Beyond Active Learning: Transformation of the Learning Space — from educause.edu by Mark S. Valenti
Excerpt:
The past decade has seen exciting developments in learning space design. All across the United States and around the world, across seemingly every discipline, there is interest in creating new, active, project-based learning spaces. Technology-rich and student-centric, the new learning spaces are often flexible in size and arrangement and are a significant departure from the lecture hall of yesterday. These developments are not the result of any one factor but are occurring as the result of changes in student demographics, technology advances, and economic pressures on higher education and as the result of increasing demands from employers. The nature of work today is inherently team-based and collaborative, often virtual, and geographically distant. Companies are seeking creative, collaborative employees who have an exploratory mindset. Employers seek graduates who can be more immediately productive in today’s fast-paced economy. Colleges and universities around the country are responding by creating flexible, multimodal, and authentic learning experiences. It’s a complex ecosystem of education—and it’s evolving right before our eyes. What an amazing time to be in education and to be a part of the transformation of the learning space!
…
The next generation of learning spaces will take all the characteristics of an active learning environment—flexibility, collaboration, team-based, project-based—and add the capability of creating and making. Project teams will be both interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary and will likely need access to a broad array of technologies. High-speed networks, video-based collaboration, high-resolution visualization, and 3-D printing are but a few of the digital tools that will find their way into the learning space.
Figure 1. The T-Shaped Professional
Credit: Developed by IBM (Jim Spohrer, IBM Labs) and Michigan State University and
modified on March 16, 2015. Reprinted with permission.
CMU’s active learning classrooms improve STEM students’ learning — from cmich.edu; with thanks to Krista Spahr for this item
Environments support collaborative conversation, development of real-world skills
Excerpt:
The active learning difference
Through state-of-the-art technology, students spend their class time in active learning classrooms collaborating on assignments and solving problems rather than listening to lectures. Faculty become coaches and guides instigating thoughtful discussions and debates. Often, students watch faculty members’ online lectures before each class session begins.
Studies have shown that active learning classrooms and their settings allow students to learn up to three times more and retain greater knowledge, strengthen student-faculty relationships and improve student performance. Active learning also is proven to increase the likelihood that students in STEM disciplines will continue in those programs and removes the gap between the success of male and female students.
…
The flipped classroom can be associated with more collaborative, experiential, constructivist learning. “Faculty become coaches and guides instigating thoughtful discussions and debates. Often, students watch faculty members’ online lectures before each class session begins.”
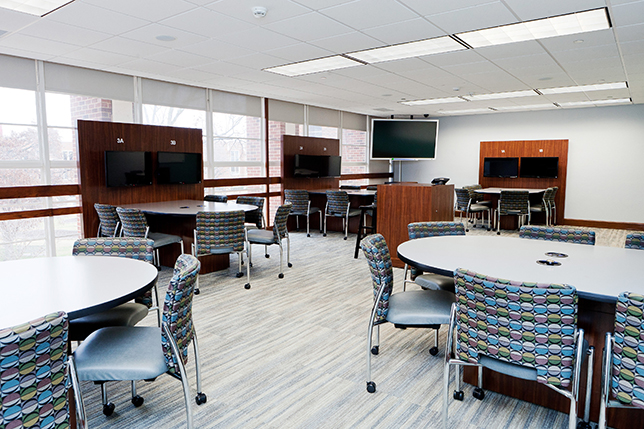
6 Secrets of Active Learning Classroom Design — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
While the basic elements of active learning classrooms are well known, no one-size-fits-all template exists. Here’s how to achieve the custom fit your school needs.
Excerpt:
4 Questions to Guide Classroom Design
By next year, the University of Oklahoma will have nearly a dozen active learning spaces, up from one in 2012. Every single classroom looks different from the others, and that’s by design. Chris Kobza, manager of IT learning spaces, and Erin Wolfe, director of strategic initiatives, have honed their process down to four simple questions:
- What’s the vision?
- What’s the focus?
- How flexible?
- What’s the budget?
The process starts when they sit down with the person or people who want to redo a room to find out what they envision — is it maximum technology or maximum flexibility? “It’s a real casual conversation but you can learn enough about what their expectations for the space are, what the expectations for their faculty are, what they hope the students get out of the space,” said Kobza.

Kelly references the
Learning Spaces compilation out at Educause:
From DSC:
Don’t like the phrase “active learning?” I’m compiling a list of other words/phrases/thoughts that one can use:
- Collaborating on assignments and solving problems
- Collaborative learning
- Actively engaged learning
- Peer instruction
- Thinking out loud with one another
- Constructionist / constructivist learning
- Developing real-world skills such as problem solving, critical thinking, negotiating, and teamwork
- Students have the opportunity to work in groups, solve complex problems and be creative
- Emphasis on small-group activities
- Immersed in discussion
- Flexible in size and arrangement
- Experiences and opportunities to better understand the material
- Students are extremely engaged in what they are doing, and their thinking is being refined.
- Creating and making; creativity
- Effective interactions of small groups of people within communal spaces
- Putting the focus on students doing the work of learning
- Increased motivation via more hands-on opportunities
- Sharing / exchanging ideas
- Participatory
‘The shift is changing the way teachers plan, present lessons and share information. Students no longer need to all do the same thing to learn about a topic. This change is enhancing the quality of work teachers are receiving back from students, and is creating an environment where students are involved in the creation (versus consumption) of content that aids their learning. “A major change comes in the direct instruction piece. As teachers, we’re moving from simply giving information and offering a passive learning experience, to serving as a facilitator and guiding student inquiries. This method is allowing them to be active participants in their own education,” said Alder Creek Middle School teacher Vicki Decker. (Source)
Addendum on 7/17/15:
- Designing Active Learning Classrooms — from dbctle.erau.edu; with thanks to Tim Holt out at holtthink.tumblr.com for the original posting that led me to this resource
Excerpt:
Active Learning Classrooms (also known as Active Learning Spaces or Learning Studios) are classrooms or other physical spaces designed with active learning in mind. In particular they are student-centered rather than instructor-centered. Students often sit in groups instead of rows to support collaborative learning, and some classrooms even have movable tables or desks. Students also sometimes have their own computers or tablets, and there may be multiple displays around the classroom, since students are not facing in one direction. Researchers have found that active learning classrooms have positive influences on student learning and engagement. Below are videos, examples, research studies, and assessment instruments related to active learning spaces.
A somewhat related addendum:
- 50 alternatives to lecturing — from teachthought.com