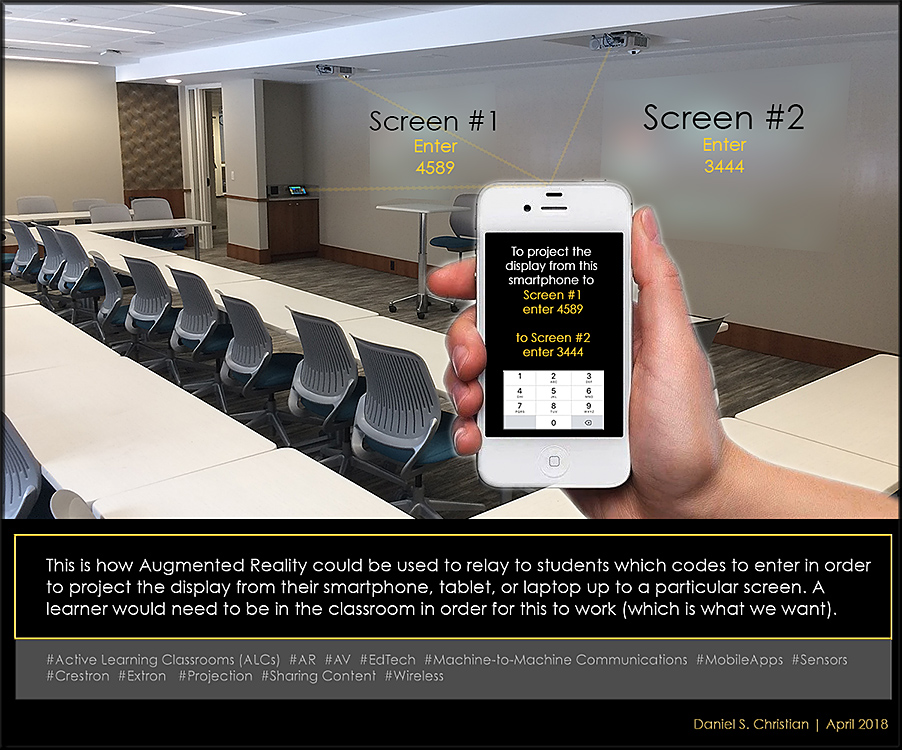
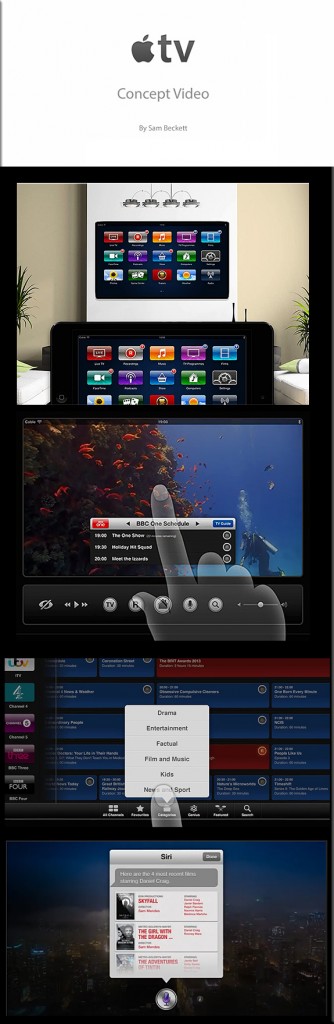
From DSC:
If the first wave of the Coronavirus continues — and is joined by a second wave later this year or early next year — I think a more permanent, game-changing situation is inevitable. As such, now’s the time to change the paradigms that we’ve been operating under.
It’s time to move to *a team-based approach.* To build up the set of skills an organization needs to pivot and adapt — regardless of what comes their way.
Let’s stop asking one faculty member to do it all! Consider this:
- Would you fly in a plane that was engineered/designed/built by one person?
- Would you drive a car that was engineered/designed/built by one person?
