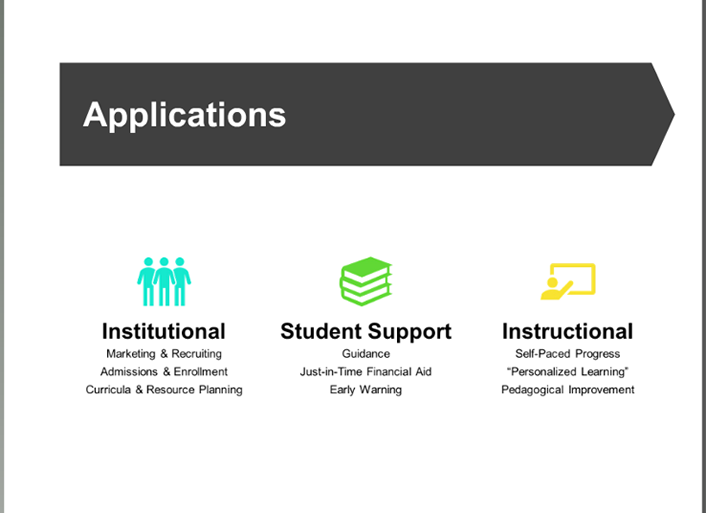
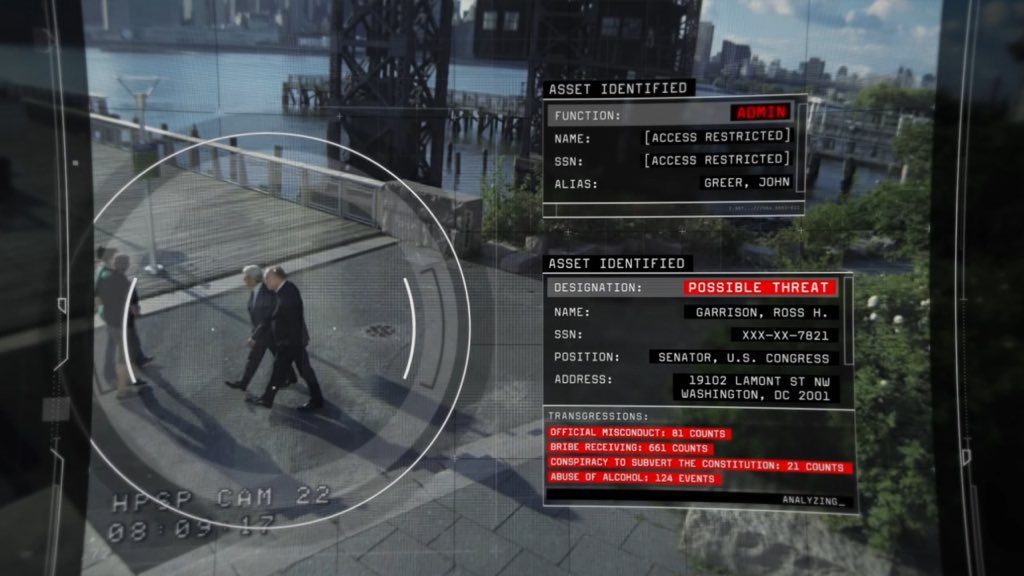
After 40 Years of Constant Change, What’s Next for the Legal Industry? — from law.com by Dan Packel
Few could have anticipated the dramatic shift in scope and scale the industry has undergone since The American Lawyer’s founding 40 years ago. We asked some of the law’s brightest thinkers what we can expect over the next 10.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Technology and Upheaval
While it’s easy to conclude that the technological revolution that’s already been unleashed will continue to drive transformation over the next 10 years, it’s harder to pinpoint how.
Expect more and more tasks to become subject to automation—not just contracts and e-discovery but also areas like trademarks and due diligence for mergers, for starters.
Technology and artificial intelligence on their own are noteworthy, but what’s more compelling is the impact they will have on how firms are structured.
“Everything that can be taken out of the hands of subject-matter experts and handed over to the process experts and technologists will be,” says Orrick, Herrington & Sutcliffe Chairman and CEO Mitch Zuklie. “There will be far fewer associates sitting in rooms with documents and more strategic partnerships among law firms and legal tech providers.”
This transition could help chip away at the supremacy of the billable hour.
…
Not only will technology move up the value chain for litigation, it will also emerge as a greater player on the deal side. Jae Um, director of pricing strategy at Baker McKenzie, expects to see a much greater focus on compliance and regulatory technology in the next five years.
As AI solutions, which depend upon machine learning, are slowly deployed in the marketplace, their efficacy will inevitably grow.
How about a little wild speculation to wrap this up? With more nonlawyer specialists finding professional homes in law firms, it’s a short leap to hybrids between law firms and professional services operations. Imagine consultants and accountants working together with lawyers and technologists to solve clients’ increasingly complex problems. And what about a high-profile merger between a Big Four firm and a global law firm? I wouldn’t rule it out.