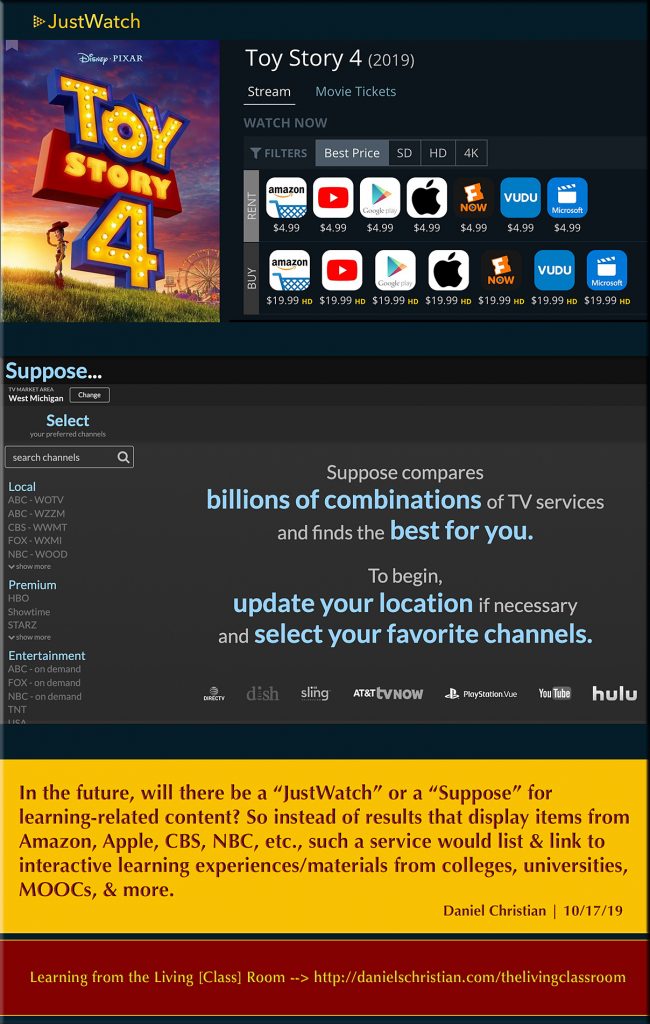
Also see:
Live from Bett: What’s new in EDU–Free resources to boost engagement and collaboration — from the Microsoft Education Team on January 22, 2020
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
In addition, on the day of a presentation, educators and students now can help every person in the classroom or audience understand what they’re saying by clicking on “Present Live.” Live Presentations enables every audience member to view the presentation on their own device, such as a laptop, tablet or phone. Each audience member can turn on live captioning and choose subtitles from more than 60 languages. They can even navigate between slides, so they don’t miss a single, important detail. The audience is engaged throughout the presentation and sends reactions in real-time. After the presentation, the audience can provide feedback on the content and delivery of the presentation, which educators and students can use to improve skills over time.
Live Presentations will be coming soon to PowerPoint for the web as part of Office Education, which educators and students can access for free. If you haven’t already done so, get started with Office 365 Education now.
From DSC:
Might this type of functionality be a solid component of a global, next generation learning platform? Hmmmm…