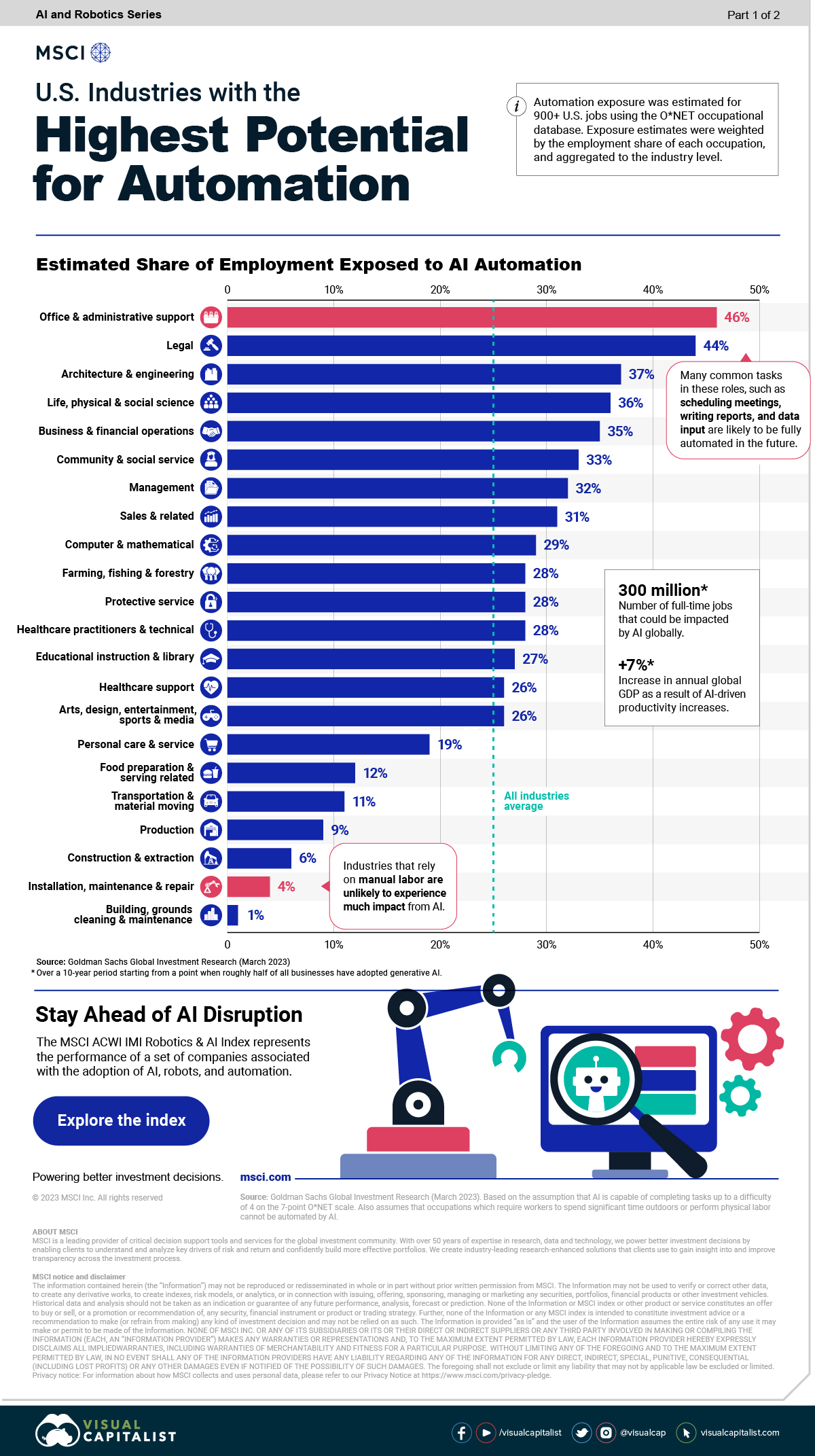
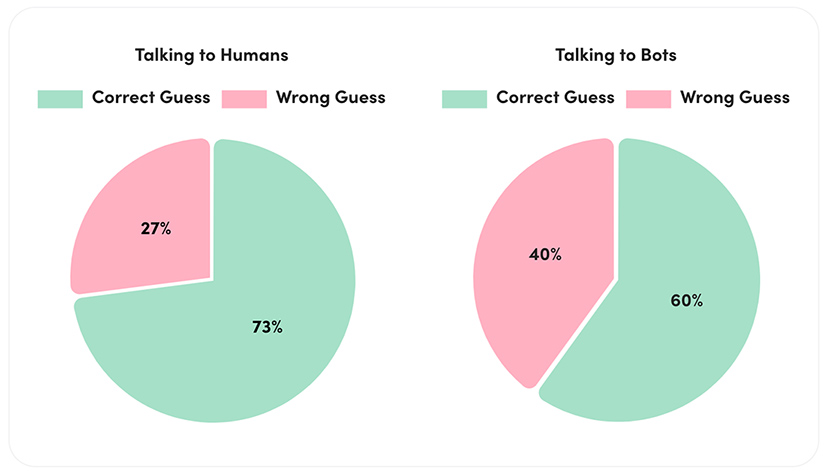
National ChatGPT Survey: Teachers Accepting AI Into Classrooms & Workflow — Even More Than Students — from the74million.org by Greg Toppo
42% of students use ChatGPT, up from 33% in a prior survey. Their teachers are way ahead of them, with now 63% saying they’ve used the tool on the job
Teachers … and parents … believe it’s legit
Teachers who use ChatGPT overwhelmingly give it good reviews. Fully 84% say it has positively impacted their classes, with about 6 in 10 (61%) predicting it will have “legitimate educational uses that we cannot ignore.”
New Book Aims to Reshape the Future of Learning (With Your Help) — from samchaltain.substack.com by Sam Chaltain
- What circumstances would be required for the existing educational model to be deemed obsolete?
- What stands in the way of those circumstances coming to pass?
- And if you were to craft a tool that actually helped people create those circumstances, what would you want that sort of resource to be, say, and do?
Last week, in Istanbul, a select group of educators, architects, students and entrepreneurs met to wrestle with those questions, as part of a yearlong collaborative design project.
What small changes could have the biggest impact and help spark the larger revolution we seek?
Will the future even have occupations — and if so, what are they most likely to be?
What is most essential to know and embody in the next 25 years?
The Great Unbundling — from educationnext.org by Joseph Olchefske and Steven Adamowski
Is the parents’ rights movement opening a new frontier in school choice?
The mindsets of parents are changing—rapidly—as they make decisions about the schooling of their children. Over the past few years, a convergence of two megatrends—pandemic desperation and parental-rights politics—has driven many families to reconsider the traditional school model and find ways of “unbundling” their children’s schooling into discrete elements that are controlled by the parent rather than the school.