- Would you go into brain surgery with only one other person in the operating room?
- Are you, like me, amazed at the long list of people (and their specialties) who contributed to a major motion picture?!? The credits go on for several minutes — even when moving at a fast pace! Would you watch a major motion picture that was written, acted, produced, directed by — and had all of the music, special effects, and audio-related work done by — only one person?
With the move to online learning, one person can’t do it all anymore — at least not at the level that the newer generations are coming to expect. They have grown accustomed to amazing, team-based/built content and products.
Plus, newer generations are going to know and experience much more telehealth-related services…then much more telelegal-related services. They will come to experience/expect high-quality learning-related products and services that way as well. Going forward, there are too many skillsets required by the creation and production of high-quality, online-based learning — not to mention the continued hard work of staying up-to-date on the main subject matter expertise at hand.
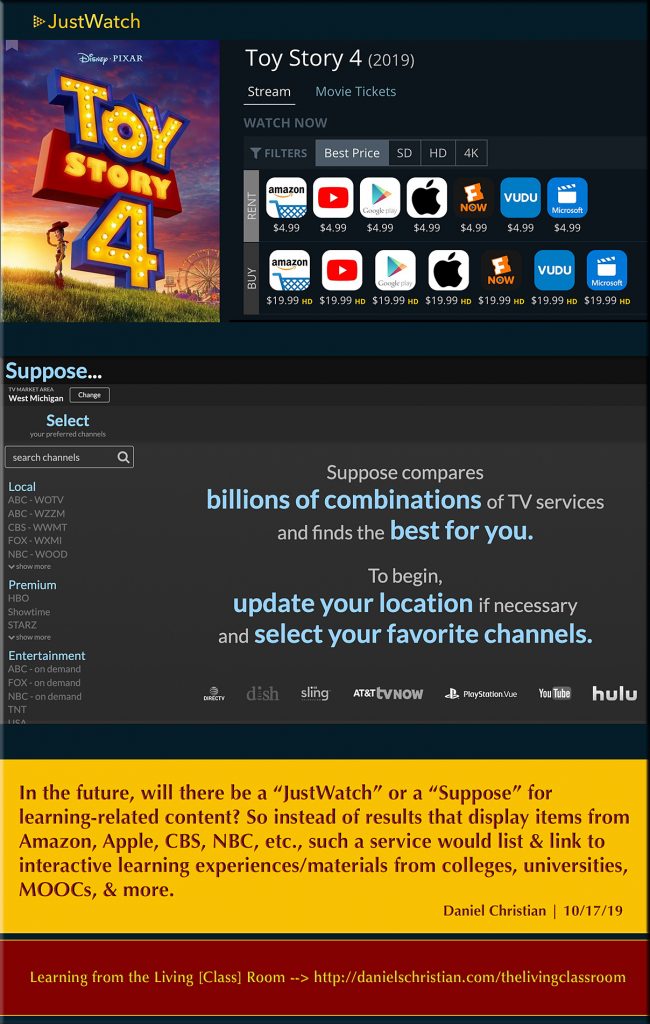
So if the kind of perspective continues as found in this piece — SURVEY: Students say they shouldn’t have to pay full price for online classes — then colleges and universities would do well to invest money in new Research & Development efforts, in team-based content creation, and in reimagining what online-learning could act/be like. Same for the vendors out there. And faculty members would be wise to invest the time and energy it takes to be able to teach online as well as in a face-to-face setting. Not only are they more marketable once they’ve done this, but they are then also more prepared to find their place within an uncertain future.
All of this will likely be an expensive process. Also, greater collaboration will be needed within a department (as we can’t be building a course per professor) as well as between organizations. Perhaps the use of consortiums will increase…I’m not sure.
