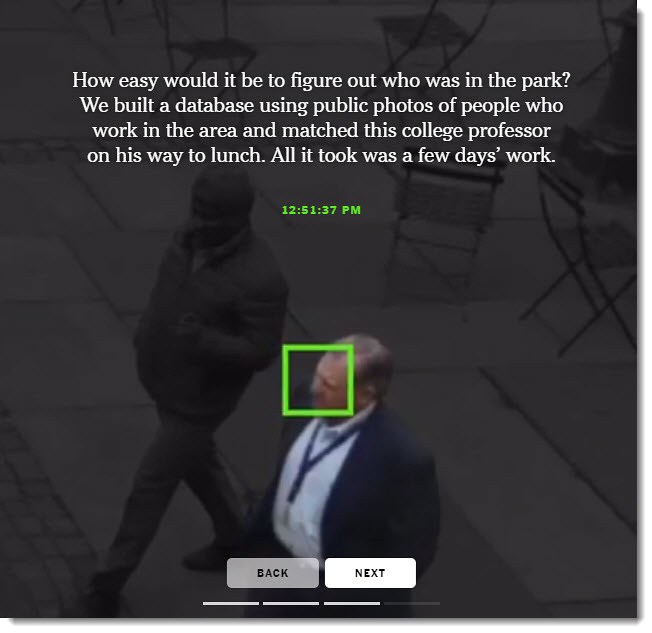
10 things we should all demand from Big Tech right now — from vox.com by Sigal Samuel
We need an algorithmic bill of rights. AI experts helped us write one.
Excerpts:
- Transparency: We have the right to know when an algorithm is making a decision about us, which factors are being considered by the algorithm, and how those factors are being weighted.
- Explanation: We have the right to be given explanations about how algorithms affect us in a specific situation, and these explanations should be clear enough that the average person will be able to understand them.
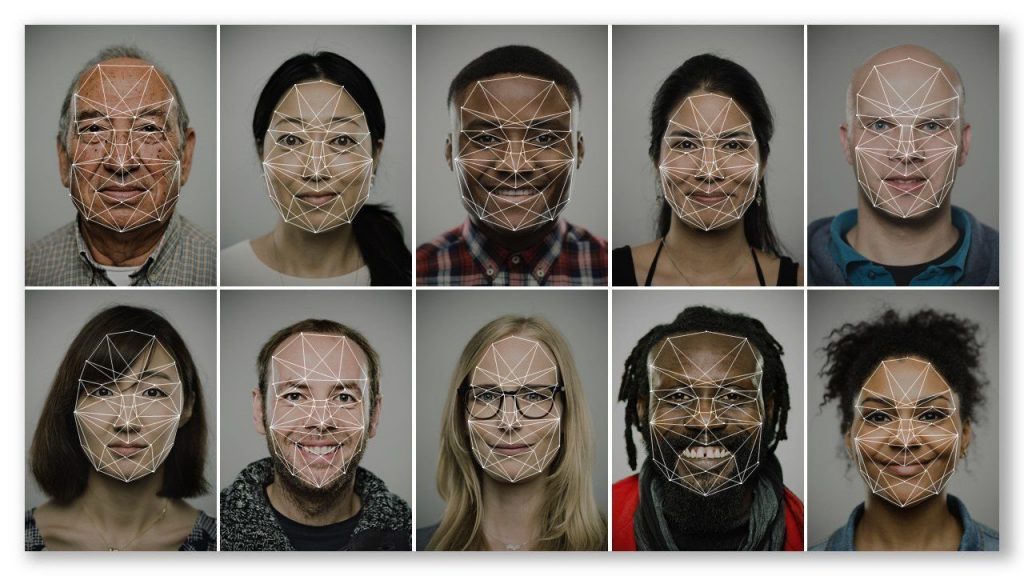
- Consent: We have the right to give or refuse consent for any AI application that has a material impact on our lives or uses sensitive data, such as biometric data.
- Freedom from bias: We have the right to evidence showing that algorithms have been tested for bias related to race, gender, and other protected characteristics — before they’re rolled out. The algorithms must meet standards of fairness and nondiscrimination and ensure just outcomes. (Inserted comment from DSC: Is this even possible? I hope so, but I have my doubts especially given the enormous lack of diversity within the large tech companies.)
- Feedback mechanism: We have the right to exert some degree of control over the way algorithms work.
- Portability: We have the right to easily transfer all our data from one provider to another.
- Redress: We have the right to seek redress if we believe an algorithmic system has unfairly penalized or harmed us.
- Algorithmic literacy: We have the right to free educational resources about algorithmic systems.
- Independent oversight: We have the right to expect that an independent oversight body will be appointed to conduct retrospective reviews of algorithmic systems gone wrong. The results of these investigations should be made public.
- Federal and global governance: We have the right to robust federal and global governance structures with human rights at their center. Algorithmic systems don’t stop at national borders, and they are increasingly used to decide who gets to cross borders, making international governance crucial.
This raises the question: Who should be tasked with enforcing these norms? Government regulators? The tech companies themselves?