While parent-led unbundling is not a new phenomenon, the current movement has expanded so quickly that it’s been dubbed “the Great Unbundling” of K–12 schooling.
The Great Unbundling is now influencing the education marketplace, as a broad set of nonschool vendors have responded to this unprecedented demand by pitching their education services directly to families: “microschools,” online courses, private tutoring, learning pods, and outdoor learning experiences.
Yes, AI could profoundly disrupt education. But maybe that’s not a bad thing — from theguardian.com by Rose Luckin; with thanks to Will Richardson and Homa Tavangar for this resource
Humans need to excel at things AI can’t do – and that means more creativity and critical thinking and less memorisation
Staying ahead of AI will mean radically rethinking what education is for, and what success means. Human intelligence is far more impressive than any AI system we see today. We possess a rich and diverse intelligence, much of which is unrecognised by our current education system.
How we can teach children so they survive AI – and cope with whatever comes next — from theguardian.com by George Monbiot
It’s not enough to build learning around a single societal shift. Students should be trained to handle a rapidly changing world
I don’t claim to have definitive answers. But I believe certain principles would help. One is that rigidity is lethal. Any aspect of an education system that locks pupils in to fixed patterns of thought and action will enhance their vulnerability to rapid and massive change. For instance, there could be no worse preparation for life than England’s Standard Assessment Tests, which dominate year 6 teaching. If the testimony of other parents I know is representative, SATs are a crushing experience for the majority of pupils, snuffing out enthusiasm, forcing them down a narrow, fenced track and demanding rigidity just as their minds are seeking to blossom and expand.