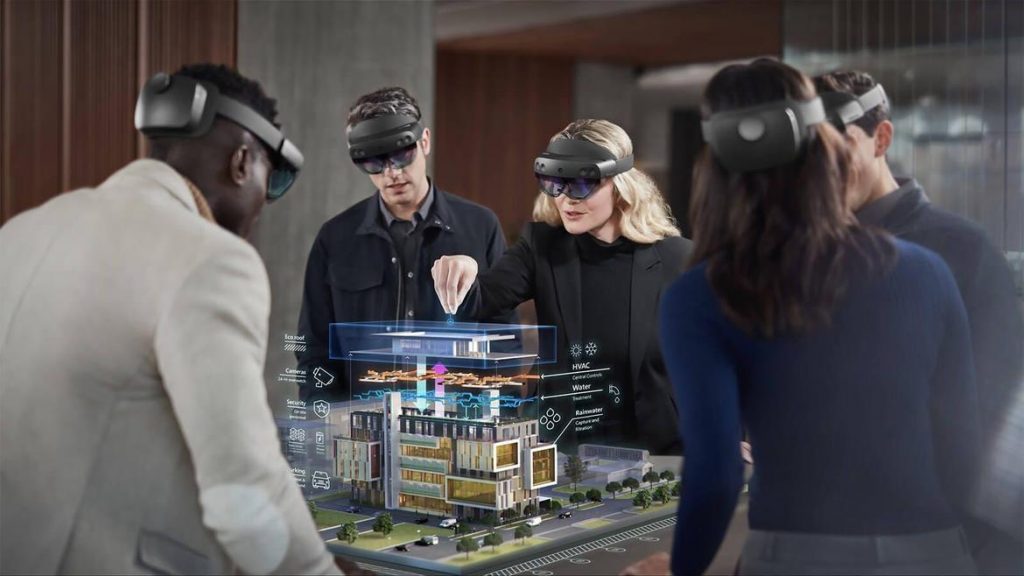
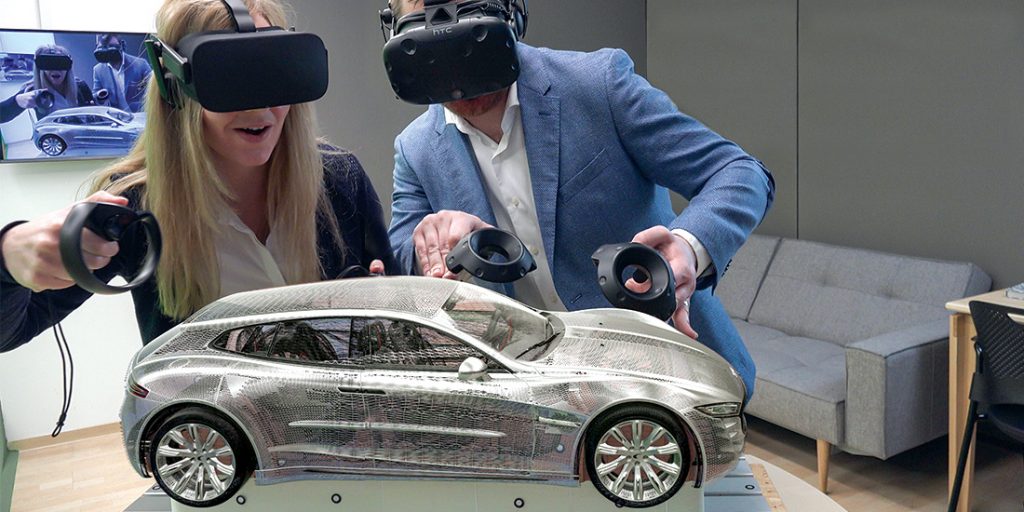
Perhaps a new platform will develop — similar to what’s contained in this vision. Such a platform will feature content that was designed and built by a team. Such a learning-related platform will offer streams of highly-relevant content — while providing continuous, affordable, up-to-date, convenient, and very well done means of staying marketable/employed.

For another paradigm shift, accreditation bodies/practices are going to have to also change, adapt, pivot, and help innovative ideas come to fruition. But that’s another posting for another day.