Education, to the greatest extent possible, should be joyful and delightful, not only because joy and delight are essential to our wellbeing, but also because we are more likely to withstand major change if we see acquiring new knowledge and skills as a fascinating challenge, not a louring threat.
BRINGING AI TO SCHOOL: TIPS FOR SCHOOL LEADERS— a mini ebook from ISTE
Artificial Intelligence is having a major impact on education. Whether you are excited or
concerned about AI, as a school leader you have a responsibility to ensure AI is approached
thoughtfully and appropriately in your school community and informs your vision for teaching and learning. This guide will help you quickly gain the background you need as a learning leader in an AI infused world.
Schools that have been successful in bringing AI into their schools in purposeful ways have some common strategies. The following five strategies are critical for a successful AI culture in your school.
The Potential Impact of AI Technology on Education. — from medium.com by Happiness Uduak
In this article, we’ll explore the potential impact of AI on education, and then take a look at how it could shape the human view of learning for good.
Teaching Through Asking Rather Than Telling — from edutopia by Jay Schauer
High school teachers can promote active learning by strategically replacing some direct instruction with questions that produce thoughtful conversations.
Does much of your teaching resemble the lectures you and 20 or 50 or 400 of your closest college friends received from a “sage on the stage”? Are you frustrated that most of your students won’t remember much from the fascinating information you just delivered to them for 15 or 30 or 55 minutes? If so, maybe it’s time to implement more ARTT—Ask, Rather Than Tell—into your teaching.
I started doing a lot of asking in order to help students make connections, establish common baseline understandings, and identify knowledge gaps or areas of misunderstanding, rather than telling them information. My lectures then evolved into more meaningful conversations.
Best Free Virtual Labs — from techlearning.com by Diana Restifo
These best virtual lab sites and apps are all free, highly engaging, and informative—and most don’t require registration
Many schools don’t have robust in-person laboratory facilities, instead relying primarily on dry textbooks to teach difficult STEM topics. But even schools with quality labs can benefit from these innovative and flexible online simulations.
The following top virtual lab sites and apps are all free, highly engaging, and informative—and most don’t require registration. Since most browsers no longer support Java or Flash, sites built exclusively with those outdated technologies have been excluded.
Gov. Gretchen Whitmer launching new education-focused state department — from detroitnews.com by Craig Mauger and Chad Livengood
Whitmer’s office said Wednesday the new Michigan Department of Lifelong Education, Achievement and Potential, or MiLEAP, will feature offices governing early childhood education, higher education and “education partnerships.”
“Establishing MiLEAP ensures all available resources, data and dollars are aligned around a single vision — supporting an education system focused on lifelong learning that can support the economy of the future and helping anyone make it in Michigan,” according to a “talking points” document obtained by The Detroit News on Wednesday morning.
How to Get Kids to Read for Fun — from nataliewexler.substack.com by Natalie Wexler
An overemphasis on analytical skills can make reading a joyless task.
Schools have been giving students isolated bits of text rather than letting them sink their teeth into engaging novels, and they’ve prioritized teaching analytical reading skills over allowing kids to immerse themselves in a good story.
Celebrating Student Interests to Create a Positive High School Culture — from edutopia.org by Nicole Rossi-Mumpower
Events that center students’ picks in art, music, and food can create powerful opportunities for them to increase their sense of belonging.
Modeled after the First Friday events that take place in many cities and towns (when community members gather to experience local culture), First Fridays at school offer students a chance to listen to music, view art, and sample cuisine.?The tradition has become a cornerstone of our school community and is replicable across school sites.
THE IMPORTANCE OF A MEANINGFUL SCHOOL CULTURE
Creating a positive school climate and culture is essential for student success. When students feel like they are an important part of the community, they’re more likely to be engaged in their learning and have a positive attitude toward school.